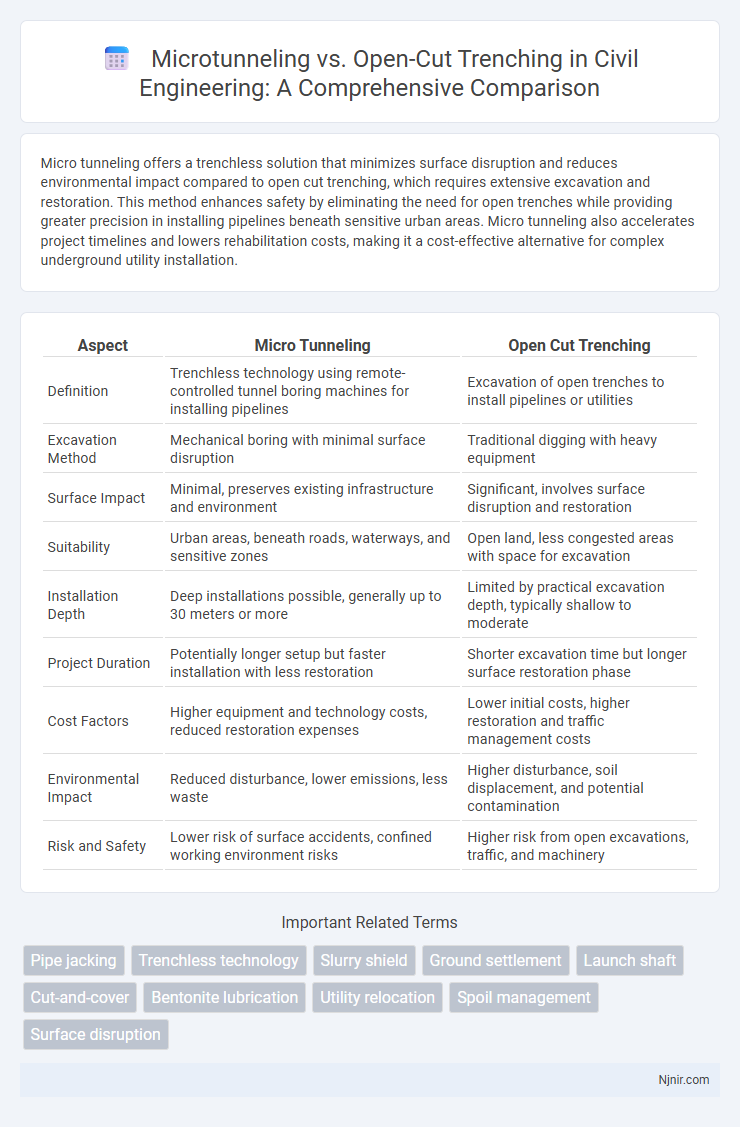
Micro tunneling offers a trenchless solution that minimizes surface disruption and reduces environmental impact compared to open cut trenching, which requires extensive excavation and restoration. This method enhances safety by eliminating the need for open trenches while providing greater precision in installing pipelines beneath sensitive urban areas. Micro tunneling also accelerates project timelines and lowers rehabilitation costs, making it a cost-effective alternative for complex underground utility installation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Micro Tunneling | Open Cut Trenching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trenchless technology using remote-controlled tunnel boring machines for installing pipelines | Excavation of open trenches to install pipelines or utilities |
| Excavation Method | Mechanical boring with minimal surface disruption | Traditional digging with heavy equipment |
| Surface Impact | Minimal, preserves existing infrastructure and environment | Significant, involves surface disruption and restoration |
| Suitability | Urban areas, beneath roads, waterways, and sensitive zones | Open land, less congested areas with space for excavation |
| Installation Depth | Deep installations possible, generally up to 30 meters or more | Limited by practical excavation depth, typically shallow to moderate |
| Project Duration | Potentially longer setup but faster installation with less restoration | Shorter excavation time but longer surface restoration phase |
| Cost Factors | Higher equipment and technology costs, reduced restoration expenses | Lower initial costs, higher restoration and traffic management costs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced disturbance, lower emissions, less waste | Higher disturbance, soil displacement, and potential contamination |
| Risk and Safety | Lower risk of surface accidents, confined working environment risks | Higher risk from open excavations, traffic, and machinery |
Overview of Micro Tunneling and Open Cut Trenching
Micro tunneling is a trenchless construction method that utilizes remotely controlled, guided machines to install pipelines with minimal surface disruption, making it ideal for urban and environmentally sensitive areas. Open cut trenching involves excavating a surface trench to lay pipes directly, offering straightforward installation but causing significant surface disturbance and longer restoration times. Both methods are chosen based on project depth, soil conditions, environmental impact, and urban infrastructure constraints.
Core Principles and Processes
Micro tunneling utilizes remote-controlled guided boring machines to create small-diameter tunnels with minimal surface disruption, relying on precision steering and slurry or auger systems for soil removal. Open cut trenching involves excavating a trench from the surface to install pipelines or utilities, emphasizing direct access and traditional heavy machinery for soil removal and backfill. Micro tunneling excels in environmentally sensitive areas by reducing surface impact, while open cut trenching offers simplicity and lower upfront costs for less complex projects.
