Vue offers a lightweight framework with a gentle learning curve, making it ideal for small to medium-sized projects that require rapid development and flexibility. Angular provides a comprehensive, full-featured platform with built-in tools and strong typing through TypeScript, suited for large-scale applications demanding robust architecture and scalability. Choosing between Vue and Angular depends on project complexity, team expertise, and long-term maintenance goals.
Table of Comparison
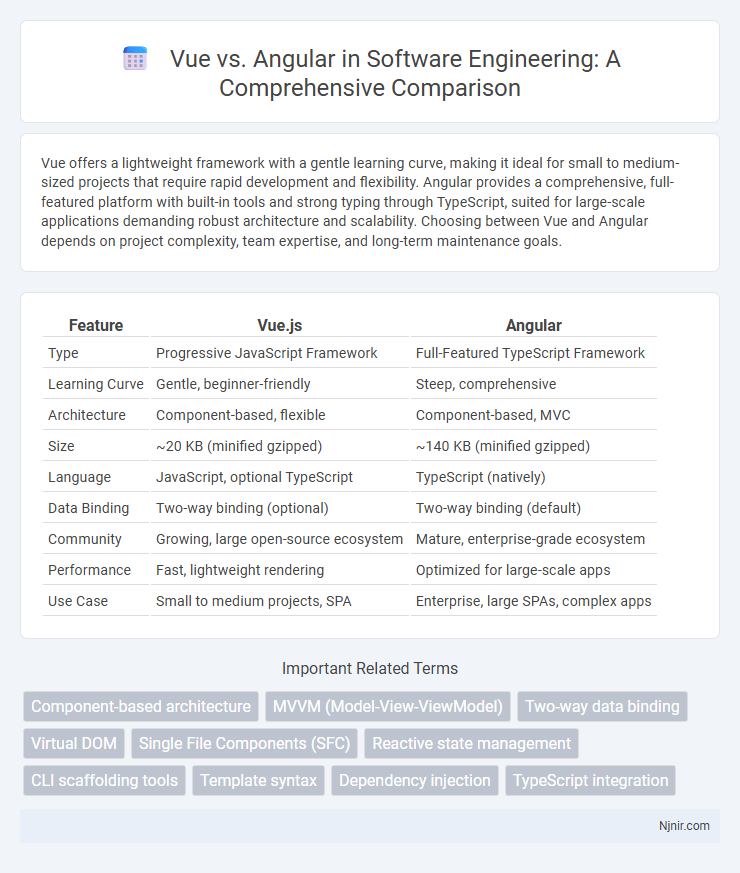
| Feature | Vue.js | Angular |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Progressive JavaScript Framework | Full-Featured TypeScript Framework |
| Learning Curve | Gentle, beginner-friendly | Steep, comprehensive |
| Architecture | Component-based, flexible | Component-based, MVC |
| Size | ~20 KB (minified gzipped) | ~140 KB (minified gzipped) |
| Language | JavaScript, optional TypeScript | TypeScript (natively) |
| Data Binding | Two-way binding (optional) | Two-way binding (default) |
| Community | Growing, large open-source ecosystem | Mature, enterprise-grade ecosystem |
| Performance | Fast, lightweight rendering | Optimized for large-scale apps |
| Use Case | Small to medium projects, SPA | Enterprise, large SPAs, complex apps |
Overview: Introduction to Vue and Angular
Vue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework renowned for its simplicity, flexibility, and ease of integration in building user interfaces and single-page applications. Angular, developed by Google, is a comprehensive TypeScript-based framework featuring a robust architecture ideal for large-scale, enterprise-level web applications. Both frameworks offer reactive data binding and component-based structures, but Vue emphasizes lightweight and incremental adoption while Angular provides an all-in-one solution with built-in tooling and extensive features.
Popularity and Community Support
Vue boasts a rapidly growing popularity with a strong developer community, facilitated by its approachable learning curve and flexible architecture. Angular maintains a large, well-established community backed by Google, offering extensive resources and long-term support for enterprise-level applications. Both frameworks benefit from active ecosystems, but Vue's surge in adoption is reflected in GitHub stars and npm downloads surpassing Angular in recent years.
Architecture Comparison
Vue employs a progressive framework architecture centered around a virtual DOM and reactive data binding, promoting flexibility through single-file components that combine HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Angular utilizes a component-based architecture with a dependency injection system, TypeScript integration, and an MVC (Model-View-Controller) structure that emphasizes modular development and strong typing. Vue's lightweight and incrementally adoptable design allows easier integration into projects, whereas Angular's comprehensive framework offers a robust solution for enterprise-scale applications requiring extensive tooling and structure.
Learning Curve and Documentation
Vue offers a gentler learning curve compared to Angular, making it more accessible for beginners and developers transitioning from other frameworks. The Vue documentation is praised for its clarity, simplicity, and practical examples, facilitating faster onboarding and implementation. Angular provides a comprehensive but complex documentation set, which, combined with its steep learning curve due to TypeScript and advanced concepts, can require a longer adjustment period for developers.
