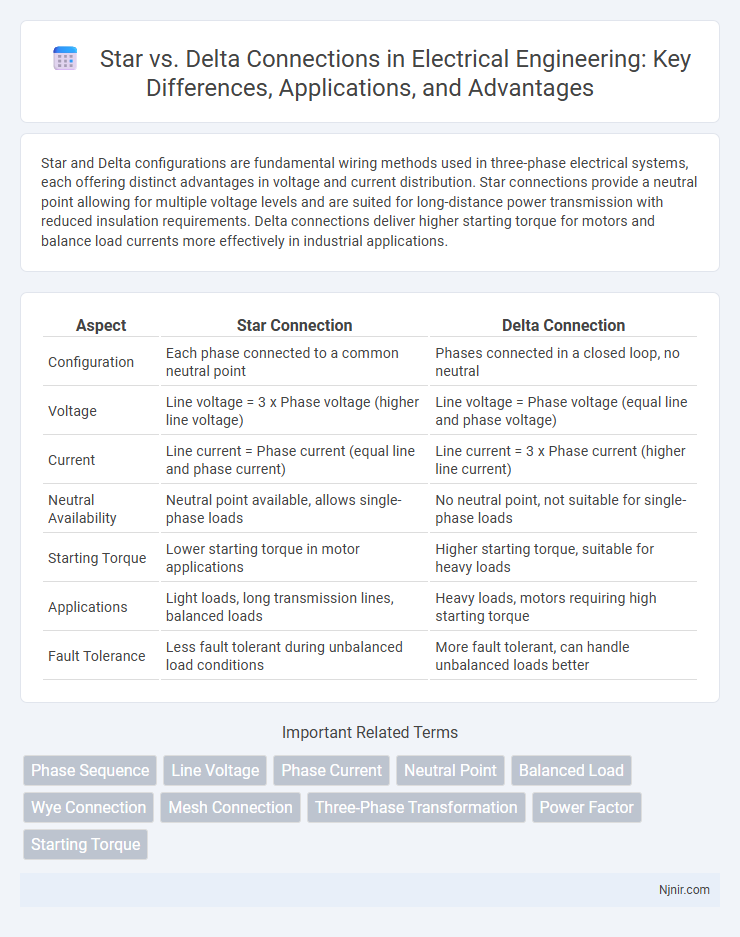
Star and Delta configurations are fundamental wiring methods used in three-phase electrical systems, each offering distinct advantages in voltage and current distribution. Star connections provide a neutral point allowing for multiple voltage levels and are suited for long-distance power transmission with reduced insulation requirements. Delta connections deliver higher starting torque for motors and balance load currents more effectively in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Star Connection | Delta Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Each phase connected to a common neutral point | Phases connected in a closed loop, no neutral |
| Voltage | Line voltage = 3 x Phase voltage (higher line voltage) | Line voltage = Phase voltage (equal line and phase voltage) |
| Current | Line current = Phase current (equal line and phase current) | Line current = 3 x Phase current (higher line current) |
| Neutral Availability | Neutral point available, allows single-phase loads | No neutral point, not suitable for single-phase loads |
| Starting Torque | Lower starting torque in motor applications | Higher starting torque, suitable for heavy loads |
| Applications | Light loads, long transmission lines, balanced loads | Heavy loads, motors requiring high starting torque |
| Fault Tolerance | Less fault tolerant during unbalanced load conditions | More fault tolerant, can handle unbalanced loads better |
Introduction to Star and Delta Connections
Star and Delta connections are fundamental configurations for three-phase electric motors and transformers, defining how the windings are interconnected to manage voltage and current characteristics. In a Star (Y) connection, each winding is connected to a common neutral point, resulting in phase voltages that are lower than line voltages by a factor of 3, which enhances safety and reduces insulation requirements. The Delta (D) connection links the windings in a closed loop, providing equal line and phase voltages, enabling higher starting torque and continuous operation under heavy loads.
Basic Principles of Star (Y) Connection
The basic principle of the Star (Y) connection involves connecting three components at a common neutral point, forming a Y shape, which allows for a neutral wire to provide a return path for current. This configuration enables the use of line-to-neutral voltage, which is lower than the line-to-line voltage, making it suitable for supplying loads with different voltage requirements. The Star connection is widely used in three-phase power systems for motor starting and distribution networks due to its ability to balance loads and reduce phase currents.
Basic Principles of Delta (Δ) Connection
Delta (D) connection is a three-phase wiring method where each end of a coil is connected to form a closed loop resembling a triangle, allowing currents to circulate continuously through the coils. This configuration provides a phase voltage equal to the line voltage and enables higher starting torque in motors due to the line current being 3 times the phase current. Delta connections are commonly used in industrial applications for load balancing and efficient power distribution in three-phase systems.
