Personalized medicine tailors medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient, enhancing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing adverse effects by considering genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. In contrast, population-based medicine applies standardized treatment protocols derived from epidemiological data, aiming for broad applicability and cost-effectiveness across large groups. Advances in biomedical engineering technologies enable precise diagnostics and targeted drug delivery systems that bridge the gap between these approaches, promoting more effective and patient-centered healthcare solutions.
Table of Comparison
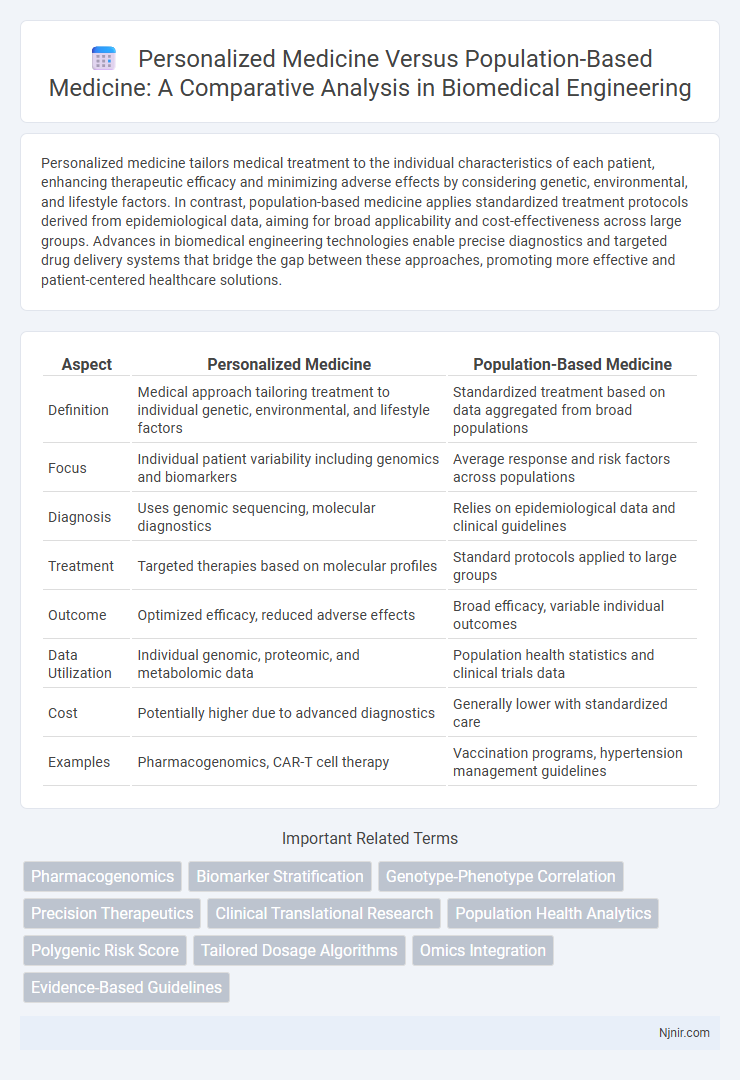
| Aspect | Personalized Medicine | Population-Based Medicine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Medical approach tailoring treatment to individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors | Standardized treatment based on data aggregated from broad populations |
| Focus | Individual patient variability including genomics and biomarkers | Average response and risk factors across populations |
| Diagnosis | Uses genomic sequencing, molecular diagnostics | Relies on epidemiological data and clinical guidelines |
| Treatment | Targeted therapies based on molecular profiles | Standard protocols applied to large groups |
| Outcome | Optimized efficacy, reduced adverse effects | Broad efficacy, variable individual outcomes |
| Data Utilization | Individual genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data | Population health statistics and clinical trials data |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to advanced diagnostics | Generally lower with standardized care |
| Examples | Pharmacogenomics, CAR-T cell therapy | Vaccination programs, hypertension management guidelines |
Introduction to Personalized and Population-Based Medicine
Personalized medicine tailors medical treatment to an individual's genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors, enhancing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing adverse effects. Population-based medicine relies on epidemiological data and standardized treatment protocols derived from large groups to address public health needs broadly. Understanding these approaches highlights the shift towards precision health by integrating personal and population-level insights for optimized care delivery.
Historical Evolution of Medical Approaches
Personalized medicine emerged from advancements in genomics and biotechnology in the late 20th century, allowing tailored treatments based on individual genetic profiles, contrasting with the traditional population-based medicine that relied on generalized data from large groups. Historically, population-based medicine dominated healthcare with standardized protocols aimed at broad populations, improving public health outcomes through widespread vaccination and epidemiological studies. The shift towards personalized medicine reflects a historical evolution driven by the Human Genome Project and the integration of big data analytics, enabling precision diagnostics and customized therapeutic interventions.
Core Principles of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine tailors medical treatment to individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, enhancing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing adverse effects. Core principles include genomic profiling, biomarker identification, and patient-specific data integration to guide precise diagnosis and treatment decisions. Unlike population-based medicine, which applies generalized protocols, personalized medicine emphasizes individualized care based on molecular and phenotypic patient characteristics.
