Star ground systems create a single central grounding point, minimizing ground loops and reducing noise interference in sensitive electronic circuits. Mesh ground configurations provide multiple interconnected grounding paths, enhancing fault tolerance and current distribution in large-scale electrical installations. Choosing between star and mesh grounding depends on the application's noise sensitivity, system size, and safety requirements.
Table of Comparison
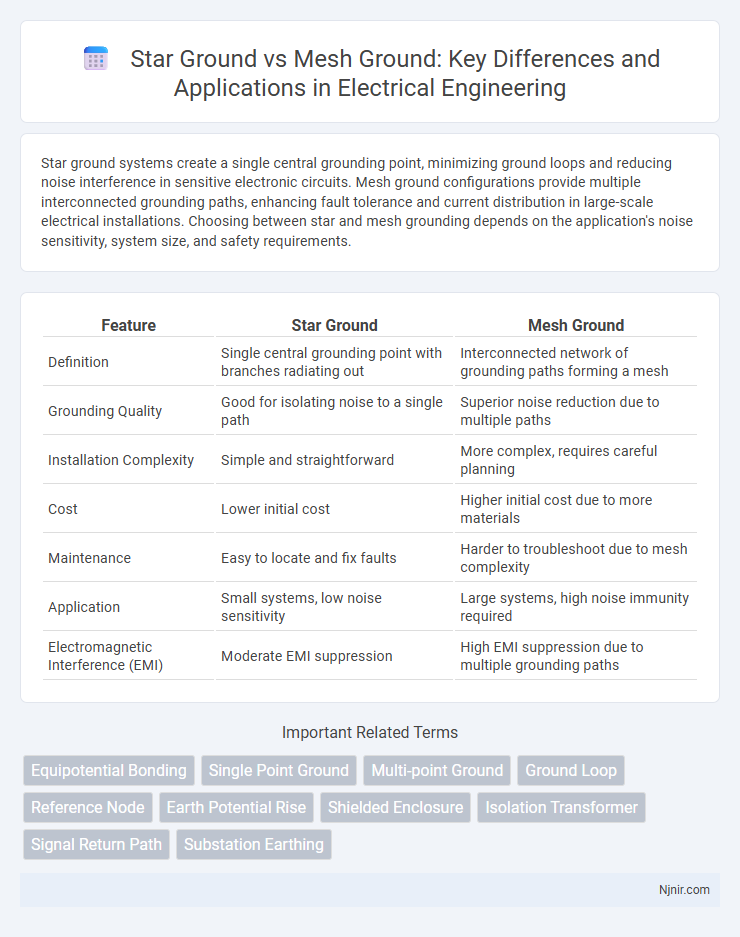
| Feature | Star Ground | Mesh Ground |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single central grounding point with branches radiating out | Interconnected network of grounding paths forming a mesh |
| Grounding Quality | Good for isolating noise to a single path | Superior noise reduction due to multiple paths |
| Installation Complexity | Simple and straightforward | More complex, requires careful planning |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to more materials |
| Maintenance | Easy to locate and fix faults | Harder to troubleshoot due to mesh complexity |
| Application | Small systems, low noise sensitivity | Large systems, high noise immunity required |
| Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) | Moderate EMI suppression | High EMI suppression due to multiple grounding paths |
Introduction to Grounding in Electrical Systems
Star ground systems centralize all grounding connections at a single point, minimizing voltage differences and reducing noise in sensitive electrical circuits. Mesh ground configurations create multiple interconnected grounding paths, enhancing overall system reliability and reducing impedance in large installations. Effective grounding in electrical systems prevents equipment damage, ensures user safety, and improves electromagnetic compatibility.
Overview of Star Grounding Configuration
Star grounding configuration features a single central grounding point where all equipment grounds are connected, minimizing ground loops and reducing electrical noise interference. This centralized approach improves signal integrity in sensitive electronic systems, particularly in audio and communication applications. Effective implementation of star grounding enhances system reliability by providing a stable reference point for voltage levels and preventing potential differences between equipment grounds.
Overview of Mesh Grounding Configuration
Mesh grounding configuration utilizes a network of interconnected conductors distributed beneath the earth's surface, enhancing fault current dissipation and reducing ground resistance. This system improves safety and reliability in electrical installations by providing multiple low-resistance paths for fault currents, minimizing potential differences across grounded equipment. Mesh grounding is preferred in high-voltage substations and large industrial facilities due to its superior performance in controlling step and touch voltages.
Key Differences Between Star and Mesh Grounding
Star grounding features a single central grounding point where all ground connections converge, minimizing ground loops and interference. Mesh grounding distributes multiple interconnected grounding points forming a grid, providing low impedance paths and enhanced fault tolerance. Star grounding excels in sensitive analog circuits due to reduced noise coupling, while mesh grounding is preferred in high-frequency and complex systems for superior electromagnetic compatibility.
