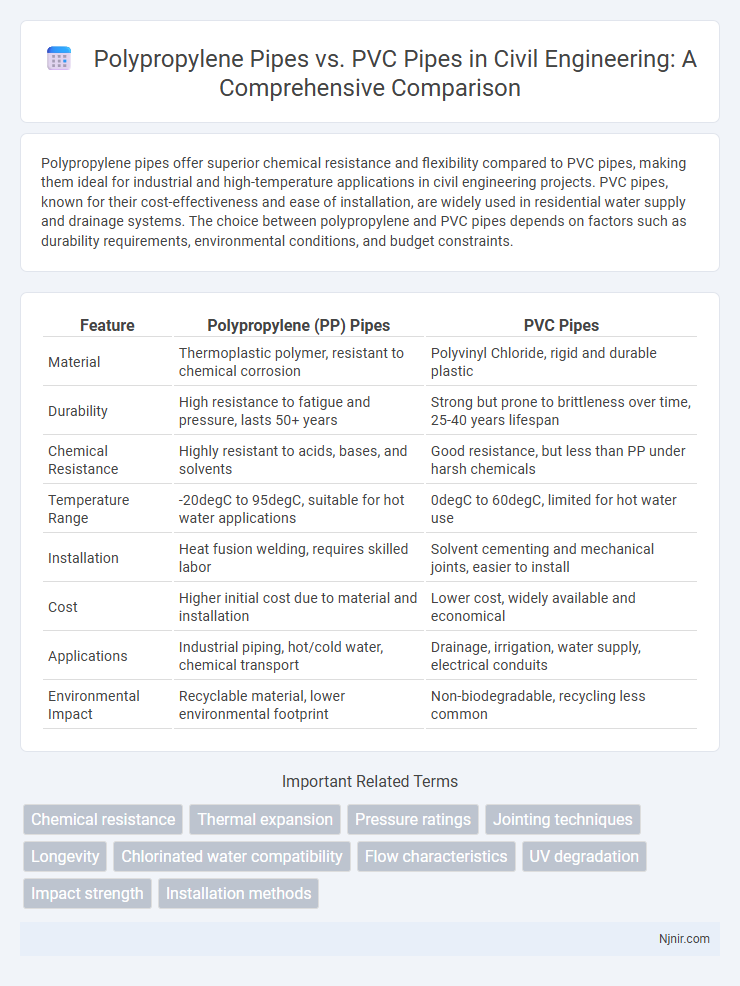
Polypropylene pipes offer superior chemical resistance and flexibility compared to PVC pipes, making them ideal for industrial and high-temperature applications in civil engineering projects. PVC pipes, known for their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, are widely used in residential water supply and drainage systems. The choice between polypropylene and PVC pipes depends on factors such as durability requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polypropylene (PP) Pipes | PVC Pipes |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thermoplastic polymer, resistant to chemical corrosion | Polyvinyl Chloride, rigid and durable plastic |
| Durability | High resistance to fatigue and pressure, lasts 50+ years | Strong but prone to brittleness over time, 25-40 years lifespan |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance, but less than PP under harsh chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 95degC, suitable for hot water applications | 0degC to 60degC, limited for hot water use |
| Installation | Heat fusion welding, requires skilled labor | Solvent cementing and mechanical joints, easier to install |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to material and installation | Lower cost, widely available and economical |
| Applications | Industrial piping, hot/cold water, chemical transport | Drainage, irrigation, water supply, electrical conduits |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable material, lower environmental footprint | Non-biodegradable, recycling less common |
Introduction to Polypropylene and PVC Pipes
Polypropylene (PP) pipes are known for their high chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability in various plumbing and industrial applications. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipes offer excellent rigidity, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them widely used in water supply and drainage systems. Both materials provide lightweight alternatives to metal pipes, with polypropylene excelling in heat resistance and PVC favored for its ease of installation and affordability.
Material Properties Comparison
Polypropylene pipes exhibit higher chemical resistance and flexibility compared to PVC pipes, making them ideal for applications involving corrosive fluids and temperature fluctuations. PVC pipes offer superior rigidity and UV resistance, which enhances their durability for outdoor and structural uses. Both materials have distinct thermal properties; polypropylene tolerates higher temperatures up to 95degC, while PVC typically withstands up to 60degC before deformation.
Durability and Longevity
Polypropylene pipes demonstrate superior durability due to their high resistance to chemical corrosion, abrasion, and temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for hot water applications and industrial use. PVC pipes offer excellent longevity in cold water systems and irrigation due to their rigidity and resistance to UV degradation but may become brittle under prolonged exposure to heat. Choosing polypropylene over PVC maximizes lifespan in environments with thermal stress and aggressive chemicals, whereas PVC provides reliable long-term performance in less demanding conditions.
