Trunking provides a versatile and easily accessible solution for routing electrical cables, allowing for quick installation and modifications without extensive structural work. Conduit offers superior protection for wiring, especially in harsh or outdoor environments, by enclosing cables within rigid or flexible tubing to prevent physical damage and exposure to moisture. Choosing between trunking and conduit depends on project requirements such as environmental conditions, flexibility for future changes, and the level of mechanical protection needed.
Table of Comparison
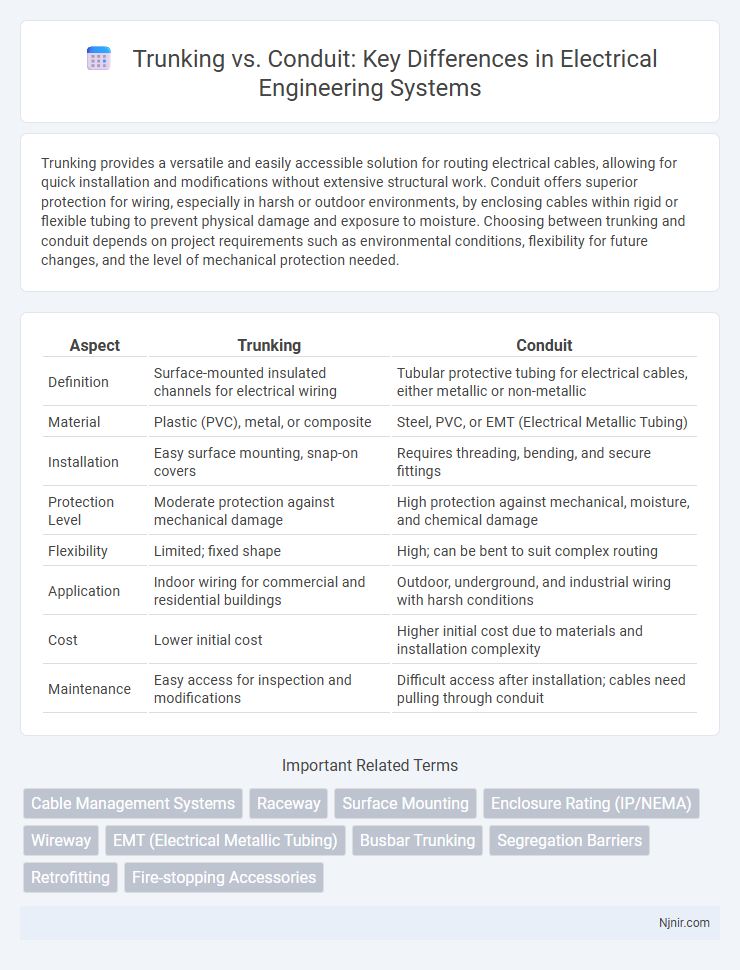
| Aspect | Trunking | Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Surface-mounted insulated channels for electrical wiring | Tubular protective tubing for electrical cables, either metallic or non-metallic |
| Material | Plastic (PVC), metal, or composite | Steel, PVC, or EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) |
| Installation | Easy surface mounting, snap-on covers | Requires threading, bending, and secure fittings |
| Protection Level | Moderate protection against mechanical damage | High protection against mechanical, moisture, and chemical damage |
| Flexibility | Limited; fixed shape | High; can be bent to suit complex routing |
| Application | Indoor wiring for commercial and residential buildings | Outdoor, underground, and industrial wiring with harsh conditions |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to materials and installation complexity |
| Maintenance | Easy access for inspection and modifications | Difficult access after installation; cables need pulling through conduit |
Understanding Trunking and Conduit Systems
Trunking systems provide a flexible, modular solution for routing electrical cables along walls and ceilings, enabling easy access for maintenance and future upgrades. Conduit systems, typically made of metal or plastic tubing, offer robust protection for cables against physical damage, moisture, and corrosion, making them ideal for harsh environments. Choosing between trunking and conduit depends on factors such as installation environment, accessibility needs, and compliance with electrical codes.
Key Differences Between Trunking and Conduit
Trunking is a modular, surface-mounted system designed for housing and protecting multiple cables, allowing easy access for maintenance and expansion, while conduit is a closed tubing system typically made of metal or plastic used to physically protect and route electrical wiring underground or within walls. Trunking offers flexibility in cable management with removable covers, ideal for environments requiring frequent changes, whereas conduit provides superior mechanical protection and is more suitable for harsh or outdoor conditions. The choice between trunking and conduit depends on factors such as installation environment, accessibility needs, and protection requirements for electrical cabling systems.
Applications of Trunking in Electrical Installations
Trunking in electrical installations provides organized routing for multiple cables, offering flexibility for frequent modifications in commercial buildings and data centers. It protects cables from mechanical damage and environmental factors while allowing easy access for maintenance or future expansion. Commonly used in offices, hospitals, and industrial facilities, trunking supports efficient cable management and compliance with safety standards.
