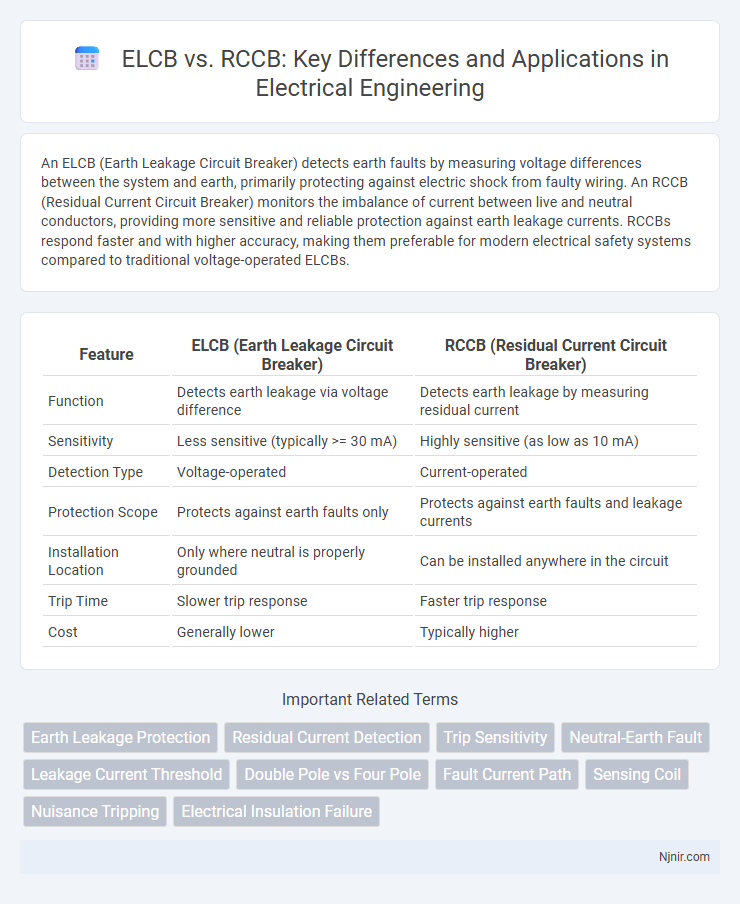
An ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) detects earth faults by measuring voltage differences between the system and earth, primarily protecting against electric shock from faulty wiring. An RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) monitors the imbalance of current between live and neutral conductors, providing more sensitive and reliable protection against earth leakage currents. RCCBs respond faster and with higher accuracy, making them preferable for modern electrical safety systems compared to traditional voltage-operated ELCBs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) | RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects earth leakage via voltage difference | Detects earth leakage by measuring residual current |
| Sensitivity | Less sensitive (typically >= 30 mA) | Highly sensitive (as low as 10 mA) |
| Detection Type | Voltage-operated | Current-operated |
| Protection Scope | Protects against earth faults only | Protects against earth faults and leakage currents |
| Installation Location | Only where neutral is properly grounded | Can be installed anywhere in the circuit |
| Trip Time | Slower trip response | Faster trip response |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
Introduction to ELCB and RCCB
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) and RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) are electrical safety devices designed to prevent electric shock and fire hazards by detecting earth leakage currents. ELCB monitors voltage on the earth wire to detect leakage, whereas RCCB senses imbalance in the current between live and neutral wires for more precise detection. RCCBs offer improved sensitivity and faster response times compared to traditional voltage-operated ELCBs, making them more reliable for modern electrical installations.
Understanding the Working Principle of ELCB
An Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) detects earth faults by measuring voltage differences between the earth and neutral conductors, tripping the circuit when this voltage exceeds a predefined threshold, thus preventing electric shock and equipment damage. Unlike Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCB), which monitor current imbalances between live and neutral wires, ELCBs rely on voltage sensing for operation. Understanding the working principle of ELCB highlights its dependence on earth voltage detection to ensure electrical safety in systems with proper grounding.
RCCB Operating Mechanism Explained
RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) operates by continuously monitoring the current balance between live and neutral wires, instantly detecting any leakage current that deviates from normal flow, typically as low as 30mA, to prevent electric shock. It trips the circuit within milliseconds when it senses an imbalance caused by current leakage to the earth, offering superior protection compared to ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker), which relies on earth voltage sensing. RCCBs are widely preferred for enhanced safety in residential and industrial electrical installations due to their fast and sensitive response to leakage currents.
Key Differences Between ELCB and RCCB
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) detects earth faults by sensing voltage leakage to the ground, while RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) measures the imbalance between live and neutral currents to identify leakage. ELCB relies on earth voltage detection and may fail in cases without proper grounding, whereas RCCB provides faster and more sensitive protection by detecting current leakage directly irrespective of grounding conditions. RCCB is more widely used in modern electrical systems due to its enhanced accuracy and reliability in preventing electric shocks and fire hazards.