Chemical Resistance
Polypropylene pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to PVC pipes, making them ideal for handling aggressive acids, alkalis, and organic solvents in industrial applications. Unlike PVC, polypropylene maintains its structural integrity and performance when exposed to high temperatures and corrosive chemicals. This resilience ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in chemically demanding environments.
Installation Processes
Polypropylene (PP) pipes feature a heat-fusion welding installation method, creating seamless, leak-proof joints ideal for high-temperature applications, while PVC pipes rely on solvent cement bonding, offering quicker assembly but potentially weaker connections under stress. PP pipes require specialized fusion equipment and trained personnel, increasing initial setup time and cost, whereas PVC pipes installation is simpler and more cost-effective, suitable for most cold-water plumbing needs. The durability and flexibility of PP pipes result in fewer joint failures, making them preferable in industrial and hot water systems compared to the more rigid, brittle nature of PVC pipes.
Cost Analysis
Polypropylene pipes generally offer lower material costs and better resistance to chemical corrosion compared to PVC pipes, making them cost-effective for industrial applications. PVC pipes are typically less expensive in terms of initial purchase but may incur higher maintenance costs over time due to their lower temperature resistance and potential for brittleness. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including installation, durability, and repair expenses, reveals polypropylene pipes as more economical in long-term plumbing systems.
Environmental Impact
Polypropylene pipes exhibit a lower environmental impact due to their recyclability and resistance to chemical leaching, reducing soil and water contamination risks. PVC pipes, while durable, involve the release of harmful dioxins and require energy-intensive manufacturing processes, contributing more significantly to pollution and carbon emissions. The biodegradability and eco-friendly disposal options of polypropylene pipes make them a preferable choice for sustainable plumbing solutions.
Common Applications in Civil Engineering
Polypropylene pipes are widely used in civil engineering for hot and cold water supply systems, chemical handling, and drainage applications due to their high chemical resistance and thermal stability. PVC pipes are preferred for underground drainage, sewage, and irrigation systems because of their durability, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness. Both materials offer corrosion resistance but differ in temperature tolerance and flexibility, influencing their selection for specific infrastructure projects.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Polypropylene pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance and flexibility, reducing the frequency of repairs compared to PVC pipes, which are more prone to cracking under stress or temperature fluctuations. Maintenance of polypropylene pipes typically involves less frequent inspections due to their resilience against corrosion and scaling, whereas PVC pipes may require regular checks for joint leaks and brittle failures. Repairing polypropylene pipes is generally simpler with heat fusion techniques, while PVC pipe repairs often rely on solvent cementing, which can be less durable under varying environmental conditions.
Future Trends in Pipe Technologies
Polypropylene pipes are increasingly favored for their superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for future applications in industrial and plumbing systems. PVC pipes continue to dominate due to cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, but advancements in UV resistance and recycling technologies are set to enhance their sustainability. Emerging trends emphasize smart piping systems integrating sensors for real-time monitoring, with both polypropylene and PVC materials being adapted to support these innovations.
Chemical resistance
Polypropylene pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents compared to PVC pipes, making them ideal for industrial applications involving aggressive chemicals.
Thermal expansion
Polypropylene pipes exhibit higher thermal expansion rates compared to PVC pipes, requiring careful consideration in temperature-variable applications to prevent deformation or joint failure.
Pressure ratings
Polypropylene pipes typically withstand higher pressure ratings up to 25 bar compared to PVC pipes, which usually handle pressures up to 16 bar, making polypropylene more suitable for high-pressure water systems.
Jointing techniques
Polypropylene pipes use heat fusion and socket welding for strong, leak-proof joints, while PVC pipes rely on solvent cement and mechanical fittings for quick, effective connections.
Longevity
Polypropylene pipes have a longer lifespan due to superior chemical resistance and flexibility compared to the more brittle PVC pipes prone to cracking over time.
Chlorinated water compatibility
Polypropylene pipes demonstrate superior resistance to chlorinated water compared to PVC pipes, making them the preferred choice for plumbing systems exposed to high levels of chlorine.
Flow characteristics
Polypropylene pipes exhibit superior flow characteristics due to their smoother interior surface and higher chemical resistance, while PVC pipes offer consistent flow rates but may experience more frictional resistance over time.
UV degradation
Polypropylene pipes exhibit superior UV resistance compared to PVC pipes, resulting in enhanced longevity and reduced degradation when exposed to prolonged sunlight.
Impact strength
Polypropylene pipes exhibit higher impact strength and better resistance to cracking under sudden stress compared to PVC pipes, making them more durable in demanding applications.
Installation methods
Polypropylene pipes require heat fusion or solvent welding for secure joints, while PVC pipes primarily use solvent cementing with primer for quick and reliable installation.
Polypropylene Pipes vs PVC Pipes Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com