Star and delta connections are fundamental methods for wiring three-phase electrical systems, each offering distinct advantages in voltage and current distribution. Star connections provide a neutral point for grounding and allow for the use of two different voltages within the same system, enhancing safety and flexibility in power distribution. Delta connections enable higher starting torque and are often preferred for motors and heavy-duty industrial applications due to their ability to handle larger currents without a neutral wire.
Table of Comparison
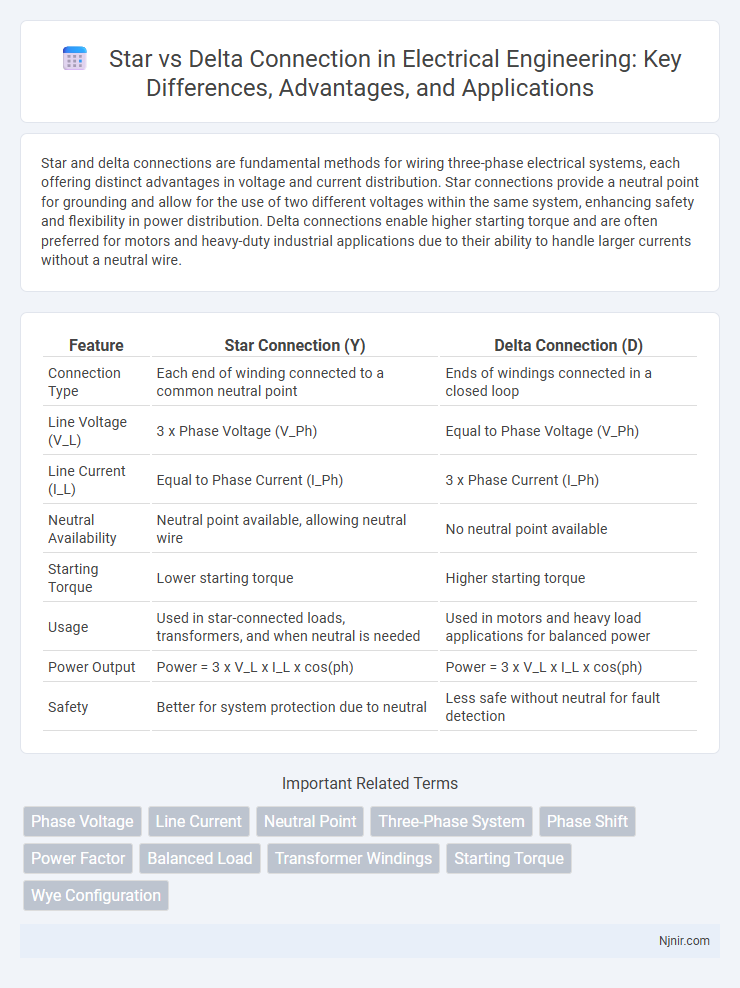
| Feature | Star Connection (Y) | Delta Connection (D) |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Each end of winding connected to a common neutral point | Ends of windings connected in a closed loop |
| Line Voltage (V_L) | 3 x Phase Voltage (V_Ph) | Equal to Phase Voltage (V_Ph) |
| Line Current (I_L) | Equal to Phase Current (I_Ph) | 3 x Phase Current (I_Ph) |
| Neutral Availability | Neutral point available, allowing neutral wire | No neutral point available |
| Starting Torque | Lower starting torque | Higher starting torque |
| Usage | Used in star-connected loads, transformers, and when neutral is needed | Used in motors and heavy load applications for balanced power |
| Power Output | Power = 3 x V_L x I_L x cos(ph) | Power = 3 x V_L x I_L x cos(ph) |
| Safety | Better for system protection due to neutral | Less safe without neutral for fault detection |
Introduction to Star and Delta Connections
Star and delta connections are fundamental wiring configurations used in three-phase electrical systems to connect transformers and motors. The star connection, also known as the Y-connection, links one end of each phase winding to a common neutral point, enabling a neutral line and providing phase-to-neutral voltage. The delta connection forms a closed loop by connecting the end of each phase winding to the beginning of the next, resulting in a system with no neutral and delivering phase-to-phase voltage.
Fundamental Differences Between Star and Delta
Star and delta connections differ primarily in their wiring configuration and phase relationships; a star connection has each phase connected to a common neutral point, resulting in phase voltages that are lower than the line voltages by a factor of 3, while a delta connection forms a closed loop with each phase connected end-to-end, making line and phase voltages equal. Star connections are typically used for long-distance power transmission due to reduced insulation requirements and availability of neutral for grounding, whereas delta connections are favored in industrial applications for their ability to provide higher starting torque and handle unbalanced loads effectively. The fundamental electrical difference also impacts current distribution, with star connections having line current equal to phase current, contrasting with delta connections where line current is 3 times the phase current.
