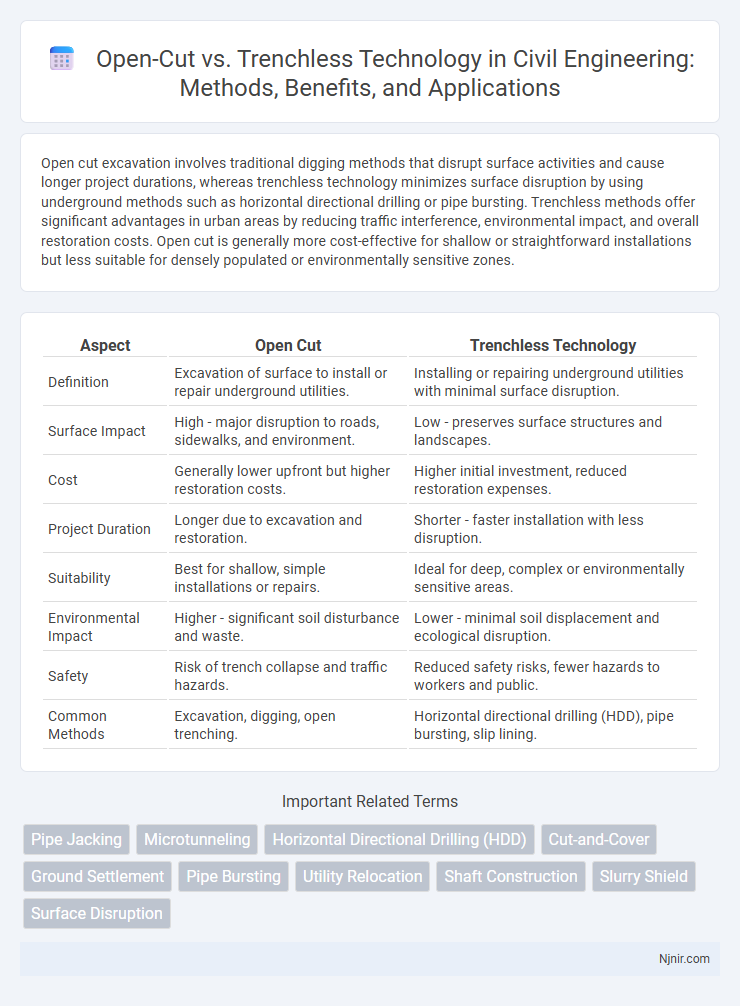
Open cut excavation involves traditional digging methods that disrupt surface activities and cause longer project durations, whereas trenchless technology minimizes surface disruption by using underground methods such as horizontal directional drilling or pipe bursting. Trenchless methods offer significant advantages in urban areas by reducing traffic interference, environmental impact, and overall restoration costs. Open cut is generally more cost-effective for shallow or straightforward installations but less suitable for densely populated or environmentally sensitive zones.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Open Cut | Trenchless Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excavation of surface to install or repair underground utilities. | Installing or repairing underground utilities with minimal surface disruption. |
| Surface Impact | High - major disruption to roads, sidewalks, and environment. | Low - preserves surface structures and landscapes. |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront but higher restoration costs. | Higher initial investment, reduced restoration expenses. |
| Project Duration | Longer due to excavation and restoration. | Shorter - faster installation with less disruption. |
| Suitability | Best for shallow, simple installations or repairs. | Ideal for deep, complex or environmentally sensitive areas. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher - significant soil disturbance and waste. | Lower - minimal soil displacement and ecological disruption. |
| Safety | Risk of trench collapse and traffic hazards. | Reduced safety risks, fewer hazards to workers and public. |
| Common Methods | Excavation, digging, open trenching. | Horizontal directional drilling (HDD), pipe bursting, slip lining. |
Introduction to Open Cut and Trenchless Technology
Open cut technology involves excavating a large trench to install or repair underground utilities, providing direct access but causing significant surface disruption and longer restoration times. Trenchless technology enables underground pipeline installation or rehabilitation without extensive digging by using methods such as horizontal directional drilling (HDD) or pipe bursting, resulting in reduced environmental impact and faster project completion. Both methods serve critical roles in infrastructure development, with trenchless techniques becoming increasingly preferred for urban environments due to minimized surface disturbances.
Key Differences Between Open Cut and Trenchless Methods
Open Cut and Trenchless Technology differ primarily in excavation approach and surface disruption; Open Cut involves extensive digging and surface removal, causing significant environmental and traffic disturbances. Trenchless methods, such as horizontal directional drilling and pipe bursting, minimize surface impact by accessing underground utilities with minimal excavation. Cost and project duration also vary, with Open Cut generally being less expensive but more disruptive, while Trenchless offers higher initial costs offset by shorter restoration times and reduced community impact.
Advantages of Open Cut Excavation Techniques
Open cut excavation techniques offer significant advantages such as direct access to underground utilities, enabling faster and more straightforward installation and repairs. This method provides clear visibility and easier quality control, reducing the risk of errors during construction. Cost-effectiveness and suitability for a wide range of soil conditions make open cut excavation a preferred choice for extensive pipeline and infrastructure projects.
