Tethered capsule endoscopy offers a less invasive alternative to standard endoscopy by utilizing a swallowable capsule connected to a thin tether, enabling visualization of the gastrointestinal tract without sedation. This method enhances patient comfort and reduces procedural risks while providing real-time imaging for early disease detection. Despite limitations in maneuverability compared to traditional endoscopy, tethered capsules are advancing diagnostic capabilities through improved sensor integration and wireless technology.
Table of Comparison
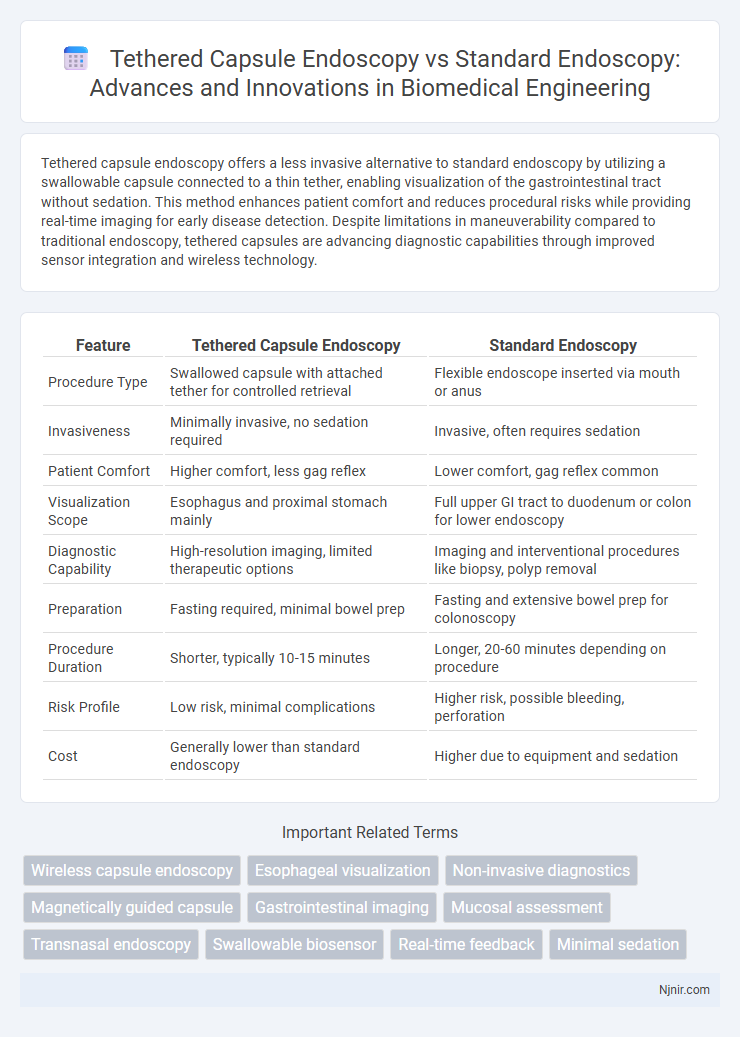
| Feature | Tethered Capsule Endoscopy | Standard Endoscopy |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure Type | Swallowed capsule with attached tether for controlled retrieval | Flexible endoscope inserted via mouth or anus |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive, no sedation required | Invasive, often requires sedation |
| Patient Comfort | Higher comfort, less gag reflex | Lower comfort, gag reflex common |
| Visualization Scope | Esophagus and proximal stomach mainly | Full upper GI tract to duodenum or colon for lower endoscopy |
| Diagnostic Capability | High-resolution imaging, limited therapeutic options | Imaging and interventional procedures like biopsy, polyp removal |
| Preparation | Fasting required, minimal bowel prep | Fasting and extensive bowel prep for colonoscopy |
| Procedure Duration | Shorter, typically 10-15 minutes | Longer, 20-60 minutes depending on procedure |
| Risk Profile | Low risk, minimal complications | Higher risk, possible bleeding, perforation |
| Cost | Generally lower than standard endoscopy | Higher due to equipment and sedation |
Introduction to Capsule and Standard Endoscopy
Tethered capsule endoscopy uses a swallowable capsule connected by a thin tether, enabling real-time visualization of the esophagus and upper gastrointestinal tract without sedation, enhancing patient comfort and procedure feasibility. Standard endoscopy utilizes a flexible endoscope inserted through the mouth to directly visualize and perform interventions in the gastrointestinal tract, typically requiring sedation and posing higher patient discomfort. Both methods provide valuable diagnostic insights, but tethered capsule endoscopy offers a less invasive alternative with easy repeatability and minimal preparation.
Evolution of Tethered Capsule Endoscopy Technology
Tethered capsule endoscopy has evolved significantly with advancements in miniaturized imaging sensors, improved wireless data transmission, and enhanced patient comfort compared to standard endoscopy. Innovations such as high-resolution cameras, flexible capsule designs, and real-time video monitoring have expanded its diagnostic capabilities in gastrointestinal examinations. These technological improvements have made tethered capsule endoscopy a less invasive, more accessible alternative for detecting esophageal and small bowel conditions.
Technical Principles: Tethered vs. Standard Endoscopy
Tethered capsule endoscopy employs a swallowable capsule attached to a thin, flexible tether that transmits real-time images of the gastrointestinal tract, enabling continuous visualization without sedation. Standard endoscopy utilizes a flexible, fiber-optic or video-equipped endoscope inserted through the mouth or rectum, offering direct control and manipulation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. The tethered capsule's non-invasive approach contrasts with the invasiveness of standard endoscopy, impacting patient comfort and procedural complexity.
