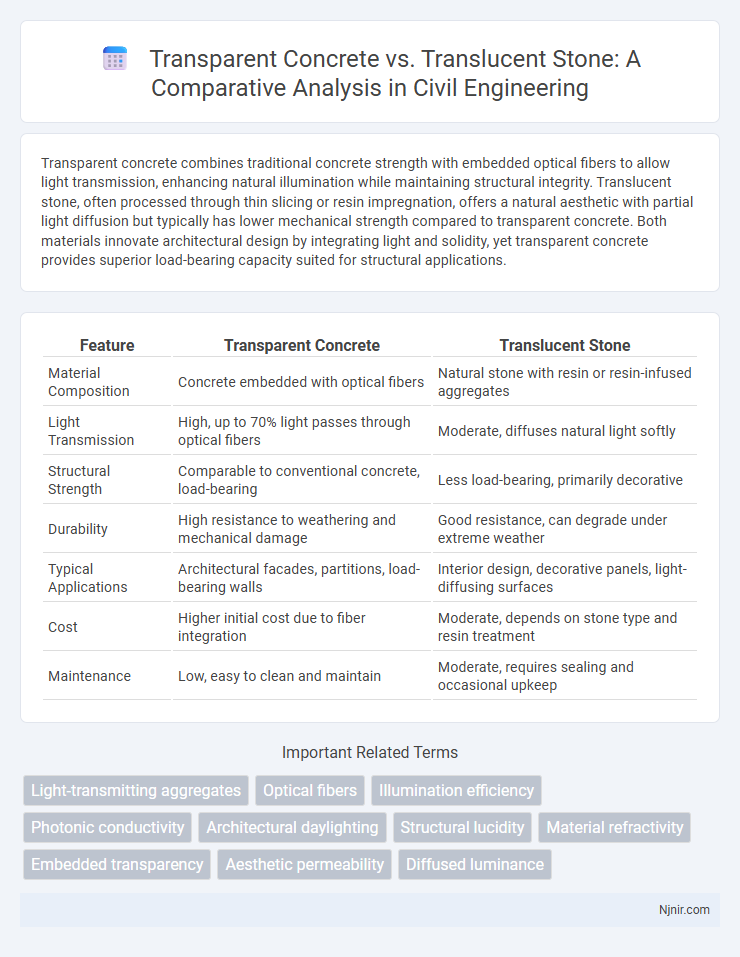
Transparent concrete combines traditional concrete strength with embedded optical fibers to allow light transmission, enhancing natural illumination while maintaining structural integrity. Translucent stone, often processed through thin slicing or resin impregnation, offers a natural aesthetic with partial light diffusion but typically has lower mechanical strength compared to transparent concrete. Both materials innovate architectural design by integrating light and solidity, yet transparent concrete provides superior load-bearing capacity suited for structural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Concrete | Translucent Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Concrete embedded with optical fibers | Natural stone with resin or resin-infused aggregates |
| Light Transmission | High, up to 70% light passes through optical fibers | Moderate, diffuses natural light softly |
| Structural Strength | Comparable to conventional concrete, load-bearing | Less load-bearing, primarily decorative |
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and mechanical damage | Good resistance, can degrade under extreme weather |
| Typical Applications | Architectural facades, partitions, load-bearing walls | Interior design, decorative panels, light-diffusing surfaces |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to fiber integration | Moderate, depends on stone type and resin treatment |
| Maintenance | Low, easy to clean and maintain | Moderate, requires sealing and occasional upkeep |
Introduction to Transparent Concrete and Translucent Stone
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers or light-transmitting materials embedded within the cement matrix, allowing light to pass through while maintaining structural integrity. Translucent stone, often made by embedding resin or synthetic fibers into natural stone, diffuses light to create a glowing effect without full transparency. Both materials are innovative architectural solutions that blend aesthetics with functionality by harnessing natural or artificial light.
Material Composition and Structure
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers embedded within a cement matrix, enabling light transmission through the material while maintaining structural integrity, whereas translucent stone relies on natural or treated mineral crystals with inherent light-diffusing properties. The optical fibers in transparent concrete create channels that guide light, yielding a consistent illumination effect, while translucent stone's microstructures scatter light, resulting in a softer, diffused glow. Material composition greatly influences mechanical strength and light transmission efficiency, with transparent concrete balancing durability and transparency, whereas translucent stone prioritizes aesthetic translucency over load-bearing capacity.
Light Transmission Mechanisms
Transparent concrete achieves light transmission through embedded optical fibers or light-conducting elements that channel natural daylight across the material's surface. Translucent stone relies on its natural microstructure and thin slicing, allowing light to diffuse softly through mineral grains and pores. The distinct mechanisms influence their applications: concrete enables precise directional lighting, while stone creates ambient, diffuse illumination.
