Warm mix asphalt lowers production temperatures by 20-40degC compared to hot mix asphalt, reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Its enhanced workability allows for longer paving seasons and improved compaction, leading to extended pavement life. Warm mix asphalt also offers cost savings through reduced fuel use and diminished aging of asphalt binder during mixing and laying.
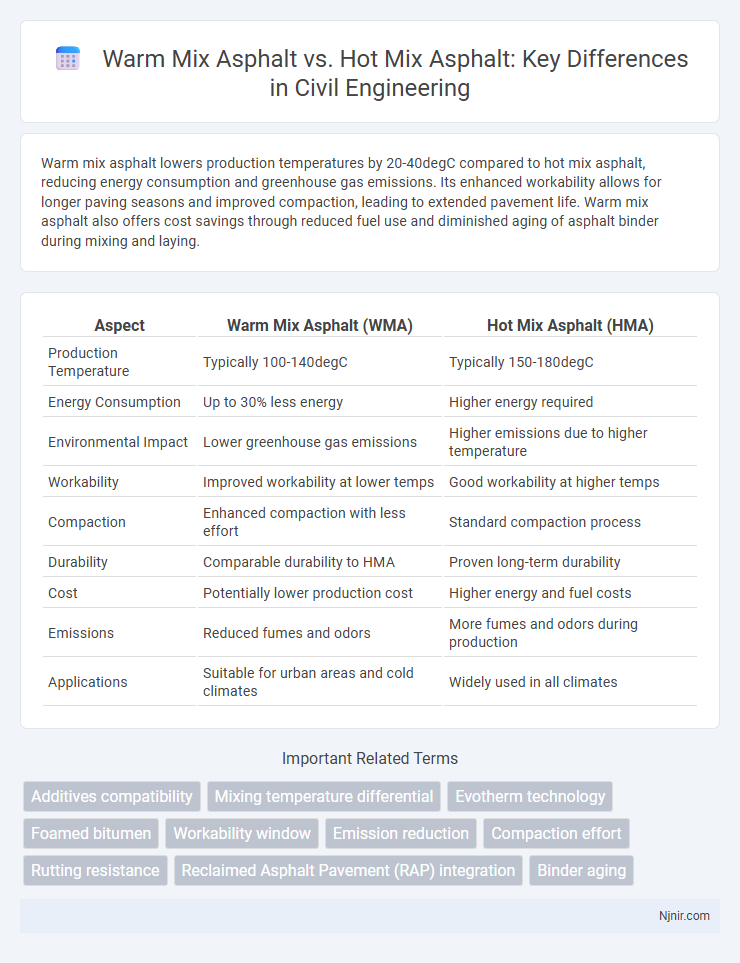
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA) | Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Production Temperature | Typically 100-140degC | Typically 150-180degC |
| Energy Consumption | Up to 30% less energy | Higher energy required |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions | Higher emissions due to higher temperature |
| Workability | Improved workability at lower temps | Good workability at higher temps |
| Compaction | Enhanced compaction with less effort | Standard compaction process |
| Durability | Comparable durability to HMA | Proven long-term durability |
| Cost | Potentially lower production cost | Higher energy and fuel costs |
| Emissions | Reduced fumes and odors | More fumes and odors during production |
| Applications | Suitable for urban areas and cold climates | Widely used in all climates |
Introduction to Asphalt Mixtures
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) and hot mix asphalt (HMA) differ primarily in production temperature, with WMA produced at temperatures between 212degF and 284degF, significantly lower than HMA's typical range of 300degF to 350degF. Both mixtures consist of aggregates bound with asphalt binder, but WMA incorporates additives or processes to reduce viscosity and improve workability at lower temperatures. These temperature variations impact energy consumption, emissions, and compaction quality during pavement construction.
Overview of Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA)
Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA) is produced at temperatures ranging from 20degC to 40degC lower than Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA), leading to significant energy savings and reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production. The technology incorporates additives or processes such as foaming to enhance workability at lower temperatures while maintaining performance characteristics like durability and strength. WMA offers improved compaction, extended paving seasons, and enhanced worker safety compared to traditional HMA.
Overview of Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA)
Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) is a widely used pavement material composed of aggregates thoroughly coated with asphalt binder heated to temperatures between 300degF and 350degF to ensure proper mixing and compaction. Renowned for its durability, strength, and resistance to deformation, HMA is ideal for high-traffic roadways and heavy load conditions. The production process of HMA demands significant energy consumption and emits higher greenhouse gases compared to Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA), but it provides superior performance in extreme weather and heavy-duty applications.
