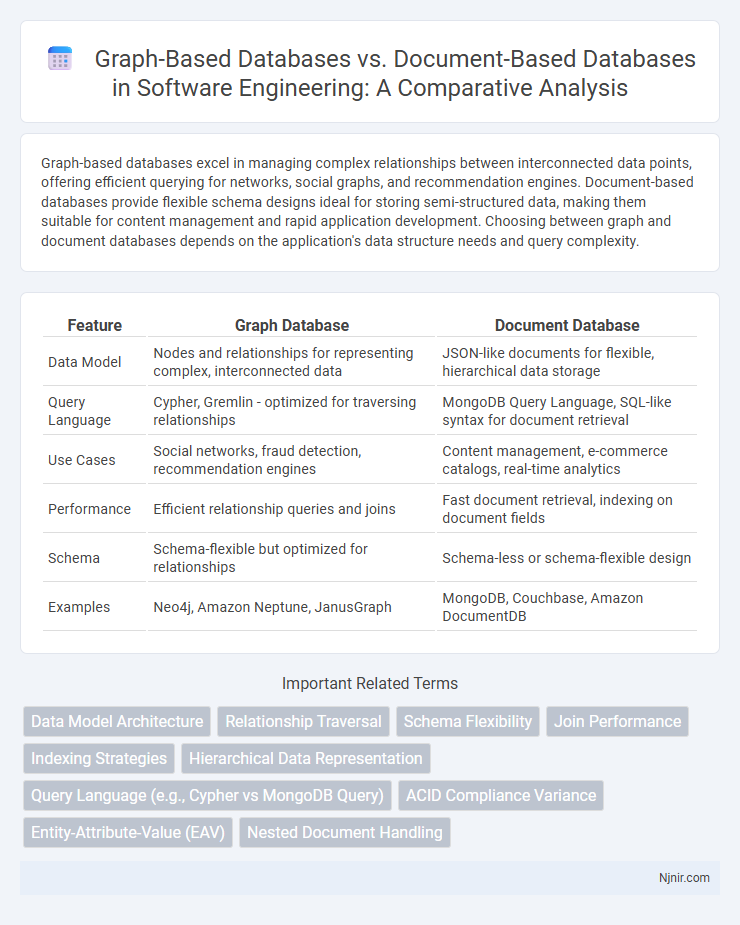
Graph-based databases excel in managing complex relationships between interconnected data points, offering efficient querying for networks, social graphs, and recommendation engines. Document-based databases provide flexible schema designs ideal for storing semi-structured data, making them suitable for content management and rapid application development. Choosing between graph and document databases depends on the application's data structure needs and query complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graph Database | Document Database |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Nodes and relationships for representing complex, interconnected data | JSON-like documents for flexible, hierarchical data storage |
| Query Language | Cypher, Gremlin - optimized for traversing relationships | MongoDB Query Language, SQL-like syntax for document retrieval |
| Use Cases | Social networks, fraud detection, recommendation engines | Content management, e-commerce catalogs, real-time analytics |
| Performance | Efficient relationship queries and joins | Fast document retrieval, indexing on document fields |
| Schema | Schema-flexible but optimized for relationships | Schema-less or schema-flexible design |
| Examples | Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, JanusGraph | MongoDB, Couchbase, Amazon DocumentDB |
Introduction to Database Models in Software Engineering
Graph-based databases utilize nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data relationships, offering efficient querying for complex, interconnected data often found in social networks and recommendation systems. Document-based databases store data as JSON-like documents, providing flexible schema designs ideal for handling unstructured or semi-structured information in content management and real-time analytics. Both models support modern software engineering needs, but graph databases excel in relationship-heavy applications while document databases prioritize scalability and schema flexibility.
Core Concepts: Graph-Based vs Document-Based Databases
Graph-based databases model data as nodes, relationships, and properties, enabling efficient traversal and querying of complex, interconnected data. Document-based databases store data in flexible, JSON-like documents, allowing for schema-less designs and easy storage of hierarchical information. Graph databases excel in use cases requiring relationship analysis, while document databases are optimized for handling nested data structures and rapid data retrieval.
Data Structure and Storage Mechanisms
Graph-based databases utilize nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data, enabling efficient handling of complex relationships and connections through adjacency lists or matrices. Document-based databases store data in JSON-like documents, allowing hierarchical, schema-flexible structures that are optimized for nested data retrieval and aggregation. The storage mechanism in graph databases focuses on relationship traversal performance, while document databases emphasize fast access to semi-structured, self-contained data units.
Query Languages and Data Retrieval Approaches
Graph-based databases utilize query languages like Cypher and Gremlin, designed to efficiently traverse relationships and uncover complex patterns within connected data. Document-based databases employ query languages such as MongoDB's query language and N1QL, optimized for retrieving hierarchical data structures stored as JSON-like documents. The data retrieval approach in graph databases focuses on relationship-centric queries enabling deep joins and pattern matching, whereas document databases emphasize flexible, schema-less data access with nested object retrieval.