Application Areas of ELCB and RCCB
ELCBs (Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers) are primarily applied in older electrical systems to detect earth faults by monitoring the voltage to earth, making them suitable for installations with high earth resistance. RCCBs (Residual Current Circuit Breakers) are widely used in modern residential, commercial, and industrial settings due to their ability to detect leakage currents directly by comparing live and neutral currents, enhancing protection against electric shocks. RCCBs are preferred where sensitive and precise earth leakage detection is required, especially in environments with varying earthing conditions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ELCB
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) primarily offers protection against earth faults by detecting voltage differences between the earth and neutral, which reduces the risk of electric shock and electrical fires. However, ELCBs are limited by their sensitivity to grounding issues and may not detect leakage currents that do not flow through the grounding system, potentially leaving some faults unnoticed. Comparison with RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) highlights ELCB's simplicity and cost-effectiveness for specific installations but lower reliability and broader protection coverage.
Pros and Cons of RCCB
RCCBs (Residual Current Circuit Breakers) offer precise detection and fast disconnection in case of earth leakage currents, significantly enhancing electrical safety by preventing electric shocks and fire hazards. They provide sensitive protection for both residential and industrial installations, but RCCBs do not offer overload or short-circuit protection, which requires the use of additional circuit breakers like MCBs. While RCCBs are highly reliable for leakage detection, their vulnerability to nuisance tripping in environments with electrical noise or transient faults can be considered a drawback.
Installation Guidelines for ELCB and RCCB
ELCB installation requires connection to the earth electrode system to detect earth leakage currents, ensuring proper grounding and minimal resistance less than 1 ohm for effective operation. RCCB installation involves wiring in series with the load, focusing on neutral line monitoring, and requires accurate polarity connection to detect imbalance between live and neutral currents. Both devices must be installed according to manufacturer specifications and local electrical codes to ensure safety and reliable earth fault detection.
Common Causes of Tripping in ELCB vs RCCB
Common causes of tripping in ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) include earth faults due to insulation failure, moisture ingress, and grounded equipment, which cause current leakage to the earth. RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) trips primarily due to imbalance between live and neutral currents caused by leakage currents from damaged appliances, faulty wiring, or insulation breakdown. Both devices activate as safety measures against electric shock and fire hazards, but RCCB is more sensitive to minor leakages, leading to more frequent tripping in presence of transient faults.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Compliance
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) and RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) both adhere to strict international safety standards such as IEC 61008 and IEC 61009, ensuring reliable protection against electrical faults. RCCBs typically offer enhanced sensitivity and faster response times, meeting more rigorous regulatory compliance requirements for residential and industrial electrical installations. Compliance with these standards ensures effective prevention of electric shock hazards and minimizes fire risks caused by earth faults.
Earth Leakage Protection
RCCB provides more sensitive and reliable earth leakage protection by detecting small leakage currents faster than ELCB, which primarily monitors earth voltage.
Residual Current Detection
ELCB detects earth faults by monitoring voltage to earth, while RCCB directly detects residual current imbalance for faster and more accurate ground fault protection.
Trip Sensitivity
ELCB typically has a lower trip sensitivity detecting earth faults above 30mA, whereas RCCB offers higher sensitivity with trip thresholds as low as 5mA for enhanced protection against electrical leakage.
Neutral-Earth Fault
ELCB detects earth faults by monitoring neutral to earth voltage, while RCCB detects leakage currents caused by neutral-earth faults to provide faster and more sensitive protection.
Leakage Current Threshold
ELCB typically has a higher leakage current threshold of 30-50 mA while RCCB offers more sensitive detection with thresholds as low as 10-30 mA for enhanced electrical safety.
Double Pole vs Four Pole
ELCBs typically feature double pole protection for basic earth leakage detection, while RCCBs offer advanced four pole designs providing comprehensive protection for both single-phase and three-phase electrical systems.
Fault Current Path
An ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) detects earth faults through voltage sensing across the earth wire, while an RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) monitors imbalance in current between live and neutral conductors to interrupt the fault current path.
Sensing Coil
An ELCB uses earth leakage current sensing through voltage detection, while an RCCB employs a sensing coil (differential current transformer) to detect imbalance between live and neutral currents for precise leakage detection.
Nuisance Tripping
Nuisance tripping in RCCBs occurs more frequently than in ELCBs due to their sensitivity to residual current fluctuations and electromagnetic interference.
Electrical Insulation Failure
RCCBs provide faster and more sensitive protection against electrical insulation failure by detecting residual current leakage, whereas ELCBs primarily monitor earth voltage and may not effectively detect all insulation faults.
ELCB vs RCCB Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com