Drone surveying offers higher resolution data and real-time imaging for detailed topographic mapping, making it ideal for precise site analysis and progress monitoring in civil engineering projects. Satellite surveying covers larger areas quickly and is valuable for regional planning and environmental impact assessments, though it generally provides lower spatial resolution compared to drones. Combining both technologies enhances project accuracy by leveraging drones for localized detail and satellites for broad-scale contextual data.
Table of Comparison
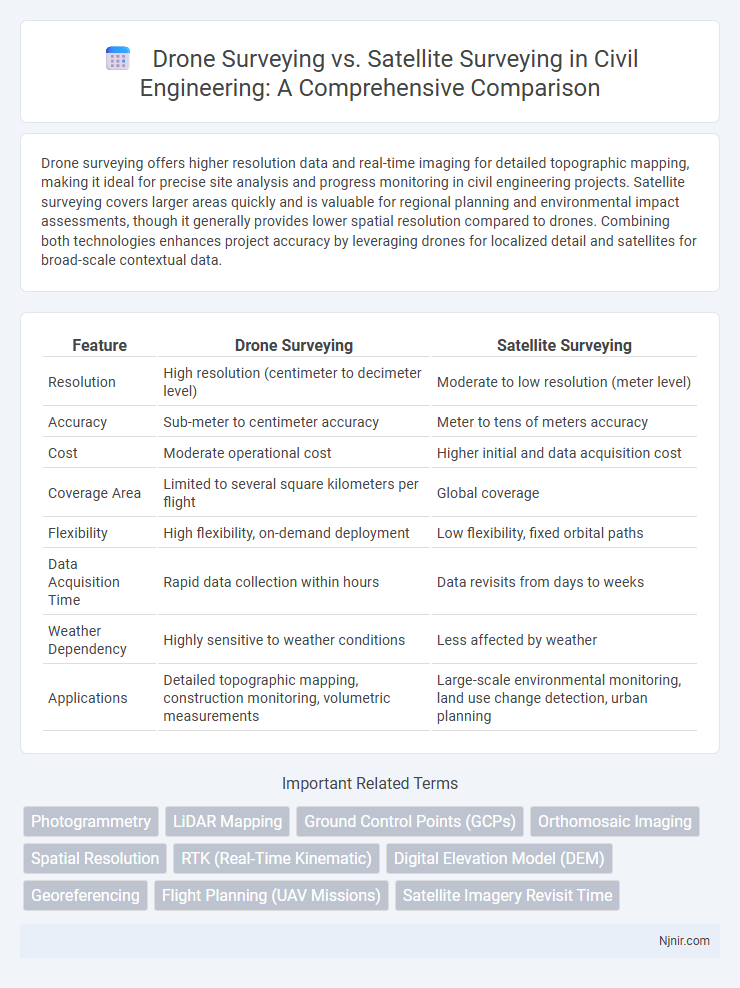
| Feature | Drone Surveying | Satellite Surveying |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | High resolution (centimeter to decimeter level) | Moderate to low resolution (meter level) |
| Accuracy | Sub-meter to centimeter accuracy | Meter to tens of meters accuracy |
| Cost | Moderate operational cost | Higher initial and data acquisition cost |
| Coverage Area | Limited to several square kilometers per flight | Global coverage |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, on-demand deployment | Low flexibility, fixed orbital paths |
| Data Acquisition Time | Rapid data collection within hours | Data revisits from days to weeks |
| Weather Dependency | Highly sensitive to weather conditions | Less affected by weather |
| Applications | Detailed topographic mapping, construction monitoring, volumetric measurements | Large-scale environmental monitoring, land use change detection, urban planning |
Overview of Drone and Satellite Surveying in Civil Engineering
Drone surveying in civil engineering offers high-resolution aerial data collection with rapid deployment and precise site mapping, enhancing project accuracy and monitoring. Satellite surveying provides extensive geographic coverage and consistent temporal data, essential for large-scale infrastructure planning and environmental assessment. Integrating both technologies optimizes data accuracy and project outcomes by balancing detailed local insights with broad regional perspectives.
Key Technologies Behind Drone and Satellite Surveys
Drone surveying relies on advanced UAVs equipped with high-resolution cameras, LiDAR sensors, and GPS modules to capture precise aerial imagery and topographic data. Satellite surveying utilizes remote sensing technologies such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and multispectral imaging sensors that collect large-scale geospatial data from orbit. Both methods employ sophisticated processing algorithms and GNSS for accurate georeferencing and data integration in mapping applications.
Accuracy Comparison: Drone vs Satellite Data
Drone surveying provides higher spatial resolution and more accurate topographic data compared to satellite surveying, with centimeter-level precision achievable in drone-derived models. Satellite surveying, while offering broader coverage and frequent updates, generally produces data with meter-level accuracy, which may be insufficient for detailed mapping or construction planning. The enhanced accuracy of drone data suits applications requiring precise measurements such as infrastructure inspection, agriculture monitoring, and land surveying.
Cost Analysis of Drone and Satellite Surveying
Drone surveying offers significantly lower operational costs compared to satellite surveying, with expenses primarily tied to drone purchase, maintenance, and pilot training. Satellite surveying incurs high initial satellite deployment and data acquisition costs, making it less economical for small-scale or frequent surveys. Cost efficiency of drone surveying increases with project size and frequency, while satellite surveying is more advantageous for large-scale, global data analysis despite its higher costs.
