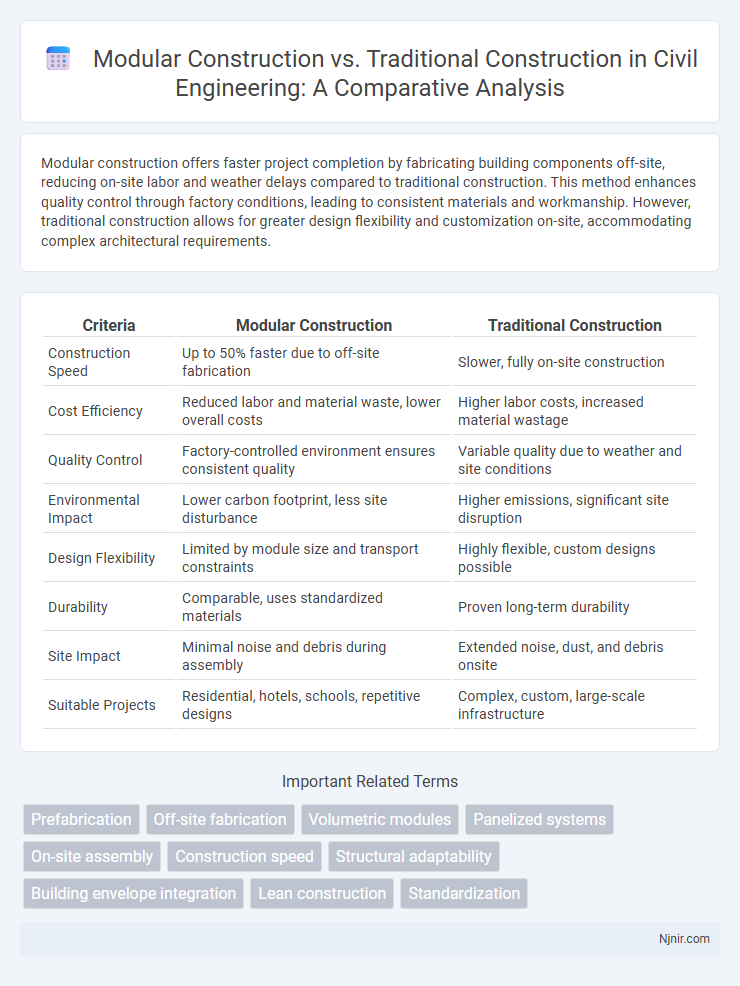
Modular construction offers faster project completion by fabricating building components off-site, reducing on-site labor and weather delays compared to traditional construction. This method enhances quality control through factory conditions, leading to consistent materials and workmanship. However, traditional construction allows for greater design flexibility and customization on-site, accommodating complex architectural requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Modular Construction | Traditional Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Speed | Up to 50% faster due to off-site fabrication | Slower, fully on-site construction |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced labor and material waste, lower overall costs | Higher labor costs, increased material wastage |
| Quality Control | Factory-controlled environment ensures consistent quality | Variable quality due to weather and site conditions |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, less site disturbance | Higher emissions, significant site disruption |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by module size and transport constraints | Highly flexible, custom designs possible |
| Durability | Comparable, uses standardized materials | Proven long-term durability |
| Site Impact | Minimal noise and debris during assembly | Extended noise, dust, and debris onsite |
| Suitable Projects | Residential, hotels, schools, repetitive designs | Complex, custom, large-scale infrastructure |
Introduction to Modular and Traditional Construction
Modular construction involves prefabricating building sections in a controlled factory setting before transporting and assembling them on-site, significantly reducing construction time and waste. Traditional construction relies on building structures entirely on-site, often resulting in longer project timelines and greater exposure to weather-related delays. Both methods have distinct implications for project efficiency, cost, and quality control, with modular construction gaining traction for its scalability and sustainability benefits.
Key Principles of Modular Construction
Modular construction relies on prefabrication of building components in controlled factory environments, enabling precise quality control and faster project completion compared to traditional construction methods. This approach emphasizes standardization, repeatability, and efficient use of materials, reducing waste and environmental impact. Key principles include off-site manufacturing, integration of design and engineering, and streamlined on-site assembly, enhancing consistency and cost-effectiveness.
