Rapid bridge construction significantly reduces onsite work time by utilizing prefabricated components, minimizing traffic disruptions and enhancing safety. Conventional construction often requires extended closures and extensive onsite labor, leading to higher costs and longer project durations. The accelerated timeline of rapid methods improves project efficiency and reduces environmental impacts compared to traditional techniques.
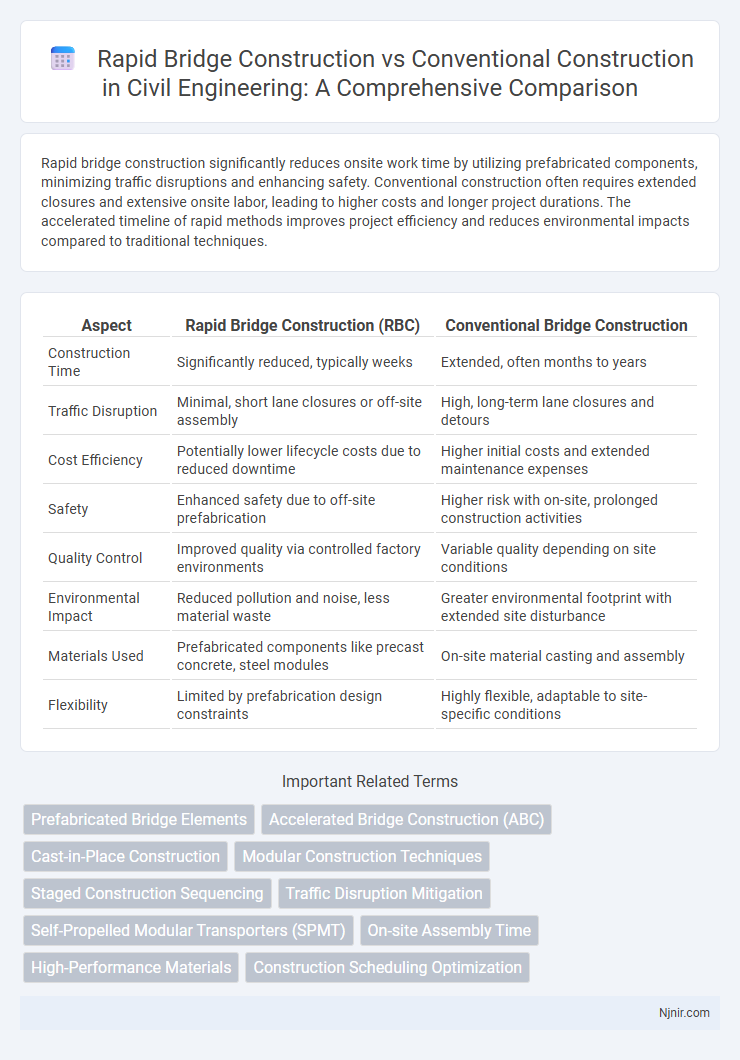
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Rapid Bridge Construction (RBC) | Conventional Bridge Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Time | Significantly reduced, typically weeks | Extended, often months to years |
| Traffic Disruption | Minimal, short lane closures or off-site assembly | High, long-term lane closures and detours |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially lower lifecycle costs due to reduced downtime | Higher initial costs and extended maintenance expenses |
| Safety | Enhanced safety due to off-site prefabrication | Higher risk with on-site, prolonged construction activities |
| Quality Control | Improved quality via controlled factory environments | Variable quality depending on site conditions |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced pollution and noise, less material waste | Greater environmental footprint with extended site disturbance |
| Materials Used | Prefabricated components like precast concrete, steel modules | On-site material casting and assembly |
| Flexibility | Limited by prefabrication design constraints | Highly flexible, adaptable to site-specific conditions |
Overview of Rapid Bridge Construction and Conventional Methods
Rapid bridge construction (RBC) utilizes prefabricated components and modular designs to significantly reduce onsite construction time and minimize traffic disruptions. Conventional bridge construction typically involves extensive in-situ work, including formwork, concrete pouring, and curing, resulting in longer project durations and higher traffic impacts. RBC techniques enhance project efficiency and safety by streamlining erection processes and leveraging advanced materials and robotics.
Key Differences Between Rapid and Conventional Bridge Construction
Rapid bridge construction utilizes prefabricated components and advanced techniques like accelerated curing and modular assembly, significantly reducing on-site construction time compared to conventional methods. Conventional bridge construction typically involves cast-in-place concrete and extensive formwork, leading to longer project durations and higher traffic disruption. Key differences include speed of completion, reduced environmental impact, and minimized traffic interference, making rapid bridge construction more efficient and cost-effective in urban settings.
Time Efficiency: Speed of Project Completion
Rapid bridge construction techniques reduce project completion time by up to 50% compared to conventional methods, significantly minimizing traffic disruptions and associated economic losses. Modular components and prefabrication allow for faster on-site assembly, cutting down traditional construction phases from months or years to weeks. This accelerated timeline enhances infrastructure resilience by enabling quicker restoration of transportation networks after damage or wear.
