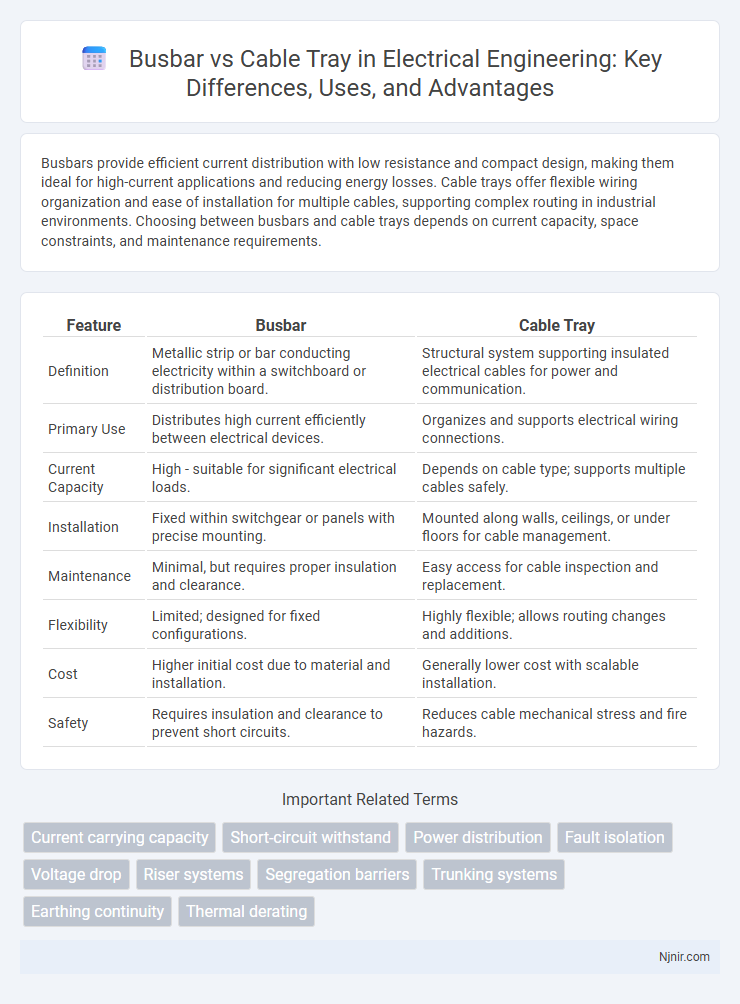
Busbars provide efficient current distribution with low resistance and compact design, making them ideal for high-current applications and reducing energy losses. Cable trays offer flexible wiring organization and ease of installation for multiple cables, supporting complex routing in industrial environments. Choosing between busbars and cable trays depends on current capacity, space constraints, and maintenance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Busbar | Cable Tray |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Metallic strip or bar conducting electricity within a switchboard or distribution board. | Structural system supporting insulated electrical cables for power and communication. |
| Primary Use | Distributes high current efficiently between electrical devices. | Organizes and supports electrical wiring connections. |
| Current Capacity | High - suitable for significant electrical loads. | Depends on cable type; supports multiple cables safely. |
| Installation | Fixed within switchgear or panels with precise mounting. | Mounted along walls, ceilings, or under floors for cable management. |
| Maintenance | Minimal, but requires proper insulation and clearance. | Easy access for cable inspection and replacement. |
| Flexibility | Limited; designed for fixed configurations. | Highly flexible; allows routing changes and additions. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to material and installation. | Generally lower cost with scalable installation. |
| Safety | Requires insulation and clearance to prevent short circuits. | Reduces cable mechanical stress and fire hazards. |
Introduction to Busbars and Cable Trays
Busbars are metallic strips or bars used to conduct electricity within switchboards, panel boards, and busway enclosures, designed for high-current power distribution. Cable trays provide a structural support system to route and protect electrical cables, facilitating organized cable management in industrial and commercial installations. Both busbars and cable trays are essential for efficient electrical distribution, with busbars offering compact, low-resistance current paths and cable trays enabling flexible cable routing and easy maintenance.
Basic Functions and Applications
Busbars provide efficient electrical power distribution by conducting high current in compact spaces, ensuring minimal energy loss and enhanced safety in industrial settings. Cable trays serve as supportive frameworks for organizing and protecting electrical cables, facilitating maintenance and scalability in commercial and residential installations. Both systems optimize electrical infrastructure but differ in function, with busbars emphasizing current conduction and cable trays focusing on cable management.