Electrical Noise and Interference Management
Star Ground topology minimizes electrical noise by providing a single reference point that reduces ground loops and interference in sensitive circuits. Mesh Ground creates multiple interconnected paths, enhancing noise immunity through distributed current flow but can introduce complexity in managing ground potential differences. Effective noise and interference management depends on circuit design requirements, with Star Ground favored in low-noise analog systems and Mesh Ground preferred in high-frequency or digital environments.
Safety Considerations in Star vs Mesh Grounding
Star grounding reduces the risk of ground loops and electromagnetic interference by providing a single, low-impedance path to earth, enhancing safety in sensitive electrical systems. Mesh grounding forms a network of interconnected electrodes that improves fault current distribution and ensures rapid dissipation of electrical faults, increasing protection against electric shock and fire hazards. Selecting between star and mesh grounding depends on system complexity, with mesh grounding generally preferred in high-safety environments due to its superior fault tolerance and reliability.
Applications Suited for Star Grounding
Star grounding is ideal for low-noise applications such as audio amplifiers, precision measurement equipment, and sensitive analog circuits where minimizing ground loop interference is critical. It ensures a single reference point by connecting all ground paths to one central node, reducing voltage differences and preventing ground loops that can cause signal distortion. This grounding method is particularly suited for environments requiring high signal integrity and precise electronic performance.
Applications Suited for Mesh Grounding
Mesh grounding is ideal for complex industrial facilities, data centers, and substations requiring enhanced fault current distribution and minimized ground potential rise. Its interconnected network provides superior stability and resistance to electromagnetic interference compared to star grounding. This makes mesh grounding particularly suited for high-sensitivity electronic environments and large-scale power distribution systems.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Star ground configurations offer straightforward implementation with a single reference point, minimizing ground loop noise but require careful layout to avoid long ground paths that can introduce interference. Mesh ground systems provide robust noise immunity through multiple interconnected ground points, yet demand meticulous planning to ensure low-impedance loops and prevent circulating currents in complex PCB designs. Best practices include using short, thick grounding conductors in star grounds and ensuring symmetrical mesh layouts with controlled impedance in mesh grounds to optimize EMC performance and signal integrity.
Conclusion and Grounding Selection Criteria
Star Ground systems minimize ground loops by connecting all ground paths to a single point, improving noise immunity in sensitive electronic circuits. Mesh Ground networks offer lower impedance paths with multiple connections, making them ideal for high-frequency or large-scale installations to reduce electromagnetic interference. Selecting between Star and Mesh Ground depends on factors like circuit sensitivity, environmental noise levels, and system complexity to ensure optimal grounding performance.
Equipotential Bonding
Star Ground minimizes potential differences by connecting all ground points to a single node, enhancing Equipotential Bonding, whereas Mesh Ground forms a grid-like connection promoting uniform voltage distribution and reduced ground loop interference.
Single Point Ground
Single Point Ground in Star Ground systems centralizes all ground connections at a single node to minimize noise and interference, whereas Mesh Ground distributes grounding paths to reduce impedance and improve fault tolerance.
Multi-point Ground
Multi-point ground systems use mesh ground configurations to minimize impedance and enhance signal integrity by providing multiple low-resistance return paths compared to single-point star grounds.
Ground Loop
Star Ground minimizes ground loop interference by connecting all ground points to a single node, while Mesh Ground reduces ground loop noise through multiple interconnected ground paths.
Reference Node
Star ground features a single reference node connecting all ground paths to minimize noise and voltage differences, whereas mesh ground uses multiple interconnected ground loops to enhance fault tolerance but may introduce ground loop interference.
Earth Potential Rise
Star ground systems minimize Earth Potential Rise by providing a single, low-impedance reference point, whereas mesh grounds distribute fault currents over multiple paths, reducing voltage gradients and enhancing safety in electrical installations.
Shielded Enclosure
Star ground minimizes noise by connecting all ground points to a single node, enhancing shielded enclosure effectiveness compared to mesh ground, which distributes grounding paths and can introduce noise loops.
Isolation Transformer
Star Ground systems often reduce noise by providing a single reference point, while Mesh Ground paired with an isolation transformer enhances electrical isolation and minimizes ground loop interference in complex setups.
Signal Return Path
Star ground minimizes signal return path interference by providing a single central grounding point, while mesh ground offers multiple interconnected grounding paths to reduce noise and improve signal integrity.
Substation Earthing
Star ground configuration in substations centralizes grounding to minimize potential differences, while mesh ground systems provide extensive low-resistance paths enhancing fault current dissipation and overall safety.
Star Ground vs Mesh Ground Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com