Cost Considerations: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Rapid bridge construction significantly reduces initial costs by minimizing onsite labor and equipment usage through prefabrication and accelerated techniques. Conventional construction often incurs higher initial expenses due to prolonged traffic control, extended labor hours, and material storage onsite. Long-term expenses for rapid methods tend to decrease as improved quality control and fewer disruptions reduce maintenance and rehabilitation costs over the bridge's lifespan.
Safety Implications for Workers and the Public
Rapid bridge construction significantly reduces the time workers spend in hazardous environments, lowering exposure to heavy machinery, traffic, and adverse weather conditions. Conventional construction methods often involve prolonged on-site activities, increasing risks of accidents and injuries for both workers and the public due to extended traffic disruptions and construction zone interactions. Enhanced safety protocols in rapid construction minimize disruptions and improve overall safety outcomes by consolidating work phases and utilizing prefabricated components.
Quality and Durability of Finished Structures
Rapid bridge construction techniques utilize prefabricated components and advanced materials, enhancing quality control by allowing construction in controlled environments, which reduces defects and improves structural integrity. Conventional construction methods often involve onsite assembly, increasing exposure to environmental variables that may affect durability and result in inconsistent quality. Studies indicate that rapid bridge construction achieves comparable or superior durability through precision manufacturing and reduced onsite disruption, leading to longer service life and lower maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rapid bridge construction significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing onsite disturbance, lowering emissions from prolonged equipment use, and decreasing traffic disruptions that contribute to air pollution. Prefabricated components and accelerated timelines promote sustainability by conserving resources and reducing waste generated during conventional construction processes. These methods enhance durability and extend bridge lifespan, supporting long-term environmental stewardship compared to traditional construction techniques.
Traffic Disruption and Community Effects
Rapid bridge construction significantly reduces traffic disruption by minimizing road closure times and maintaining better traffic flow compared to conventional construction, which often requires lengthy lane closures or full shutdowns. This approach lessens noise, dust, and pollution exposure for nearby communities, improving residents' quality of life during the project. Reduced construction duration also limits economic impacts on local businesses reliant on consistent traffic patterns.
Innovations and Technologies in Rapid Construction
Rapid bridge construction utilizes innovations such as prefabricated bridge elements, accelerated curing techniques, and advanced materials like ultra-high-performance concrete to significantly reduce project timelines compared to conventional methods. Technologies including 3D modeling, modular construction, and automated machinery enable precise, efficient assembly, minimizing traffic disruptions and environmental impact. These advancements enhance structural durability and safety while optimizing resource allocation and labor costs in large-scale infrastructure projects.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Rapid bridge construction (RBC) methods have demonstrated significant time savings and reduced traffic disruption in case studies like the I-74 Mississippi River Bridge, completed in two years versus a projected five with traditional techniques. Lessons learned emphasize the importance of meticulous planning and prefabrication quality control to minimize costly on-site errors. Successful RBC projects highlight enhanced safety for workers and the public by limiting exposure time on busy transportation corridors.
Prefabricated Bridge Elements
Prefabricated bridge elements accelerate rapid bridge construction by minimizing onsite work, reducing traffic disruptions, and enhancing quality control compared to conventional cast-in-place methods.
Accelerated Bridge Construction (ABC)
Accelerated Bridge Construction (ABC) reduces project timelines by up to 50% through prefabricated components, minimizing traffic disruption and enhancing safety compared to conventional bridge construction methods.
Cast-in-Place Construction
Rapid Cast-in-Place bridge construction accelerates project timelines by utilizing advanced formwork and accelerated curing techniques compared to conventional methods that rely on slower, sequential pouring and longer curing periods.
Modular Construction Techniques
Modular construction techniques accelerate bridge building by prefabricating sections off-site, reducing on-site labor and traffic disruptions compared to conventional methods.
Staged Construction Sequencing
Rapid bridge construction employs efficient staged construction sequencing techniques that significantly reduce on-site assembly time compared to conventional methods, enhancing project safety and minimizing traffic disruptions.
Traffic Disruption Mitigation
Rapid bridge construction significantly reduces traffic disruption by minimizing onsite work duration compared to conventional construction methods.
Self-Propelled Modular Transporters (SPMT)
Self-Propelled Modular Transporters (SPMT) enable rapid bridge construction by transporting and installing large prefabricated bridge sections efficiently, reducing project timelines compared to conventional construction methods.
On-site Assembly Time
Rapid bridge construction reduces on-site assembly time by up to 70% compared to conventional methods, significantly minimizing traffic disruption and improving project efficiency.
High-Performance Materials
High-performance materials accelerate rapid bridge construction by enhancing durability and reducing curing times compared to conventional construction methods.
Construction Scheduling Optimization
Rapid bridge construction reduces project timelines by up to 50% compared to conventional methods through advanced scheduling optimization techniques that streamline resource allocation and minimize on-site work duration.
rapid bridge construction vs conventional construction Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com