Key Differences Between Star and Delta Configurations
Star configuration connects each winding end to a common neutral point, resulting in lower phase voltage and is commonly used for high voltage, low current applications. Delta configuration connects windings in series to form a closed loop, providing higher phase current and is preferred for low voltage, high current scenarios. The key differences impact starting current, torque, and motor efficiency, with star offering reduced starting current and delta delivering higher torque and power.
Voltage and Current Characteristics
Star connection features phase voltage equal to the line voltage divided by 3, resulting in lower phase voltage and current in each winding, enhancing insulation life and reducing copper losses. Delta connection maintains phase voltage equal to line voltage, causing higher phase current and increased power output capacity, suitable for heavy loads. Star connection is preferred for starting motors due to lower starting current, while delta connection provides full power during normal operation with higher line current.
Applications of Star Connection
Star connection is widely used in electrical power distribution systems for its ability to provide a neutral point, enabling the supply of both single-phase and three-phase loads. It is essential in transformer winding configurations for stepping up or down voltage levels, particularly in power grids and industrial equipment. The star connection's balanced phase voltages and reduced insulation requirements make it ideal for long-distance transmission and low-voltage distribution networks.
Applications of Delta Connection
Delta connections are widely used in industrial applications such as heavy machinery, manufacturing plants, and electric motors due to their ability to provide high starting torque and handle unbalanced loads efficiently. This configuration is ideal for three-phase power systems where constant power delivery and reduced harmonics are critical, such as in conveyor belts, compressors, and large pumps. The delta connection also allows the use of three-phase transformers in power distribution networks to supply balanced and stable voltage under varying load conditions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Star and Delta
Star connections offer the advantage of reduced starting current and smooth startup for three-phase motors, minimizing electrical stress and enhancing motor life. However, star configurations may result in lower torque and are less suitable for high power applications. Delta connections provide higher torque and better efficiency in high power loads but cause higher starting currents, which can increase mechanical stress and electrical disturbances.
Star-Delta Transformation and Conversion
Star-Delta transformation is a mathematical technique used in electrical engineering to simplify the analysis of three-phase circuits by converting a star (Y) connected network into an equivalent delta (D) network, or vice versa. This conversion is crucial for solving complex circuit problems, as it allows the calculation of currents, voltages, and impedances by changing the configuration without altering the overall network characteristics. Precise formulas link the resistances or impedances in star and delta configurations, facilitating the transformation and enabling engineers to analyze and design balanced and unbalanced three-phase systems effectively.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Star or Delta Connection
Star connection suits applications requiring a neutral point and lower starting current, making it ideal for light loads and long-distance power distribution. Delta connection is preferred when high starting torque and full line voltage supply are necessary, commonly used in heavy machinery and industrial motors. Choice depends on load nature, starting current limits, and voltage requirements to optimize performance and equipment protection.
Phase Sequence
Phase sequence in Star vs Delta motor starters determines the direction of rotation by controlling the order in which the three-phase power is applied to the motor windings.
Line Voltage
Star connection line voltage equals phase voltage, while Delta connection line voltage is 3 times the phase voltage.
Phase Current
In Star vs Delta connections, the phase current in Delta configuration is 3 times higher than in Star configuration for the same line current.
Neutral Point
The neutral point in Star vs Delta configurations serves as the common connection in the Star setup, enabling the balancing of phase voltages and providing a return path for unbalanced currents.
Balanced Load
Star and Delta configurations enhance balanced load distribution by equally sharing current across phases, reducing unbalanced voltage and improving motor efficiency.
Wye Connection
The Wye connection in Star vs Delta configurations provides a neutral point for load balancing and enables safer, more efficient distribution of three-phase electrical power in industrial and commercial systems.
Mesh Connection
The Star-Delta motor starting method reduces inrush current by initially connecting the motor windings in a star configuration before switching to a delta configuration, which contrasts with a mesh connection that involves complex interconnected loops for enhanced redundancy and load distribution.
Three-Phase Transformation
Star vs Delta connections in three-phase transformation optimize motor startup by reducing current in the star configuration and delivering full power in the delta configuration, enhancing efficiency and minimizing electrical stress.
Power Factor
Star connection improves power factor by providing a balanced load and reducing current phase difference compared to Delta connection in three-phase systems.
Starting Torque
Star connection reduces starting torque to one-third compared to Delta connection, making Star ideal for low-torque startup in three-phase induction motors.
Star vs Delta Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com