Pull requests and merge requests serve the same purpose in collaborative software development by enabling code reviews before integration. Pull requests are typically associated with GitHub, allowing developers to propose changes and initiate discussions around the code. Merge requests, used primarily in GitLab, offer similar functionality but often include integrated CI/CD pipelines for automated testing and deployment.
Table of Comparison
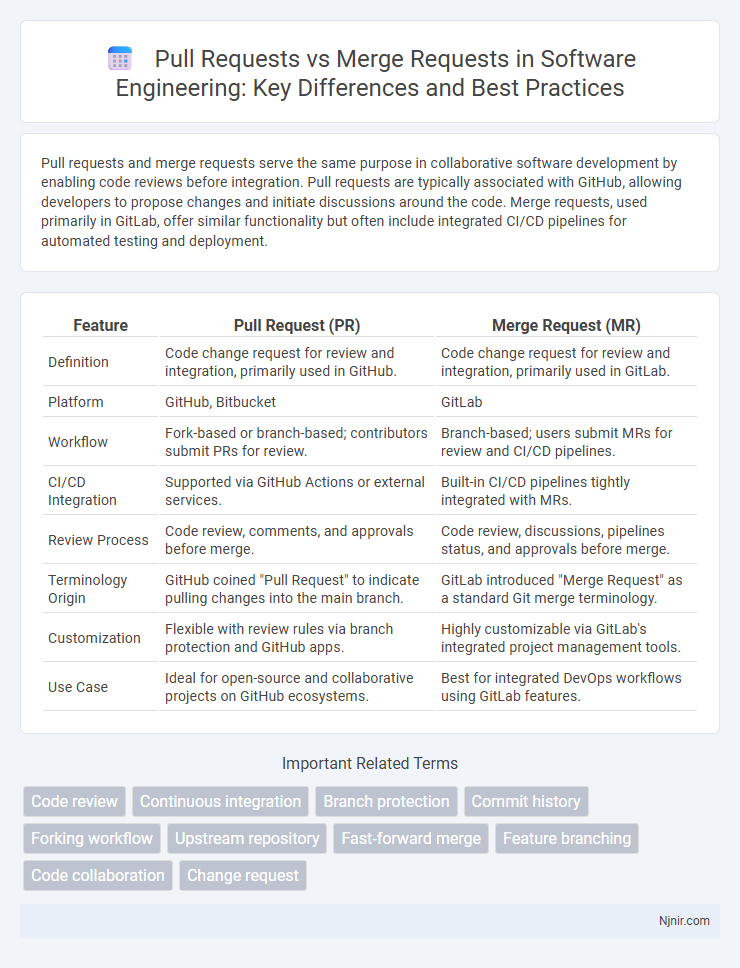
| Feature | Pull Request (PR) | Merge Request (MR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Code change request for review and integration, primarily used in GitHub. | Code change request for review and integration, primarily used in GitLab. |
| Platform | GitHub, Bitbucket | GitLab |
| Workflow | Fork-based or branch-based; contributors submit PRs for review. | Branch-based; users submit MRs for review and CI/CD pipelines. |
| CI/CD Integration | Supported via GitHub Actions or external services. | Built-in CI/CD pipelines tightly integrated with MRs. |
| Review Process | Code review, comments, and approvals before merge. | Code review, discussions, pipelines status, and approvals before merge. |
| Terminology Origin | GitHub coined "Pull Request" to indicate pulling changes into the main branch. | GitLab introduced "Merge Request" as a standard Git merge terminology. |
| Customization | Flexible with review rules via branch protection and GitHub apps. | Highly customizable via GitLab's integrated project management tools. |
| Use Case | Ideal for open-source and collaborative projects on GitHub ecosystems. | Best for integrated DevOps workflows using GitLab features. |
Introduction to Pull Requests and Merge Requests
Pull requests and merge requests are collaborative code review tools used in version control systems to propose changes before merging them into the main codebase. Pull requests are primarily associated with GitHub, while merge requests are used in GitLab, both facilitating peer review, discussion, and automated testing. These mechanisms improve code quality by enabling developers to review changes, suggest improvements, and ensure integration aligns with project standards.
Key Concepts: Pull Requests Explained
Pull requests are a crucial collaboration feature in GitHub that enable developers to propose code changes before integrating them into the main codebase. They facilitate peer review, discussion, and automated testing, ensuring code quality and reducing integration errors. Pull requests consist of source and target branches, commit history, and conversation threads, providing transparency and traceability throughout the development workflow.
Understanding Merge Requests
Merge requests are a feature primarily used in GitLab that facilitate code review and collaboration by allowing developers to propose changes before integrating them into the main branch. They provide a structured workflow that includes discussions, automated testing, and approval processes to ensure code quality and maintain project stability. Understanding merge requests is essential for effective team collaboration and maintaining a clean, stable codebase during continuous integration.