Benefits of Trenchless Technology in Civil Engineering
Trenchless technology offers significant benefits in civil engineering by minimizing surface disruption and reducing environmental impact compared to traditional open cut methods. This approach enhances project efficiency through faster installation and lower restoration costs, making it ideal for urban infrastructure upgrades. Its precision and reduced excavation volume also improve safety and decrease the risk of damaging existing underground utilities.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Open cut excavation significantly disrupts the environment by causing extensive soil erosion, vegetation loss, and increased carbon emissions from heavy machinery. Trenchless technology minimizes surface disturbance, preserving ecosystems and reducing greenhouse gas emissions due to shorter project durations and less heavy equipment use. Studies indicate trenchless methods lower environmental impact by up to 70% compared to open cut, making them a sustainable choice for underground utility installation and repair.
Cost Considerations: Open Cut vs Trenchless
Open Cut methods typically incur higher costs due to extensive excavation, surface restoration, and traffic disruption expenses, making them less economical for urban areas with heavy infrastructure. Trenchless Technology reduces surface disruption and restoration costs by minimizing excavation, leading to lower overall project expenses, especially for pipes under roads or sensitive landscapes. However, initial equipment and specialized labor costs for trenchless methods can be higher, so cost-effectiveness depends on project scale and site conditions.
Safety Aspects in Open Cut and Trenchless Projects
Open cut construction presents significant safety risks due to open excavations, including hazards of cave-ins, falls, and exposure to underground utilities, requiring extensive shoring and protective systems. Trenchless technology minimizes these risks by eliminating open trenches, reducing worker exposure to confined spaces and heavy equipment while enhancing site safety and operational efficiency. The adoption of trenchless methods results in fewer workplace injuries and lower incident rates compared to traditional open cut excavation projects.
Typical Applications and Suitability Criteria
Open cut excavation is ideal for large-scale projects requiring extensive access to underground utilities, such as water mains, sewer lines, and road construction, where surface disruption is acceptable. Trenchless technology suits urban areas demanding minimal surface impact, often used for installing or repairing pipelines beneath roads, railways, and environmentally sensitive zones. Suitability criteria hinge on factors like soil conditions, existing infrastructure density, project scale, environmental constraints, and cost considerations, guiding the choice between open cut and trenchless methods.
Case Studies: Successful Project Implementations
Case studies reveal that open cut methods excel in projects with shallow utilities and straightforward layouts, offering cost-effective excavation despite surface disruption. Trenchless technology demonstrates significant success in urban settings where minimizing traffic interference and environmental impact is critical, employing techniques like horizontal directional drilling and pipe bursting. Projects such as the New York City sewer rehabilitation and the Los Angeles water pipeline replacement highlight trenchless methods' ability to reduce restoration costs and project timelines compared to open cut approaches.
Future Trends in Excavation and Pipeline Installation
Future trends in excavation and pipeline installation emphasize the rise of trenchless technology due to its minimal environmental impact, reduced surface disruption, and cost-efficiency in urban infrastructure projects. Innovations such as horizontal directional drilling (HDD), pipe bursting, and microtunneling are enabling faster, safer, and more precise underground installation compared to traditional open cut methods. Integration of smart sensors and real-time monitoring systems further enhances trenchless techniques, driving adoption in water, gas, and telecom pipeline networks globally.
Pipe Jacking
Pipe jacking, a trenchless technology method, minimizes surface disruption and environmental impact compared to traditional open cut excavation for installing underground pipelines.
Microtunneling
Microtunneling offers a trenchless alternative to traditional open cut construction by enabling precise, minimally invasive underground pipe installation with reduced surface disruption and environmental impact.
Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD)
Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) offers a trenchless technology alternative to traditional open cut methods by minimizing surface disruption, reducing environmental impact, and enabling efficient installation of underground utilities beneath obstacles such as roads and waterways.
Cut-and-Cover
Cut-and-cover construction in open cut methods offers cost-effective installation for shallow underground utilities compared to trenchless technology, which minimizes surface disruption but entails higher costs for deep or complex projects.
Ground Settlement
Open Cut excavation typically causes significant ground settlement due to extensive soil disruption, whereas trenchless technology minimizes ground settlement by reducing surface disturbance during underground utility installation.
Pipe Bursting
Pipe bursting in trenchless technology offers a cost-effective, less disruptive alternative to traditional open cut methods by enabling seamless pipe replacement without extensive excavation.
Utility Relocation
Trenchless technology significantly reduces disruption and excavation costs in utility relocation compared to traditional open cut methods by enabling underground installation with minimal surface impact.
Shaft Construction
Trenchless technology significantly reduces surface disruption and project time in shaft construction compared to traditional open cut methods by enabling underground access without extensive excavation.
Slurry Shield
Slurry Shield, a trenchless technology, offers minimal surface disruption and enhanced soil stabilization compared to traditional open cut excavation methods.
Surface Disruption
Trenchless technology significantly reduces surface disruption compared to open cut methods by allowing underground installations with minimal excavation.
Open Cut vs Trenchless Technology Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com