Aesthetic and Architectural Appeal
Transparent concrete offers a sleek, modern aesthetic by embedding optical fibers within cement, allowing natural light to permeate structures and create dynamic visual effects ideal for innovative architectural designs. Translucent stone provides a unique, natural texture combined with light diffusion, adding warmth and organic depth that enhances classical and rustic architectural styles. Both materials elevate building facades with enhanced light transmission, but transparent concrete leans toward contemporary minimalism while translucent stone emphasizes artisanal craftsmanship and natural beauty.
Structural Performance and Durability
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers to transmit light while maintaining significant load-bearing capacity, offering a balance between structural performance and aesthetic transparency. Translucent stone, typically thinner and more fragile, provides limited structural support and often requires additional framing or reinforcement to achieve durability in construction. Both materials exhibit varying resistance to weathering and mechanical stresses, with transparent concrete generally outperforming translucent stone in long-term durability and load resistance.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Transparent concrete enhances energy efficiency by allowing natural light to penetrate building interiors, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and lowering electricity consumption. Translucent stone, while offering diffused light transmission, provides superior thermal insulation properties, contributing to sustainable temperature regulation and minimizing HVAC energy usage. Both materials promote sustainability through durability and reduced need for supplemental lighting and heating, yet transparent concrete's integration of optical fibers offers a more innovative approach to daylight harvesting in green building design.
Applications in Modern Construction
Transparent concrete, embedded with optical fibers, enhances natural light penetration while maintaining structural integrity, making it ideal for facades, interior walls, and artistic architectural elements. Translucent stone, often manufactured by thinning natural stone or incorporating resin composites, offers a unique aesthetic with diffused light effects suitable for decorative panels, flooring, and backlit installations in luxury buildings. Both materials are increasingly employed in sustainable design to improve energy efficiency and create visually striking environments in modern construction.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Transparent concrete requires specialized installation techniques involving the precise embedding of optical fibers or light-transmitting elements to ensure consistent light diffusion, often necessitating skilled labor and careful alignment. Maintenance demands are relatively low but include periodic cleaning of both the concrete surface and the embedded fibers to preserve transparency and avoid discoloration. Translucent stone, though naturally light-permeable, involves traditional stone masonry methods that are less complex but require careful sealing to prevent moisture ingress and regular cleaning to maintain clarity and structural integrity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Transparent concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized manufacturing processes involving optical fibers embedded in cement mixtures, whereas translucent stone offers moderate expenses driven by natural stone extraction and semi-transparent resin infusion. Maintenance costs for transparent concrete tend to be lower because of its durability and resistance to weathering, while translucent stone may require more frequent upkeep to prevent surface degradation and maintain clarity. Economic considerations must weigh the balance between upfront investment in transparent concrete's innovative technology and the potentially higher long-term maintenance and replacement costs associated with translucent stone applications.
Future Trends and Innovations in Light-Transmitting Materials
Transparent concrete and translucent stone are advancing with innovations such as embedded optical fibers and nanomaterials that enhance light transmission while maintaining structural integrity. Future trends include smart materials capable of dynamic light modulation and energy-efficient designs integrating photovoltaic cells within these composites. Research is also focusing on improving sustainability and durability to expand applications in architectural facades and interior design, revolutionizing natural lighting solutions.
Light-transmitting aggregates
Light-transmitting aggregates in transparent concrete enable higher optical clarity and light diffusion compared to the more opaque crystalline structures found in translucent stone.
Optical fibers
Transparent concrete uses embedded optical fibers to transmit light through the material, while translucent stone allows light diffusion without dedicated fiber channels, resulting in differing clarity and light transmission efficiency.
Illumination efficiency
Transparent concrete offers superior illumination efficiency by allowing direct light transmission through embedded optical fibers, while translucent stone relies on light scattering, resulting in lower overall light diffusion and brightness.
Photonic conductivity
Transparent concrete demonstrates superior photonic conductivity compared to translucent stone due to its embedded optical fibers that efficiently transmit light through the material.
Architectural daylighting
Transparent concrete enhances architectural daylighting by integrating optical fibers that transmit natural light, whereas translucent stone diffuses sunlight more softly through its mineral composition, offering varied illumination effects.
Structural lucidity
Transparent concrete offers enhanced structural lucidity by embedding optical fibers that transmit light without compromising load-bearing capacity, whereas translucent stone provides limited clarity due to natural mineral opacity affecting its light diffusion and strength.
Material refractivity
Transparent concrete exhibits higher refractivity due to embedded optical fibers allowing light transmission, whereas translucent stone relies on its natural mineral structure with lower refractive efficiency.
Embedded transparency
Embedded transparency in transparent concrete utilizes optical fibers to transmit light through the material, whereas translucent stone relies on natural mineral translucency without internal light-guiding elements.
Aesthetic permeability
Transparent concrete offers superior aesthetic permeability by allowing natural light diffusion while maintaining structural integrity, whereas translucent stone provides a more textured light transmission with a distinct natural pattern.
Diffused luminance
Transparent concrete offers enhanced diffused luminance by embedding optical fibers that scatter light evenly, whereas translucent stone provides a natural but less uniform diffusion due to its inherent mineral composition.
Transparent concrete vs translucent stone Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com