Schematic Diagrams: Star vs Delta
Star connection schematic diagrams feature three coils connected at a common neutral point, forming a Y shape, allowing for phase voltages to be lower than line voltages by a factor of 3. Delta connection diagrams show coils connected end-to-end in a closed loop, creating a triangle, enabling line voltage and phase voltage to be equal. Understanding these distinct schematic representations is crucial for designing and analyzing three-phase electrical systems for specific applications like motors and power distribution.
Voltage and Current Relationships
In star (Y) connection, the line voltage (V_L) is 3 times the phase voltage (V_Ph), and the line current (I_L) equals the phase current (I_Ph). In delta (D) connection, the line voltage equals the phase voltage, while the line current is 3 times the phase current. These relationships are crucial for analyzing and designing three-phase electrical systems to ensure proper voltage levels and current distribution.
Power Distribution in Star and Delta Connections
Star and delta connections significantly impact power distribution in electrical systems, with star connections providing a neutral point for balanced load and enabling the use of both single-phase and three-phase power. Delta connections deliver higher line voltage and greater power handling capacity but lack a neutral point, limiting their use to balanced three-phase loads. The choice between star and delta affects system efficiency, fault tolerance, and suitability for industrial power distribution applications.
Applications of Star Connection
Star connection is widely used in electrical distribution systems because it provides a neutral point, enabling the supply of both single-phase and three-phase loads. It is preferred in transformer secondary windings to deliver different voltage levels and stabilize voltage during unbalanced loads. This type of connection is also crucial in reducing insulation requirements and ensuring safer operation in high-voltage power transmission.
Applications of Delta Connection
Delta connection is widely used in industrial motor applications due to its ability to provide higher starting torque and handle heavy loads efficiently. It is common in three-phase induction motors, transformers, and power distribution systems where balanced loads are critical for stable operation. Delta configuration enhances fault tolerance by allowing continuous operation even if one phase fails, making it ideal for manufacturing plants and large machinery.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Connection
Star connection offers the advantage of a neutral point, enabling the use of neutral conductors for grounding and stable voltage supply, which enhances safety and allows for multiple voltage levels. Its disadvantage lies in the lower phase voltage compared to line voltage, resulting in less power output for the same current and potential underutilization of conductor capacity. Delta connection provides higher phase voltage and power output with no neutral point, making it ideal for heavy load applications, but it lacks a neutral for grounding and is more susceptible to unbalanced loads, increasing the risk of equipment damage.
Impact on Motor Starting Performance
Star connection reduces the starting current by approximately one-third compared to delta connection, leading to lower electrical stress on the motor and supply network during startup. Delta connection provides full voltage to the motor windings at startup, resulting in higher starting torque but increased inrush current. The choice between star and delta impacts the motor's acceleration and thermal performance, with star being preferable for low starting currents and delta for high starting torque requirements.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Star or Delta
Star connection is ideal for applications requiring neutral grounding, lower starting current, and reduced phase voltage, commonly used in distribution systems and long-distance power transmission. Delta connection suits high starting torque machines and scenarios demanding higher phase voltage without neutral, often employed in industrial motor loads and heavy electrical equipment. Selection depends on load type, voltage requirements, starting current limitations, and grounding needs to optimize performance and safety.
Phase Voltage
In star connection, the phase voltage is equal to the line voltage divided by 3, whereas in delta connection, the phase voltage equals the line voltage.
Line Current
In a star connection, the line current equals the phase current, while in a delta connection, the line current is 3 times the phase current.
Neutral Point
The neutral point in a star connection provides a common return path for current and stabilizes phase voltages, whereas a delta connection lacks a neutral point, resulting in no neutral current flow.
Three-Phase System
Star connection in a three-phase system provides a neutral point for phase voltage measurement, while delta connection enables higher line current capacity without a neutral point.
Phase Shift
Star connection induces a 0deg phase shift between line and phase voltages, while delta connection causes a 30deg phase shift, affecting power system analysis and transformer vector groups.
Power Factor
Star connection typically results in higher power factor improvement due to balanced phase voltages, while delta connection offers better current handling but may have lower power factor efficiency.
Balanced Load
A balanced load in star and delta connections ensures equal voltage distribution and current flow, improving system stability and minimizing power losses.
Transformer Windings
Transformer windings use star connection for neutral grounding and phase voltage reduction, while delta connection provides phase displacement and balances load currents.
Starting Torque
Delta connection provides higher starting torque than star connection due to increased line current and power output during motor startup.
Wye Configuration
The Wye (Star) connection in three-phase systems offers a neutral point for stable voltage distribution and is commonly used for balanced and unbalanced loads in power transmission.
star vs delta connection Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com