Production Temperatures and Processes
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) is produced at temperatures typically ranging from 100degC to 140degC, significantly lower than hot mix asphalt (HMA), which requires production temperatures of approximately 150degC to 180degC. The lower production temperatures of WMA are achieved using additives and technologies such as foaming or chemical agents that reduce binder viscosity, leading to reduced energy consumption and emissions. In contrast, HMA relies on heating aggregates and asphalt binder to high temperatures to ensure proper coating and workability during paving and compaction.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption compared to hot mix asphalt (HMA) due to its lower production temperatures, which typically range between 100degC to 140degC compared to 150degC to 180degC for HMA. The decreased fuel usage in WMA manufacturing leads to a reduction in carbon dioxide emissions by up to 30%, contributing to improved air quality and a smaller carbon footprint in road construction. Furthermore, WMA facilitates longer hauling distances and extended paving seasons, minimizing environmental disruptions and enhancing sustainability in asphalt pavement projects.
Performance and Durability
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) offers enhanced workability and compaction at lower temperatures, resulting in reduced thermal cracking and improved long-term performance compared to hot mix asphalt (HMA). HMA achieves higher density and strength due to its elevated production temperatures, providing superior durability in high-traffic applications. Research indicates WMA demonstrates comparable fatigue resistance and moisture susceptibility to HMA, promoting sustainability without compromising pavement lifespan.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) typically reduces production temperatures by 20-40degC compared to hot mix asphalt (HMA), leading to lower energy consumption and decreased fuel costs by up to 30%. WMA's reduced emissions and extended paving seasons contribute to operational savings and improved project scheduling, offsetting the initial premium for additives often ranging from 2-5% of total material costs. While HMA generally offers lower upfront material expenses, WMA's life-cycle cost advantages emerge through decreased maintenance needs and enhanced environmental compliance, resulting in better long-term economic value.
Workability and Construction Efficiency
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) offers enhanced workability at lower temperatures compared to hot mix asphalt (HMA), resulting in easier compaction and extended paving seasons. The reduced mixing and laying temperatures in WMA improve construction efficiency by lowering fuel consumption and minimizing emissions without compromising pavement quality. These factors contribute to faster project completion times and reduced operational costs in asphalt pavement construction.
Sustainability and Recyclability
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) significantly reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions by being produced and applied at lower temperatures compared to hot mix asphalt (HMA). WMA's lower temperature process enhances recyclability by preserving binder properties, allowing higher incorporation of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) without compromising performance. This sustainable advantage positions WMA as an eco-friendlier alternative that supports circular economy practices in road construction and maintenance.
Applications and Suitability in Infrastructure Projects
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) is ideal for urban roadways and environmentally sensitive areas due to its lower production temperatures, which reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve workability in cooler climates. Hot mix asphalt (HMA) provides superior durability and load-bearing capacity, making it suitable for highways, heavy traffic pavements, and industrial infrastructure requiring long-term performance. Infrastructure projects prioritize WMA for sustainability goals and rapid construction, while HMA is favored for high-stress applications demanding enhanced resistance to deformation and wear.
Additives compatibility
Additives in warm mix asphalt must be carefully selected for compatibility to ensure proper binder modification and performance, while hot mix asphalt additives typically focus on enhancing high-temperature stability and workability.
Mixing temperature differential
Warm mix asphalt typically requires mixing temperatures between 100degC and 140degC, significantly lower than hot mix asphalt's range of 150degC to 190degC, resulting in reduced energy consumption and emissions.
Evotherm technology
Evotherm technology enables warm mix asphalt to be produced at significantly lower temperatures than hot mix asphalt, reducing energy consumption, emissions, and improving workability without compromising pavement performance.
Foamed bitumen
Foamed bitumen in warm mix asphalt reduces production temperature by up to 40%, lowering energy consumption and emissions compared to traditional hot mix asphalt.
Workability window
Warm mix asphalt offers an extended workability window compared to hot mix asphalt, allowing for longer transportation and placement times at lower temperatures while maintaining performance quality.
Emission reduction
Warm mix asphalt reduces greenhouse gas emissions by up to 30% compared to hot mix asphalt due to lower production and paving temperatures.
Compaction effort
Warm mix asphalt requires 15-35% less compaction effort than hot mix asphalt due to its lower production temperature, enabling easier density achievement and improved workability.
Rutting resistance
Warm mix asphalt exhibits improved rutting resistance due to lower production temperatures that enhance binder performance and aggregate coating compared to traditional hot mix asphalt.
Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) integration
Warm mix asphalt enables higher Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) integration rates than hot mix asphalt by reducing production temperatures and preserving binder properties, resulting in lower energy consumption and enhanced sustainability.
Binder aging
Warm mix asphalt reduces binder aging by lowering production temperatures, resulting in enhanced long-term pavement performance compared to hot mix asphalt.
Warm mix asphalt vs Hot mix asphalt Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com