Defining Features of Traditional Construction
Traditional construction involves building structures entirely on-site using conventional materials like wood, brick, and concrete, allowing for high customization and adaptability. This method often requires longer timelines due to sequential workflows and is heavily dependent on weather conditions and skilled labor availability. The construction process follows established practices involving foundation laying, framing, and finishing directly at the project location.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Modular construction significantly reduces project timelines by up to 50% compared to traditional construction due to concurrent off-site module fabrication and on-site preparation. Factory-controlled environments enhance precision and minimize material waste, improving overall efficiency and quality consistency. Traditional construction often faces delays from weather and site conditions, whereas modular methods maintain a streamlined, predictable schedule.
Cost Implications of Modular vs Traditional Methods
Modular construction significantly reduces costs by minimizing on-site labor and shortening project timelines, often resulting in savings of 10-20% compared to traditional construction. Factory-controlled environments enhance material efficiency and reduce waste, lowering overall expenses. Traditional construction typically incurs higher costs due to extended labor hours, weather delays, and inefficiencies in material usage.
Quality Assurance and Material Control
Modular construction enhances quality assurance by manufacturing components in controlled factory environments, reducing variability and defects common in traditional construction sites. Material control is optimized through precise inventory management and standardized processes, minimizing waste and ensuring consistent use of high-grade materials. Traditional construction often faces challenges with on-site environmental factors and inconsistent material handling, impacting overall quality and project timelines.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Modular construction significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing construction waste, lowering carbon emissions through efficient factory production, and enabling better resource management, compared to traditional construction methods. This approach promotes sustainability by utilizing recyclable materials, reducing site disruption, and shortening construction timelines, which collectively conserve energy and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional construction often involves higher material wastage, longer project durations, and increased energy consumption, leading to a larger carbon footprint and greater environmental degradation.
Flexibility and Design Limitations
Modular construction offers superior flexibility by enabling easy modifications and expansions through prefabricated modules, reducing on-site adjustments and construction time compared to traditional methods. Traditional construction often faces significant design limitations due to rigid site-built processes and longer timelines, restricting quick changes and customization during the building phase. The adaptability of modular systems supports innovative architectural solutions, while traditional construction may require extensive structural alterations to accommodate design changes.
Safety and Site Considerations
Modular construction enhances safety by reducing on-site labor and exposure to hazardous conditions, as most building components are fabricated in controlled factory environments with stringent quality controls. Traditional construction involves extended site presence and higher risks of accidents due to weather, heavy machinery, and variable site conditions. Site considerations favor modular methods for urban or constrained locations, minimizing noise, waste, and disruption while accelerating project timelines and improving overall site safety management.
Future Trends in Construction Methods
Modular construction is rapidly evolving with advancements in prefabrication technologies and digital integration, enabling faster project delivery and reduced waste compared to traditional construction methods. Future trends emphasize sustainability through eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs, alongside increased automation and robotics to enhance precision and cost-effectiveness. These innovations position modular construction as a leading alternative in addressing urbanization challenges and labor shortages in the construction industry.
Prefabrication
Modular construction accelerates project timelines and reduces waste by utilizing off-site prefabrication, whereas traditional construction relies on on-site building with longer schedules and higher material waste.
Off-site fabrication
Off-site fabrication in modular construction reduces project timelines by up to 50% compared to traditional construction methods by enabling simultaneous site preparation and module assembly in controlled factory environments.
Volumetric modules
Volumetric modular construction accelerates project timelines by assembling fully fabricated 3D modules offsite, reducing onsite labor and waste compared to traditional construction methods.
Panelized systems
Panelized systems in modular construction reduce on-site labor by up to 50% and cut project timelines by 30% compared to traditional stick-built methods while enhancing quality control through factory fabrication.
On-site assembly
Modular construction significantly reduces on-site assembly time by delivering pre-fabricated components, enhancing efficiency compared to traditional construction methods that require extensive on-site building and longer timelines.
Construction speed
Modular construction reduces project timelines by up to 50% compared to traditional construction due to off-site fabrication and simultaneous site preparation.
Structural adaptability
Modular construction offers superior structural adaptability through prefabricated, reconfigurable components compared to the fixed, less flexible frameworks of traditional construction.
Building envelope integration
Modular construction enhances building envelope integration by allowing precise factory-controlled assembly of walls, roofs, and insulation, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced on-site errors compared to traditional construction methods.
Lean construction
Modular construction enhances Lean construction principles by minimizing waste, reducing project timelines by up to 50%, and improving site safety compared to traditional construction methods.
Standardization
Modular construction enhances project efficiency and quality through high standardization of factory-produced components, contrasting with the variability and customization typical of traditional construction methods.
Modular construction vs Traditional construction Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com