Performance Benchmarks
Vue demonstrates faster initial load times and smaller bundle sizes compared to Angular, making it more efficient for lightweight applications. Angular's performance excels in large-scale projects with complex data-binding and dependency injection due to its Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation and hierarchical dependency injection system. Benchmarks indicate Vue's reactivity system enables quicker DOM updates, while Angular benefits from optimized change detection in enterprise-level scenarios.
Development Speed and Productivity
Vue's lightweight architecture and gentle learning curve enable faster development cycles compared to Angular's comprehensive framework, which often requires more initial setup and configuration. Developers report higher productivity with Vue due to its simpler syntax, flexibility, and seamless integration capabilities, reducing time spent on boilerplate code. Angular provides robust tooling and built-in functionalities but can slow development speed in complex projects due to its steep learning curve and extensive boilerplate requirements.
Flexibility and Scalability
Vue offers significant flexibility with its progressive architecture, allowing developers to incrementally adopt features and tailor the framework to specific project needs, making it ideal for small to medium-scale applications. Angular provides robust scalability through its comprehensive tooling, strong typing with TypeScript, and enterprise-grade features like dependency injection and modular development, supporting large, complex applications. Both frameworks support component-based architecture, but Angular's built-in solutions suit extensive projects, while Vue's simplicity enhances adaptability and rapid development.
Tooling and Ecosystem
Vue offers a lightweight, intuitive tooling system with Vue CLI and Vue Devtools, enabling rapid development and easy state management through Vuex. Angular provides a comprehensive, all-in-one framework with an extensive CLI, integrated testing utilities, and a robust ecosystem including RxJS for reactive programming and Angular Material for UI components. Both ecosystems support efficient development, but Angular's tooling is more opinionated and feature-rich, while Vue's ecosystem emphasizes flexibility and simplicity.
Real-World Use Cases
Vue excels in single-page applications and progressive web apps due to its lightweight nature and flexibility, making it ideal for startups and small to medium-sized projects. Angular, with its comprehensive framework and TypeScript integration, is favored for large-scale enterprise applications requiring robust architecture and extensive tooling. Companies like Alibaba leverage Vue for rapid UI development, while Google uses Angular extensively for complex, data-heavy applications such as Google Cloud Platform.
Choosing the Right Framework
Selecting the right framework depends on project requirements and team expertise; Vue offers a gentle learning curve and flexibility ideal for small to medium applications, while Angular provides a robust, full-featured platform suited for large-scale enterprise projects. Vue's component-based architecture and reactivity system enable rapid development with minimal setup, whereas Angular incorporates comprehensive tooling, dependency injection, and TypeScript for strong typing and maintainability. Evaluating factors such as project complexity, scalability needs, ecosystem support, and developer proficiency ensures an informed decision between Vue and Angular for optimal performance and long-term success.
Component-based architecture
Vue and Angular both utilize component-based architecture, with Vue offering a lightweight, flexible framework ideal for incremental adoption, while Angular provides a robust, full-featured platform with built-in dependency injection and comprehensive tooling.
MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel)
Vue's MVVM architecture enhances developer productivity by offering reactive data binding and a flexible ViewModel layer, while Angular implements MVVM with a more opinionated framework providing comprehensive tooling and two-way data binding for complex enterprise applications.
Two-way data binding
Vue offers more intuitive and flexible two-way data binding through its v-model directive, while Angular provides robust two-way data binding primarily via ngModel within its reactive forms framework.
Virtual DOM
Vue leverages a lightweight Virtual DOM to efficiently update UI components by minimizing direct DOM manipulation, while Angular uses a real DOM with change detection mechanisms that can be less performant for dynamic interfaces.
Single File Components (SFC)
Vue's Single File Components (SFC) offer a streamlined, integrated approach combining HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in one file, contrasting with Angular's use of separate files and decorators for component structure and styling.
Reactive state management
Vue offers a simpler and more intuitive reactive state management system with Vuex, leveraging its reactivity API, while Angular uses NgRx, which provides a more complex but scalable Redux-based state management for large-scale applications.
CLI scaffolding tools
Vue CLI offers a flexible, progressive scaffolding tool with instant hot-reload and plugin-based architecture, while Angular CLI provides a robust, opinionated scaffolding solution featuring built-in support for complex enterprise-grade applications and comprehensive code generation.
Template syntax
Vue offers a more intuitive and flexible template syntax with directives like v-bind and v-for, while Angular uses a more complex and verbose syntax with structural directives such as *ngFor and *ngIf for dynamic content rendering.
Dependency injection
Vue uses a simpler, flexible dependency injection system primarily through provide/inject APIs, while Angular offers a robust, hierarchical dependency injection framework integral to its architecture for managing services and components efficiently.
TypeScript integration
Vue offers gradual and flexible TypeScript integration with optional typings, while Angular provides comprehensive, built-in TypeScript support for robust enterprise-level application development.
Vue vs Angular Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com