Comparative Cost Analysis
Micro tunneling typically incurs higher initial equipment and setup costs compared to open cut trenching due to advanced technology and remote-controlled systems used for precise underground installation. However, micro tunneling often results in lower restoration expenses and reduced surface disruption, which can significantly decrease overall project costs in urban or environmentally sensitive areas. Open cut trenching may present lower upfront costs but can become more expensive when factoring in extensive road repairs, traffic management, and longer project durations.
Impact on Urban Infrastructure
Micro tunneling significantly reduces surface disruption compared to open cut trenching, preserving roadways, utilities, and pedestrian pathways in urban environments. This trenchless technology minimizes traffic congestion and lowers the risk of damaging existing underground infrastructure such as water, gas, and communication lines. Consequently, micro tunneling supports continuous urban activities and reduces costly restoration efforts after installation.
Environmental Considerations
Micro tunneling significantly reduces surface disruption and minimizes impact on local ecosystems compared to open cut trenching, which often leads to extensive soil erosion and habitat destruction. The closed system of micro tunneling limits airborne dust and noise pollution, preserving air quality and minimizing disturbances to nearby communities. Furthermore, micro tunneling's efficient precision prevents groundwater contamination risks typical of open cut trenching, promoting sustainable underground infrastructure development.
Suitability for Different Soil Conditions
Micro tunneling is highly suitable for soft, loose, or unstable soil conditions where open cut trenching risks collapse or groundwater intrusion. Open cut trenching works effectively in stable, dry soils but poses challenges in rocky, sandy, or water-saturated environments, requiring extensive shoring and dewatering. Soil stability, groundwater levels, and urban site constraints are critical factors influencing the choice between micro tunneling and open cut trenching methods.
Project Duration and Efficiency
Micro tunneling significantly reduces project duration by enabling continuous, automated excavation with minimal surface disruption, compared to open cut trenching which requires extensive excavation, backfilling, and restoration. The efficiency of micro tunneling is enhanced by precise guidance systems and reduced traffic impacts, leading to faster completion times and lower labor costs. Open cut trenching, although simpler, often faces delays due to weather, utility relocations, and environmental constraints, making it less efficient for complex urban projects.
Safety and Risk Management
Micro tunneling significantly reduces safety hazards by minimizing surface disruptions and exposure to open trenches, lowering the risk of collapses, falls, and utility strikes common in open cut trenching. This trenchless technology enhances risk management through remote-controlled operations and precise guidance systems, preventing accidental damage and ensuring worker safety underground. In contrast, open cut trenching involves extensive excavation that increases exposure to hazardous conditions, requiring more stringent on-site safety protocols and higher potential for environmental and structural risks.
Surface Disruption and Restoration
Micro tunneling minimizes surface disruption by creating precise underground tunnels with minimal excavation, preserving existing infrastructure and landscapes, which significantly reduces restoration efforts. Open cut trenching involves extensive surface excavation, causing considerable disruption to roads, utilities, and vegetation, leading to higher restoration costs and longer recovery times. This contrast makes micro tunneling ideal for urban environments where surface access and restoration challenges are critical concerns.
Future Trends in Trenchless Technology
Micro tunneling is rapidly advancing with automated guidance systems and real-time monitoring, reducing project time and minimizing surface disruption compared to traditional open cut trenching. Future trends emphasize integration of AI and robotics for precision excavation, enhancing safety and efficiency in complex urban environments. The growing demand for sustainable infrastructure solutions drives increased adoption of trenchless methods, positioning micro tunneling as a key technology in underground utility installation.
Pipe jacking
Micro tunneling with pipe jacking offers precise, trenchless installation of underground pipelines, minimizing surface disruption and environmental impact compared to traditional open cut trenching methods.
Trenchless technology
Micro tunneling offers a trenchless technology solution that minimizes surface disruption and environmental impact compared to traditional open cut trenching methods.
Slurry shield
Micro tunneling with slurry shield technology offers precise, low-disruption underground pipe installation compared to the extensive surface excavation and environmental impact of open cut trenching.
Ground settlement
Micro tunneling significantly reduces ground settlement compared to open cut trenching by utilizing precise, remote-controlled excavation beneath the surface, minimizing soil disturbance.
Launch shaft
Launch shafts in micro tunneling provide controlled, precise access points that minimize surface disruption compared to extensive excavation required in open cut trenching.
Cut-and-cover
Cut-and-cover trenching creates extensive surface disruption unlike micro tunneling, which offers a less invasive underground pipeline installation with precise control and minimal environmental impact.
Bentonite lubrication
Micro tunneling utilizes Bentonite lubrication to reduce friction and stabilize the tunnel face, offering a more efficient and less disruptive alternative to open cut trenching.
Utility relocation
Micro tunneling minimizes surface disruption and accelerates utility relocation compared to open cut trenching, which requires extensive excavation and longer service interruptions.
Spoil management
Micro tunneling generates precise, minimal spoil volumes easily managed onsite, whereas open cut trenching produces extensive spoil requiring significant handling and offsite disposal.
Surface disruption
Micro tunneling significantly reduces surface disruption compared to open cut trenching by minimizing excavation and preserving existing infrastructure.
Micro tunneling vs open cut trenching Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com