Material and Construction Differences
Busbars are typically made from copper or aluminum, offering high electrical conductivity and efficient current distribution, while cable trays are usually constructed from steel, aluminum, or fiberglass to provide structural support and protection for cables. Busbars consist of solid or laminated metal strips that allow for compact, low-resistance power transmission, whereas cable trays comprise open or ventilated frameworks designed to organize and secure insulated cables. The construction of busbars emphasizes minimal resistance and thermal management, contrasting with cable trays' focus on mechanical strength and ease of cable maintenance.
Installation Methods and Flexibility
Busbars simplify installation by offering pre-fabricated, modular sections that can be quickly mounted and connected with minimal tools and labor, reducing overall installation time. Cable trays require more manual routing and securing of individual cables, which can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, especially in complex layouts. Busbars provide superior flexibility for future modifications and expansions due to their modular design, while cable trays offer easier cable additions but may require more effort to reorganize or upgrade.
Electrical Performance and Efficiency
Busbars offer superior electrical performance compared to cable trays due to lower resistance and reduced power loss, enabling higher current capacity within a compact design. Their streamlined conductors minimize heat generation, enhancing overall efficiency in electrical distribution systems. Cable trays, while versatile for cable management, often introduce increased impedance and potential energy dissipation, affecting system efficiency at higher loads.
Safety Considerations and Standards
Busbars offer superior safety in electrical distribution by minimizing exposure to live parts through enclosed, insulated designs that reduce the risk of electric shock and short circuits. Cable trays require proper grounding, cable management, and adherence to standards such as NEC (National Electrical Code) and IEC 61537 to prevent overheating, mechanical damage, and fire hazards. Compliance with UL 857 for busbars and NEC Article 392 for cable trays ensures both systems meet rigorous safety and performance criteria in industrial and commercial installations.
Space Requirements and Layout Design
Busbars require significantly less space compared to cable trays due to their compact and modular design, making them ideal for areas with limited room. Cable trays occupy more physical space as they support multiple cables laid out separately, which can complicate layout design in confined environments. Efficient layout planning with busbars enhances airflow and cooling, whereas cable trays may necessitate additional considerations for cable bends and support intervals.
Cost Comparison and Budget Impact
Busbars generally offer lower installation costs and reduced labor expenses compared to cable trays due to their compact design and easier handling. Cable trays may incur higher material and maintenance costs, especially in complex or large-scale electrical systems where extensive cable management is required. Budget impact favors busbars for projects prioritizing cost efficiency and quicker deployment, while cable trays might increase overall expenditure due to longer installation times and additional support structures.
Maintenance and Reliability
Busbars offer simplified maintenance with fewer connection points, reducing the risk of loose connections and electrical faults compared to cable trays. Cable trays require more frequent inspections and upkeep due to the number of cables, connectors, and potential wear from environmental factors. The enhanced reliability of busbars stems from their solid construction and minimal maintenance needs, making them ideal for high-demand electrical distribution systems.
Choosing Between Busbars and Cable Trays
Busbars offer high current-carrying capacity and efficient power distribution in compact spaces, making them ideal for industrial switchgear and large electrical panels. Cable trays provide flexible routing for numerous cables, allowing easier installation and maintenance in building wiring systems. Selecting between busbars and cable trays depends on load demands, space constraints, installation complexity, and future scalability requirements.
Current carrying capacity
Busbars provide higher current carrying capacity compared to cable trays due to lower resistance and better heat dissipation.
Short-circuit withstand
Busbars offer higher short-circuit withstand capacity compared to cable trays due to their robust metal conductor design and superior current distribution capabilities.
Power distribution
Busbars provide efficient, low-resistance power distribution with higher current capacity and easier scalability compared to cable trays, which primarily serve as protective pathways for electrical cables.
Fault isolation
Busbars enable faster fault isolation by localizing electrical faults within specific segments, whereas cable trays typically require more extensive inspection to pinpoint and isolate faults.
Voltage drop
Busbars typically exhibit lower voltage drop compared to cable trays due to their larger cross-sectional area and shorter conductor length, enhancing electrical efficiency in power distribution systems.
Riser systems
Busbar riser systems offer higher current capacity and improved heat dissipation compared to cable tray riser systems, making them ideal for efficient vertical power distribution in commercial and industrial buildings.
Segregation barriers
Busbar systems often incorporate integrated segregation barriers to enhance electrical safety and reduce electromagnetic interference, while cable trays typically require additional retrofit barriers to achieve similar segregation and protection levels.
Trunking systems
Busbar trunking systems provide higher current capacity and easier maintenance compared to cable trays by offering modular, flexible power distribution with reduced installation time and improved safety.
Earthing continuity
Busbars provide superior earthing continuity compared to cable trays by offering a low-resistance, rigid, and direct conductive path that ensures reliable grounding in electrical systems.
Thermal derating
Busbars offer superior thermal derating compared to cable trays due to their enhanced heat dissipation and lower current-carrying resistance.
busbar vs cable tray Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com