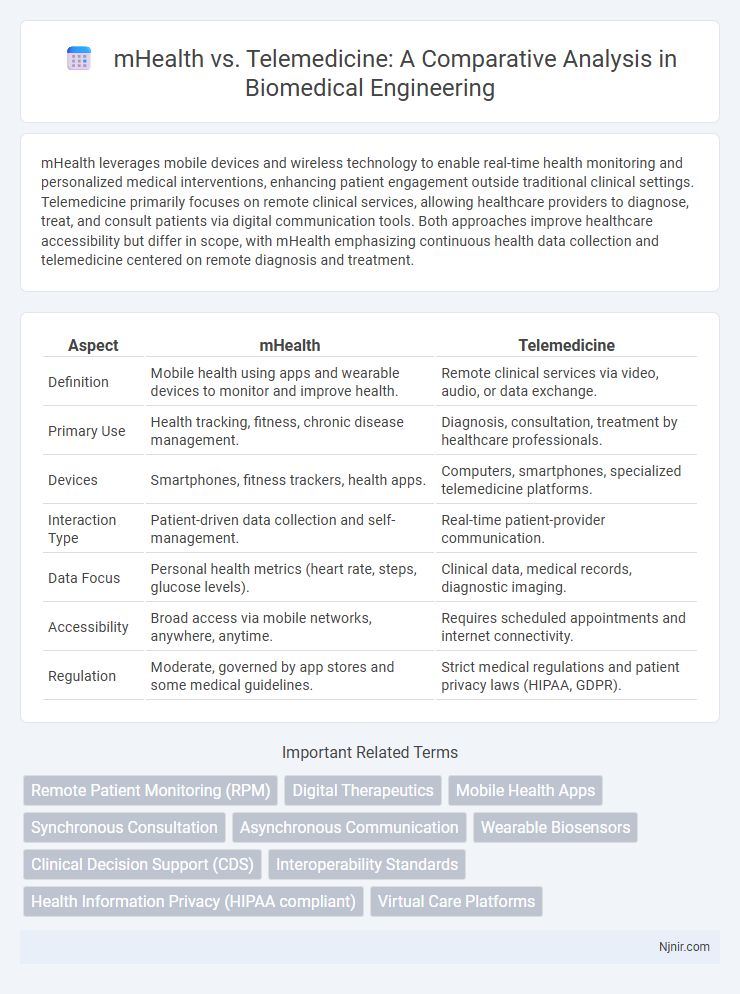
mHealth leverages mobile devices and wireless technology to enable real-time health monitoring and personalized medical interventions, enhancing patient engagement outside traditional clinical settings. Telemedicine primarily focuses on remote clinical services, allowing healthcare providers to diagnose, treat, and consult patients via digital communication tools. Both approaches improve healthcare accessibility but differ in scope, with mHealth emphasizing continuous health data collection and telemedicine centered on remote diagnosis and treatment.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | mHealth | Telemedicine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mobile health using apps and wearable devices to monitor and improve health. | Remote clinical services via video, audio, or data exchange. |
| Primary Use | Health tracking, fitness, chronic disease management. | Diagnosis, consultation, treatment by healthcare professionals. |
| Devices | Smartphones, fitness trackers, health apps. | Computers, smartphones, specialized telemedicine platforms. |
| Interaction Type | Patient-driven data collection and self-management. | Real-time patient-provider communication. |
| Data Focus | Personal health metrics (heart rate, steps, glucose levels). | Clinical data, medical records, diagnostic imaging. |
| Accessibility | Broad access via mobile networks, anywhere, anytime. | Requires scheduled appointments and internet connectivity. |
| Regulation | Moderate, governed by app stores and some medical guidelines. | Strict medical regulations and patient privacy laws (HIPAA, GDPR). |
Defining mHealth and Telemedicine
mHealth refers to the use of mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to support healthcare services, health monitoring, and patient education primarily through apps and wearable technologies. Telemedicine involves the remote diagnosis and treatment of patients through telecommunications technology, including video conferencing, remote patient monitoring, and electronic health records. Both mHealth and telemedicine enhance healthcare accessibility but differ in scope, with mHealth emphasizing mobile solutions and telemedicine encompassing broader remote clinical services.
Core Technologies Behind mHealth and Telemedicine
mHealth relies heavily on mobile communication technologies such as smartphones, wearable sensors, and wireless networks to enable real-time health monitoring and data collection. Telemedicine utilizes telecommunication infrastructure including video conferencing, electronic health records (EHR), and cloud computing to facilitate remote diagnosis and treatment. Both fields integrate advanced software platforms and artificial intelligence to enhance patient care and streamline healthcare delivery processes.
Key Differences Between mHealth and Telemedicine
mHealth primarily involves the use of mobile devices and apps to support health services and information, emphasizing patient self-management and remote monitoring. Telemedicine focuses on real-time, interactive clinical services between healthcare providers and patients via video or phone consultations. Key differences include mHealth's broader scope for health promotion and chronic disease management, whereas telemedicine centers on direct medical care delivery and diagnosis.
