Jamstack architecture enhances web performance by decoupling the frontend and backend, delivering pre-rendered static pages that load faster and improve scalability compared to traditional web apps reliant on server-side rendering. Unlike traditional monolithic systems, Jamstack leverages APIs and CDN distribution to reduce server load and enhance security. This modern approach streamlines development workflows while providing a superior user experience through improved speed, reliability, and maintainability.
Table of Comparison
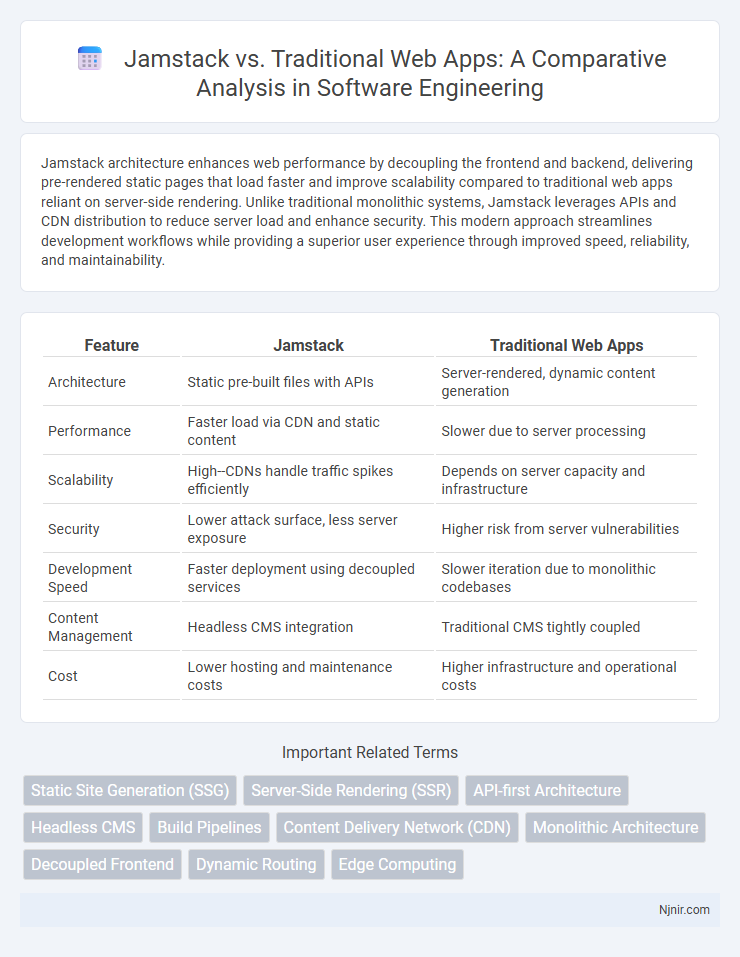
| Feature | Jamstack | Traditional Web Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Static pre-built files with APIs | Server-rendered, dynamic content generation |
| Performance | Faster load via CDN and static content | Slower due to server processing |
| Scalability | High--CDNs handle traffic spikes efficiently | Depends on server capacity and infrastructure |
| Security | Lower attack surface, less server exposure | Higher risk from server vulnerabilities |
| Development Speed | Faster deployment using decoupled services | Slower iteration due to monolithic codebases |
| Content Management | Headless CMS integration | Traditional CMS tightly coupled |
| Cost | Lower hosting and maintenance costs | Higher infrastructure and operational costs |
Introduction to Jamstack and Traditional Web Apps
Jamstack is a modern web development architecture that decouples the frontend from the backend, using static site generation, APIs, and microservices to deliver fast, secure, and scalable websites. Traditional web apps rely on server-side rendering and monolithic architectures where the backend processes requests, generates HTML dynamically, and serves content, often leading to slower load times and higher server loads. Jamstack offers enhanced performance by pre-rendering pages at build time and serving them via content delivery networks (CDNs), contrasting with the dynamic nature of traditional server-rendered web applications.
Core Architectural Differences
Jamstack architecture decouples the frontend from the backend, serving pre-rendered static pages from a CDN for faster load times and improved security, whereas traditional web apps rely on server-side rendering and dynamic page generation on-demand. Jamstack leverages APIs and microservices to handle dynamic content, reducing server dependencies, while traditional web apps often integrate business logic and data processing tightly within the server environment. This separation in Jamstack optimizes scalability and developer experience by enabling parallel development and simpler deployment workflows.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Jamstack architecture delivers superior performance and speed by serving pre-rendered static pages via CDNs, reducing server load and minimizing latency. Traditional web apps rely on server-side rendering and database queries for each request, leading to slower response times and increased server overhead. The decentralized approach of Jamstack ensures faster content delivery and improved scalability compared to conventional dynamic web app models.