Foundations of Population-Based Medicine
Population-based medicine relies on epidemiological data and clinical trials to develop standardized treatment protocols that apply broadly across demographic groups. Its foundation is built upon statistical analysis of disease incidence, risk factors, and outcomes in large populations, enabling healthcare providers to implement evidence-based interventions. This approach prioritizes scalability and cost-effectiveness while addressing common health challenges within defined populations.
Technological Innovations Driving Personalization
Cutting-edge technological innovations like genomic sequencing, artificial intelligence, and wearable health devices are driving the shift from population-based medicine to personalized medicine. These tools enable precise patient profiling, targeted therapies, and real-time health monitoring tailored to individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Integration of big data analytics and machine learning accelerates predictive diagnostics and customized treatment plans, enhancing patient outcomes.
Genomics and Biomarkers in Disease Management
Genomics and biomarkers play pivotal roles in distinguishing personalized medicine from population-based medicine by enabling tailored disease management strategies based on individual genetic profiles. Personalized medicine leverages genomic sequencing and biomarker analysis to target specific molecular pathways, improving therapeutic efficacy and minimizing adverse effects in diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders. In contrast, population-based medicine relies on epidemiological data and generalized treatment protocols, which may overlook genetic variability and biomarker heterogeneity critical for precise interventions.
Public Health Implications of Both Approaches
Personalized medicine tailors treatments based on individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, enhancing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing adverse effects. Population-based medicine emphasizes broad interventions targeting common risk factors to improve overall public health outcomes and reduce disease burden. Integrating both approaches can optimize resource allocation and health strategies, balancing precision care with large-scale preventive measures.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations in Medical Models
Personalized medicine leverages genomic data tailoring treatments to individual patients, raising significant ethical concerns regarding data privacy, informed consent, and potential genetic discrimination. Population-based medicine emphasizes broad public health strategies but may overlook individual variability, potentially compromising patient autonomy and equitable care. Ensuring robust data protection frameworks and transparent ethical guidelines is critical to balance innovation with respect for patient rights in both approaches.
Future Trends in Biomedical Engineering for Healthcare
Personalized medicine leverages genomic data, advanced biometrics, and AI-driven algorithms to tailor treatments to individual patient profiles, contrasting with population-based medicine's broad, standardized approaches. Biomedical engineering innovations such as wearable biosensors, precision drug delivery systems, and machine learning models support this shift by enabling real-time health monitoring and adaptive therapies. Future trends emphasize integrating multi-omics data and digital twin technologies to enhance predictive accuracy and optimize personalized healthcare outcomes.
Integrative Strategies for Optimal Patient Outcomes
Personalized medicine leverages genetic, environmental, and lifestyle data to tailor treatments specifically for individual patients, improving efficacy and reducing adverse effects. Population-based medicine relies on broad statistical data to develop standardized treatment guidelines aimed at large groups, emphasizing public health outcomes. Integrative strategies combine personalized data analytics with population health insights, fostering precision interventions that optimize patient outcomes while addressing community health trends.
Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics enhances personalized medicine by tailoring drug treatments to individual genetic profiles, improving efficacy and reducing adverse effects compared to traditional population-based medicine.
Biomarker Stratification
Biomarker stratification enhances personalized medicine by enabling targeted therapies based on individual molecular profiles, contrasting with population-based medicine's generalized treatment approaches.
Genotype-Phenotype Correlation
Genotype-phenotype correlation in personalized medicine enables tailored treatments by analyzing individual genetic variations, contrasting with population-based medicine's generalized approach based on average genetic and phenotypic data.
Precision Therapeutics
Precision therapeutics in personalized medicine tailors treatments based on individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, contrasting with population-based medicine's generalized approaches that apply uniform therapies across broad patient groups.
Clinical Translational Research
Clinical translational research accelerates the integration of personalized medicine by tailoring treatments to genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, contrasting with population-based medicine's broader, one-size-fits-all approach.
Population Health Analytics
Population Health Analytics leverages large-scale data to identify trends, risk factors, and outcomes across diverse groups, enabling population-based medicine to implement targeted interventions and optimize healthcare delivery.
Polygenic Risk Score
Polygenic Risk Scores enhance personalized medicine by accurately predicting individual disease risk using genetic data, outperforming traditional population-based approaches that rely on generalized risk factors.
Tailored Dosage Algorithms
Tailored dosage algorithms in personalized medicine optimize drug efficacy and minimize adverse effects by accounting for individual genetic, physiological, and environmental factors unlike population-based medicine's uniform dosing strategies.
Omics Integration
Integrating multi-omics data enhances personalized medicine by tailoring treatments to individual genetic, proteomic, and metabolomic profiles, whereas population-based medicine relies on generalized data from broad demographic groups.
Evidence-Based Guidelines
Personalized medicine leverages genetic, environmental, and lifestyle data to tailor treatments, contrasting with population-based medicine that relies on standardized evidence-based guidelines derived from large-scale clinical trials.
Personalized Medicine vs Population-Based Medicine Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com