Applications in Biomedical Engineering
mHealth leverages mobile devices and wearable sensors to continuously monitor patient health metrics, enabling real-time data collection and personalized healthcare interventions. Telemedicine utilizes advanced communication technologies for remote diagnosis, consultation, and treatment, enhancing accessibility especially in underserved areas. Both applications in biomedical engineering drive innovations in sensor development, data analytics, and secure health information systems to improve patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Patient Engagement and Accessibility
mHealth leverages mobile devices and apps to enhance patient engagement by providing real-time health monitoring, personalized reminders, and easy access to medical information, which empowers patients to take proactive control of their health. Telemedicine focuses on delivering remote clinical services through video calls and virtual consultations, improving accessibility especially for patients in rural or underserved areas by eliminating the need for physical travel. Combining mHealth and telemedicine creates a comprehensive digital health ecosystem that maximizes patient interaction, reduces barriers to healthcare services, and supports continuous care management.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
mHealth and telemedicine both revolutionize healthcare delivery by leveraging digital technologies, but they pose distinct data security and privacy challenges. mHealth apps often collect sensitive personal health data on mobile devices, increasing risks of unauthorized access, data breaches, and inadequate encryption, while telemedicine platforms must secure real-time video consultations and patient records against cyber threats and comply with HIPAA and GDPR regulations. Implementing end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits are critical to safeguarding patient information in both mHealth and telemedicine environments.
Impact on Healthcare Outcomes
mHealth leverages mobile devices to provide real-time health monitoring, increasing patient engagement and improving chronic disease management, which leads to better healthcare outcomes. Telemedicine facilitates remote consultations, allowing timely access to medical expertise and reducing hospital readmission rates. Both technologies contribute to enhanced healthcare quality by enabling continuous care and reducing geographical barriers.
Regulatory and Compliance Standards
mHealth and telemedicine each face distinct regulatory and compliance standards governed by entities such as the FDA, HIPAA, and GDPR to ensure patient data security and privacy. mHealth apps must comply with software as a medical device (SaMD) regulations, focusing on app functionality and user data protection, while telemedicine platforms primarily adhere to telehealth-specific licensure requirements and cross-state practice regulations. Both domains require robust encryption protocols and adherence to data interoperability standards like HL7 and FHIR to maintain compliance and protect sensitive health information.
Integration with Biomedical Devices
mHealth leverages mobile technologies such as smartphones and wearable sensors to collect real-time health data, enabling continuous monitoring and instant feedback through integrated biomedical devices. Telemedicine primarily facilitates remote clinical consultations and diagnostics, often relying on connected biomedical equipment like digital stethoscopes and ECG monitors to transmit patient data during virtual visits. The integration of biomedical devices in mHealth emphasizes personalized health tracking and preventive care, while telemedicine focuses on delivering remote diagnosis and treatment facilitated by device-generated medical information.
Future Trends in mHealth and Telemedicine
Future trends in mHealth emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and wearable technology, enabling personalized health monitoring and proactive disease management. Telemedicine advancements focus on expanding virtual care platforms with improved interoperability, real-time diagnostics, and augmented reality for remote procedures. The convergence of 5G connectivity and blockchain technology promises enhanced data security, faster transmission, and seamless access to health records across mHealth and telemedicine services.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) in mHealth leverages mobile devices and wireless technology to continuously collect and transmit patient health data, enhancing telemedicine by enabling real-time monitoring and proactive management outside traditional clinical settings.
Digital Therapeutics
Digital Therapeutics, a subset of mHealth, deliver evidence-based medical interventions via software to treat, manage, or prevent diseases, differentiating from Telemedicine's broader remote clinical services by emphasizing patient-centered, app-driven therapeutic protocols.
Mobile Health Apps
Mobile health apps enhance mHealth by providing users with personalized health monitoring, remote consultations, and real-time data sharing, distinguishing them from traditional telemedicine platforms that primarily facilitate virtual doctor-patient interactions.
Synchronous Consultation
Synchronous consultation in mHealth enables real-time interactive communication between patients and healthcare providers through mobile devices, enhancing access and immediacy compared to traditional telemedicine platforms.
Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication in mHealth enables patients to send health data and receive medical advice without real-time interaction, whereas telemedicine primarily involves synchronous video consultations for immediate care.
Wearable Biosensors
Wearable biosensors in mHealth provide continuous, real-time physiological monitoring, offering more personalized and immediate health data compared to traditional telemedicine's episodic, remote clinical consultations.
Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
mHealth enhances Clinical Decision Support (CDS) by delivering real-time patient data and AI-driven recommendations via mobile devices, while telemedicine primarily facilitates remote consultations with integrated CDS tools for improved diagnostic accuracy.
Interoperability Standards
Interoperability standards like HL7 FHIR and DICOM are critical for integrating mHealth applications and telemedicine platforms to enable seamless data exchange and improve patient care coordination.
Health Information Privacy (HIPAA compliant)
mHealth and telemedicine both require strict adherence to HIPAA compliance to ensure health information privacy through secure data encryption, access controls, and patient consent management.
Virtual Care Platforms
Virtual care platforms integrate mHealth technologies and telemedicine services to enhance remote patient monitoring, real-time communication, and personalized healthcare delivery.
mHealth vs Telemedicine Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com