Conduit Systems: Types and Uses
Conduit systems include various types such as rigid metal conduit (RMC), intermediate metal conduit (IMC), electrical metallic tubing (EMT), and flexible metal conduit (FMC), each designed for specific applications like indoor wiring, outdoor installations, or areas requiring flexibility. These conduits protect electrical wires from physical damage, moisture, and chemical exposure while ensuring compliance with National Electrical Code (NEC) standards for safety and performance. Common uses span commercial buildings, industrial plants, and residential wiring, where conduit selection depends on environmental conditions, mechanical requirements, and installation complexity.
Advantages of Trunking in Modern Wiring
Trunking in modern wiring offers superior flexibility and ease of installation compared to conduit systems, allowing for quicker access and modifications without extensive dismantling. Its modular design supports a wide range of cable types and sizes, enhancing organizational efficiency and reducing maintenance time in complex electrical networks. Trunking also provides better protection against physical damage and environmental factors, ensuring long-term durability and safety in commercial and industrial settings.
Benefits of Using Conduit for Cable Protection
Conduit offers robust cable protection by shielding wiring from physical damage, moisture, and chemical exposure, significantly enhancing system durability and safety. It facilitates easy cable replacement or upgrades without disturbing existing structures, reducing maintenance time and costs. Conduits also ensure organized cable management, preventing tangling and electromagnetic interference for improved signal integrity.
Trunking vs Conduit: Cost Comparison
Trunking typically offers lower installation costs due to its ease of access and adaptability for wiring changes compared to conduit systems, which require more labor-intensive cutting and fitting. Material costs for trunking are often less expensive, especially for plastic or PVC options, while conduits made from metal or PVC can vary but tend to incur higher upfront expenses. Long-term maintenance costs favor trunking, as cables can be replaced or upgraded without dismantling the entire system, reducing overall operational expenses.
Installation Requirements for Trunking and Conduit
Trunking installation requires precise measurement and cutting to fit electrical cables neatly within modular plastic or metal channels, ensuring easy access for maintenance and future upgrades. Conduit installation involves securing rigid or flexible pipes along walls or ceilings, requiring proper bending tools to navigate corners and junctions while maintaining cable protection and compliance with electrical codes. Both methods demand adherence to safety standards, but conduit systems often require more labor-intensive fittings and longer installation times compared to the relatively straightforward trunking setup.
Safety Considerations: Trunking vs Conduit
Trunking provides a safer solution for electrical wiring in environments where accessibility and protection from external damage are critical, thanks to its enclosed design that prevents accidental contact and shields cables from moisture and impact. Conduit offers superior protection against mechanical stress and environmental hazards, as its rigid structure is ideal for outdoor or industrial installations where robust physical defense is essential. Selecting between trunking and conduit depends on specific safety requirements, such as ease of maintenance, risk of impact, and exposure to corrosive elements.
Choosing Between Trunking and Conduit for Your Project
Choosing between trunking and conduit depends on factors such as installation environment, flexibility needs, and budget constraints. Trunking offers easy access for wiring changes and is ideal for commercial projects requiring frequent modifications, while conduit provides superior protection against physical damage and moisture, making it suitable for industrial or outdoor applications. Evaluating project-specific requirements like exposure to elements, maintenance frequency, and wiring complexity ensures the best fit for safety and functionality.
Cable Management Systems
Trunking offers versatile, easily accessible cable management with robust protection for large cable volumes, while conduit provides superior durability and environmental protection ideal for harsh or outdoor installations.
Raceway
Trunking offers modular, easily accessible raceway solutions ideal for flexible wiring management, while conduit provides durable, rigid protection best suited for permanent or harsh environment raceway installations.
Surface Mounting
Trunking offers flexible, easy-to-install surface mounting for electrical cables, while conduit provides a more rigid, protective surface mounting solution suited for high-durability requirements.
Enclosure Rating (IP/NEMA)
Trunking systems typically offer lower enclosure ratings (IP20/IP40) suitable for indoor cable management, whereas conduit systems provide higher protection with IP65 to NEMA 4X ratings, ideal for harsh and outdoor environments.
Wireway
Wireway provides a flexible, accessible channel for electrical wiring compared to trunking by offering easier maintenance and cable management in conduit-like enclosures.
EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing)
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) offers a lightweight, cost-effective conduit solution with superior corrosion resistance and easier installation compared to traditional trunking systems in electrical wiring applications.
Busbar Trunking
Busbar trunking systems offer superior electrical load capacity and flexible distribution compared to traditional conduit wiring, enhancing efficiency and safety in power distribution networks.
Segregation Barriers
Segregation barriers in trunking provide flexible compartmentalization for diverse cables, whereas conduits offer rigid, enclosed protection ensuring strict physical separation in electrical installations.
Retrofitting
Trunking offers easier and less invasive retrofitting for electrical wiring compared to conduit, which typically requires more extensive wall modifications and labor.
Fire-stopping Accessories
Trunking offers limited fire-stopping accessories compared to conduit systems, which provide a wider range of certified firestop solutions to maintain fire barrier integrity.
Trunking vs Conduit Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com