Relationship Modeling and Handling Complex Connections
Graph-based databases excel at relationship modeling by using nodes, edges, and properties to represent and query intricate, interconnected data, enabling efficient traversal of complex connections such as social networks or recommendation systems. Document-based databases store data in JSON-like documents, which makes them flexible for hierarchical data but less efficient for handling many-to-many relationships or deep joins across collections. In scenarios requiring rapid querying of multi-hop relationships, graph databases provide superior performance and intuitive data representation compared to document stores, which may require costly aggregation pipelines or multiple queries.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
Graph-based databases excel in managing complex, interconnected data with high query performance on relationship-heavy datasets, but can face challenges scaling horizontally due to dependencies on graph traversals. Document-based databases offer superior scalability and flexibility by distributing data across multiple nodes and efficiently handling diverse, semi-structured data formats, making them suitable for horizontal scaling and varying workloads. Performance in graph databases is optimized for deep joins and relationship queries, while document databases prioritize fast read/write speeds and scalable storage for large volumes of loosely connected data.
Use Cases: When to Choose Graph or Document Databases
Graph databases excel in managing complex relationships and interconnected data, making them ideal for social networks, recommendation engines, fraud detection, and knowledge graphs. Document databases are better suited for flexible, semi-structured data models such as content management systems, e-commerce catalogs, and real-time analytics with JSON or BSON documents. Choose graph databases when relationship depth and traversal speed are critical, while document databases fit scenarios requiring scalable, schema-less storage and rapid iteration on evolving data structures.
Integration with Modern Application Architectures
Graph-based databases excel in handling complex relationships and queries, making them ideal for recommendation systems and social networks in modern microservices architectures. Document-based databases offer flexible schema designs and seamless integration with JSON APIs, supporting rapid development and scalability in cloud-native applications. Both database types enable efficient data retrieval and storage suited to specific application needs, enhancing performance and developer productivity.
Security and Data Consistency Mechanisms
Graph-based databases implement robust security models with fine-grained access controls, supporting role-based permissions directly on nodes and relationships, enhancing data confidentiality. They utilize ACID-compliant transactions ensuring strong consistency and integrity for complex interconnected data structures. Document-based databases rely on schema validation and encryption for security, with eventual consistency models in many NoSQL implementations, which can lead to temporary data anomalies under high loads.
Future Trends in Graph and Document Database Evolution
Graph databases are increasingly integrating advanced machine learning algorithms to enhance relationship discovery and complex data pattern analysis, positioning them as critical tools for AI-driven applications. Document-based databases are evolving with improved scalability and flexible schema designs, enabling seamless handling of semi-structured and rapidly changing data typical in modern web and mobile applications. Future trends indicate a convergence where hybrid systems leverage the strengths of both graph and document models, optimizing storage efficiency and query performance across diverse data types and use cases.
Data Model Architecture
Graph-based databases use nodes, edges, and properties to model complex, interconnected relationships, while document-based databases organize data into flexible, hierarchical JSON or BSON documents optimized for nested, schema-less storage.
Relationship Traversal
Graph-based databases excel in relationship traversal by efficiently mapping and querying complex, interconnected data through nodes and edges, whereas document-based databases handle relationships less intuitively, often requiring multiple queries or embedded documents for traversal.
Schema Flexibility
Graph-based databases offer dynamic schema flexibility enabling seamless evolution of complex relationships, while document-based databases provide flexible schema structures suited for nested, document-centric data models.
Join Performance
Graph-based databases excel in join performance by efficiently traversing relationships through edges, while document-based databases often experience slower join operations due to their denormalized, hierarchical data structure.
Indexing Strategies
Graph-based databases optimize indexing with specialized graph indexes like adjacency lists and path indexes to efficiently traverse relationships, while document-based databases use inverted indexes and B-tree structures to rapidly query nested document fields and metadata.
Hierarchical Data Representation
Graph-based databases excel at representing complex hierarchical relationships through interconnected nodes and edges, whereas document-based databases store hierarchical data as nested documents but may face limitations in efficiently querying deep or highly connected structures.
Query Language (e.g., Cypher vs MongoDB Query)
Graph-based databases use Cypher for expressive pattern-matching queries on interconnected data, while document-based databases like MongoDB employ a JSON-style query language optimized for flexible, hierarchical document retrieval.
ACID Compliance Variance
Graph-based databases typically offer stronger native ACID compliance for complex relationship queries, while document-based databases often trade off strict ACID guarantees to enhance scalability and flexible schema handling.
Entity-Attribute-Value (EAV)
Graph-based databases excel at modeling complex Entity-Attribute-Value (EAV) relationships with dynamic schema flexibility and efficient traversal, unlike document-based databases which store EAV data in nested documents but face challenges in relationship querying and schema evolution.
Nested Document Handling
Graph-based databases efficiently model and query complex relationships, while document-based databases excel at storing and retrieving nested documents with flexible schemas.
Graph-based DB vs Document-based DB Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com