Security Considerations
Jamstack architecture enhances security by serving pre-built static files via a CDN, minimizing server-side vulnerabilities common in traditional web apps that rely on dynamic content generation and databases. Traditional web apps often face higher risks of SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and server misconfigurations because they process requests in real-time on the server. Jamstack reduces attack surfaces by delegating backend operations to APIs and serverless functions, isolating critical processes and improving overall security posture.
Scalability and Maintenance
Jamstack architecture enhances scalability by serving pre-rendered static files through content delivery networks (CDNs), reducing server load and handling high traffic spikes effortlessly. Traditional web apps often rely on monolithic servers that require complex scaling strategies, including load balancers and database optimizations, increasing maintenance overhead. Maintenance in Jamstack is streamlined through decoupled services and modern build tools, enabling faster updates and fewer runtime errors compared to the tightly coupled codebases typical in traditional web applications.
Developer Experience and Tooling
Jamstack architecture enhances developer experience by leveraging modern build tools, decoupled frontends, and APIs, enabling faster iterations and streamlined workflows compared to traditional web apps. Developers benefit from static site generators, automated CI/CD pipelines, and headless CMS integrations that simplify content management and deployment. Traditional web apps often rely on monolithic frameworks and server-side rendering, which can increase complexity and slow down the development cycle.
Content Management Options
Jamstack architecture utilizes headless CMS platforms like Contentful, Sanity, and Strapi that decouple content management from front-end delivery, enabling faster load times and improved scalability. Traditional web apps often rely on monolithic CMS solutions such as WordPress or Drupal, where the backend and frontend are tightly integrated, leading to slower updates and increased server load. Jamstack's API-driven content management options enhance developer flexibility and facilitate seamless integration with static site generators, improving overall performance and user experience.
SEO Implications
Jamstack architecture improves SEO by delivering pre-rendered static pages with faster load times and enhanced security, which are highly favored by search engines. Traditional web apps often rely on server-side rendering and dynamic content generation, causing slower page speed and potential crawlability issues. Leveraging Jamstack ensures better indexing, higher Core Web Vitals scores, and improved user experience compared to traditional web applications.
Use Cases and Real-World Examples
Jamstack architecture excels in static site generation and fast content delivery, making it ideal for marketing websites, blogs, and e-commerce platforms like Netlify and Shopify. Traditional web applications remain suitable for complex, data-driven use cases such as enterprise dashboards, CRM systems, and social media platforms exemplified by Salesforce and Facebook. Organizations prioritize Jamstack for scalability and performance, while traditional stacks are preferred for real-time updates and dynamic user interactions.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Choosing between Jamstack and traditional web apps depends on project requirements such as performance, scalability, and development speed. Jamstack offers enhanced security, faster load times, and easier deployment through static site generation and CDN distribution, ideal for content-heavy or high-traffic sites. Traditional web apps provide dynamic content handling and complex backend integrations, better suited for applications requiring real-time data and extensive server-side logic.
Static Site Generation (SSG)
Static Site Generation (SSG) in Jamstack delivers faster load times, improved scalability, and enhanced security compared to traditional web apps by pre-rendering HTML at build time rather than generating pages dynamically on the server.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Jamstack leverages pre-rendering and client-side rendering to enhance scalability and performance, while traditional web apps rely on Server-Side Rendering (SSR) for dynamic content generation and real-time data processing.
API-first Architecture
Jamstack leverages API-first architecture to enhance performance and scalability by decoupling the frontend from backend services, unlike traditional web apps that rely on tightly integrated server-side rendering.
Headless CMS
Jamstack leverages Headless CMS to deliver faster, scalable, and more secure websites by decoupling content management from frontend presentation, unlike traditional web apps that tightly integrate CMS with backend logic.
Build Pipelines
Jamstack build pipelines leverage static site generators and CDN deployment for faster, scalable performance while traditional web app pipelines rely on server-side rendering and monolithic deployments that increase build complexity and slower release cycles.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Jamstack websites leverage Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to deliver pre-rendered, static assets globally with low latency, outperforming traditional web apps that rely on server-based content delivery and incur higher load times.
Monolithic Architecture
Jamstack offers a decoupled approach with static site generation, reducing the complexity and scalability issues commonly associated with monolithic architecture in traditional web apps.
Decoupled Frontend
Jamstack architecture enhances performance and scalability by decoupling the frontend from the backend, unlike traditional web apps that tightly integrate both layers.
Dynamic Routing
Jamstack leverages client-side rendering and pre-generated static pages with dynamic routing handled via JavaScript frameworks, while traditional web apps rely on server-side routing for real-time URL management and content delivery.
Edge Computing
Jamstack architecture leverages edge computing by delivering pre-rendered content from global CDN nodes for faster load times and enhanced security compared to traditional web apps relying on centralized servers.
Jamstack vs traditional web apps Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com