Core Differences Between Pull Requests and Merge Requests
Pull requests and merge requests both facilitate code collaboration by enabling developers to review and integrate changes, but pull requests are primarily associated with GitHub, while merge requests are GitLab's equivalent feature. A core difference lies in terminology and interface, with GitLab's merge requests offering built-in CI/CD pipeline integration and more customizable merge options, enhancing automation and workflow control. Additionally, pull requests emphasize review comments and code discussions, whereas merge requests provide advanced project management integrations and closer integration with GitLab's DevOps lifecycle.
Workflow Comparison: GitHub vs GitLab Approaches
GitHub uses pull requests as a central collaboration tool where developers propose, discuss, and review code changes before merging into the main branch, emphasizing a streamlined interface and extensive integration with third-party tools. GitLab's merge requests offer a comprehensive workflow with built-in continuous integration, code quality checks, and rich project management features, enhancing automation and traceability within the same platform. Both approaches facilitate code review and collaboration but GitLab integrates deeper DevOps lifecycle features, whereas GitHub focuses on broad ecosystem compatibility and simplicity in the branching workflow.
Collaboration and Code Review Processes
Pull requests and merge requests both facilitate collaboration by enabling developers to propose changes while allowing team members to review, comment, and suggest improvements before integration. These processes support thorough code review, ensuring adherence to project standards and reducing errors through peer feedback. Effective use of these tools enhances transparency and accountability within development teams, promoting higher code quality and streamlined workflows.
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Pull requests and merge requests both facilitate code review and collaboration, but they differ in integration nuances with CI/CD pipelines. Pull requests, commonly used in GitHub, trigger automated pipeline jobs that run tests, builds, and deployments upon submission or updates, ensuring continuous integration. Merge requests, primarily in GitLab, offer deeper native CI/CD integration, enabling seamless automation, advanced pipeline configurations, and environment-specific deployment strategies for streamlined continuous delivery workflows.
Security and Permission Management
Pull requests and merge requests both facilitate code collaboration with distinct security and permission management features tailored to their platforms. Pull requests, commonly used in GitHub, offer granular branch protection rules and require status checks or code reviews before merging, enhancing security by preventing unauthorized changes. Merge requests in GitLab provide advanced permission controls, including role-based access levels and approval rules, enabling precise enforcement of secure development workflows and compliance standards.
Best Practices for Request Management
Effective request management in pull requests and merge requests involves clear, concise commit messages and detailed descriptions outlining purpose and changes. Implement code reviews with well-defined guidelines and enable automated testing to ensure quality and consistency. Prioritize timely feedback and systematic conflict resolution to streamline collaboration and integration processes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Team
Choosing between pull requests and merge requests depends on your team's collaboration style and platform preferences. Pull requests, primarily used on GitHub, provide a streamlined interface for code review and continuous integration, enhancing transparency and communication. Merge requests, favored on GitLab, offer integrated CI/CD pipelines and detailed permission controls that support complex workflows and tighter security requirements.
Code review
Pull requests and merge requests both facilitate code review by enabling team collaboration, inline comments, and approval workflows to ensure code quality before integration.
Continuous integration
Pull requests and merge requests both facilitate code review and integration in continuous integration pipelines by triggering automated builds and tests before merging changes into the main branch.
Branch protection
Branch protection enforces rules on pull requests and merge requests, preventing unauthorized merges and ensuring code quality before integration.
Commit history
Pull requests and merge requests both preserve commit history during code integration, but merge requests in GitLab offer advanced options for squash merging and commit message customization to maintain a cleaner and more informative commit history.
Forking workflow
Pull requests in GitHub and merge requests in GitLab both facilitate code review in the Forking workflow by enabling contributors to propose changes from feature branches in their forks to the main repository, ensuring collaborative integration and project integrity.
Upstream repository
Pull requests and merge requests both facilitate code integration, but pull requests specifically emphasize contributing changes from a forked repository to the upstream repository for review and collaboration.
Fast-forward merge
Fast-forward merges in pull requests and merge requests update the target branch by directly applying commits without creating a merge commit, ensuring a linear and clean project history.
Feature branching
Feature branching enables developers to isolate new functionalities in pull requests on GitHub or merge requests on GitLab, streamlining code review and integration workflows.
Code collaboration
Pull requests and merge requests are collaborative code review tools used in GitHub and GitLab respectively to propose, discuss, and integrate code changes efficiently within development teams.
Change request
Pull requests and merge requests are collaborative tools in Git-based workflows that facilitate code review and change requests by allowing contributors to propose, discuss, and approve modifications before integrating them into the main codebase.
pull requests vs merge requests Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com