Surveying Speed and Project Timeline Efficiency
Drone surveying offers rapid data collection with the ability to cover large areas within hours, significantly accelerating the surveying speed compared to satellite surveying, which depends on predetermined satellite passes and can take days or weeks. The high-resolution imagery and real-time data processing capabilities of drone technology enhance project timeline efficiency by enabling immediate analysis and faster decision-making. Conversely, satellite surveying, while useful for extensive geographic coverage, often requires longer intervals between data acquisition and processing, potentially delaying project milestones.
Resolution and Data Quality: Drones vs Satellites
Drone surveying offers superior resolution and data quality compared to satellite surveying due to its ability to fly at lower altitudes, capturing finer details with high-definition cameras and LiDAR sensors. Satellite surveying, while covering larger areas, provides lower spatial resolution and may be affected by atmospheric conditions, limiting the precision of data in comparison to drones. The enhanced resolution from drone imagery supports more accurate mapping, detailed inspections, and precise measurements for applications like construction, agriculture, and environmental monitoring.
Accessibility and Flexibility for Site Surveys
Drone surveying offers superior accessibility and flexibility for site surveys by enabling low-altitude, close-range data collection in challenging or remote areas, where satellite imagery may be obstructed or outdated. The ability to deploy drones quickly and adjust flight paths on-demand allows for detailed, high-resolution mapping tailored to specific project needs. Satellite surveying provides a broader geographic perspective but lacks the adaptability and precision of drones in varied terrain and rapidly changing environments.
Environmental Impact and Regulatory Considerations
Drone surveying offers reduced environmental disruption by minimizing ground disturbance and allowing targeted data collection, whereas satellite surveying involves broader land coverage with less immediate impact on ecosystems but may consume significant energy through satellite operation and data transmission. Regulatory frameworks for drone surveys often require compliance with airspace restrictions, privacy laws, and obtaining flight permits, while satellite surveys are governed by international space treaties and national remote sensing regulations that address data usage and security. Both methods necessitate careful consideration of their ecological footprints and legal guidelines to ensure sustainable and responsible environmental monitoring.
Best Use Cases for Drones and Satellites in Civil Projects
Drone surveying excels in capturing high-resolution, detailed data for small to medium-scale civil projects such as construction site monitoring, topographic mapping, and infrastructure inspections, offering rapid data collection and easy accessibility to complex terrains. Satellite surveying is ideal for large-scale geospatial analysis, environmental monitoring, and regional planning, providing broad coverage and continuous data over extensive geographic areas with lower revisit times. Combining drone and satellite data enhances civil project outcomes by leveraging drones' precision with satellites' wide-area insights for comprehensive project management and decision-making.
Future Trends in Surveying Technology for Civil Engineering
Drone surveying offers high-resolution, real-time data collection with flexibility over challenging terrains, while satellite surveying provides extensive coverage and long-term monitoring capabilities but with lower spatial resolution. Future trends in surveying technology for civil engineering emphasize integrating AI-driven data analytics, enhanced sensor accuracy, and hybrid approaches combining drone and satellite data to optimize project planning, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure maintenance. Advances in autonomous drones, cloud-based geospatial platforms, and IoT connectivity will further revolutionize precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in civil engineering surveys.
Photogrammetry
Drone surveying captures high-resolution, low-altitude images enabling precise photogrammetry for detailed 3D mapping, while satellite surveying offers broader coverage with lower resolution suitable for large-scale terrain analysis.
LiDAR Mapping
Drone surveying using LiDAR mapping offers higher resolution and greater accuracy for detailed terrain analysis compared to satellite surveying, which provides broader coverage but lower spatial resolution.
Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Drone surveying offers higher accuracy in mapping by utilizing Ground Control Points (GCPs) for precise georeferencing, whereas satellite surveying relies more on satellite positioning systems with limited GCP integration, affecting spatial resolution and positional accuracy.
Orthomosaic Imaging
Drone surveying provides high-resolution orthomosaic imaging with greater spatial detail and flexibility compared to satellite surveying, which offers broader area coverage but lower image resolution.
Spatial Resolution
Drone surveying offers spatial resolution up to a few centimeters, significantly surpassing satellite surveying, which typically provides spatial resolution ranging from a few meters to tens of meters.
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic)
Drone surveying with RTK provides centimeter-level positioning accuracy and faster data acquisition compared to satellite surveying, which often relies on slower, less precise GNSS corrections without real-time updates.
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
Drone surveying generates higher-resolution Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) with greater accuracy and flexibility compared to satellite surveying, which offers broader coverage but lower spatial detail.
Georeferencing
Drone surveying offers higher accuracy and resolution in georeferencing by capturing detailed ground control points compared to satellite surveying, which relies on broader, less precise geospatial data.
Flight Planning (UAV Missions)
Drone surveying enables precise UAV mission flight planning with customizable routes and altitude control, offering higher resolution data compared to satellite surveying.
Satellite Imagery Revisit Time
Satellite surveying offers longer revisit times, ranging from hours to days, compared to drone surveying's ability to capture high-resolution images on demand.
Drone Surveying vs Satellite Surveying Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com