Indications and Contraindications
Tethered capsule endoscopy is indicated primarily for patients requiring minimally invasive visualization of the esophagus and upper gastrointestinal tract, particularly when sedation risks are a concern or conventional endoscopy is contraindicated. Standard endoscopy remains the preferred method for comprehensive examination, biopsy, and therapeutic interventions in patients with suspected or confirmed gastrointestinal pathology. Contraindications for tethered capsule endoscopy include strictures, obstruction, or severe dysphagia, whereas standard endoscopy contraindications involve unstable cardiopulmonary conditions and lack of patient cooperation.
Comparative Diagnostic Accuracy and Clinical Efficacy
Tethered capsule endoscopy demonstrates comparable diagnostic accuracy to standard endoscopy in detecting mucosal abnormalities of the esophagus, with sensitivity and specificity rates nearing 90-95%. Clinical efficacy is enhanced by its minimally invasive nature, enabling outpatient procedures without sedation, thus reducing patient discomfort and risk. However, standard endoscopy maintains superiority in therapeutic interventions and biopsies, supporting its role as the gold standard for comprehensive gastrointestinal evaluation.
Patient Comfort, Tolerability, and Preferences
Tethered capsule endoscopy offers enhanced patient comfort compared to standard endoscopy by eliminating the need for sedation and reducing throat irritation, which improves tolerability during the procedure. Patients report a preference for tethered capsule endoscopy due to its less invasive nature, decreased gag reflex, and quicker recovery time. Studies indicate higher satisfaction scores and willingness to repeat the procedure with tethered capsule endoscopy, highlighting its patient-centric advantages in gastrointestinal diagnostics.
Procedure Workflow and Operational Efficiency
Tethered capsule endoscopy streamlines the procedure workflow by enabling patients to swallow a capsule attached to a thin tether, reducing the need for sedation and minimizing recovery time compared to standard endoscopy. This method allows real-time image transmission and swift navigation through the gastrointestinal tract, enhancing operational efficiency by decreasing procedure duration and increasing patient throughput. Standard endoscopy requires specialized equipment and personnel for insertion and monitoring, leading to longer preparation and recovery phases, thus impacting overall clinical workflow and resource allocation.
Safety Profiles and Potential Complications
Tethered capsule endoscopy offers a less invasive approach with a lower risk of sedation-related complications compared to standard endoscopy, enhancing patient safety during esophageal examinations. While standard endoscopy may involve risks such as perforation, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia, tethered capsule endoscopy minimizes these by eliminating the need for sedation and invasive instrument passage. Potential complications of tethered capsule endoscopy are generally mild, including transient discomfort or capsule retention, making it a safer alternative with fewer severe adverse events.
Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Utilization
Tethered capsule endoscopy offers a cost-effective alternative to standard endoscopy by reducing the need for sedation, specialized personnel, and dedicated procedure rooms, thus lowering overall healthcare expenses. Resource utilization improves as tethered capsules enable high-throughput screening with minimal recovery time, allowing better allocation of endoscopy units and staff. Studies demonstrate tethered capsule endoscopy maintains diagnostic accuracy while significantly decreasing per-patient costs and increasing procedural efficiency compared to conventional endoscopy methods.
Future Trends and Innovations in Endoscopic Techniques
Tethered capsule endoscopy is poised to revolutionize diagnostic gastroenterology by offering a less invasive, patient-friendly alternative to standard endoscopy with real-time imaging and remote monitoring capabilities. Advances in miniaturization, AI-driven image analysis, and wireless data transmission are driving innovations that enhance diagnostic accuracy and patient comfort. Future trends include integrating multi-spectral imaging and enhanced tissue characterization to improve early detection of gastrointestinal diseases.
Wireless capsule endoscopy
Wireless capsule endoscopy offers a non-invasive alternative to tethered capsule endoscopy and standard endoscopy by enabling real-time, wireless imaging of the gastrointestinal tract without the discomfort and sedation associated with traditional methods.
Esophageal visualization
Tethered capsule endoscopy provides enhanced esophageal visualization through non-invasive, real-time imaging, offering greater patient comfort and accessibility compared to standard endoscopy.
Non-invasive diagnostics
Tethered capsule endoscopy offers a non-invasive diagnostic alternative to standard endoscopy by enabling painless, sedation-free visualization of the esophagus and upper gastrointestinal tract, enhancing patient comfort and accessibility.
Magnetically guided capsule
Magnetically guided tethered capsule endoscopy offers a less invasive, radiation-free alternative to standard endoscopy with enhanced navigation control and improved patient comfort.
Gastrointestinal imaging
Tethered capsule endoscopy offers a less invasive, patient-friendly alternative to standard endoscopy, enabling high-resolution gastrointestinal imaging without sedation or air insufflation.
Mucosal assessment
Tethered capsule endoscopy offers improved patient comfort and detailed mucosal assessment compared to standard endoscopy by enabling real-time imaging of the entire esophageal mucosa without sedation.
Transnasal endoscopy
Tethered capsule endoscopy offers a less invasive, sedation-free alternative to standard transnasal endoscopy by using a swallowable, tethered capsule to provide high-resolution imaging of the esophagus without discomfort or the need for nasal insertion.
Swallowable biosensor
Tethered capsule endoscopy utilizes a swallowable biosensor embedded in a capsule to provide real-time, minimally invasive imaging of the gastrointestinal tract, offering enhanced patient comfort and continuous data monitoring compared to standard endoscopy.
Real-time feedback
Tethered capsule endoscopy provides real-time feedback through continuous wireless data transmission, enhancing immediate diagnostic accuracy compared to standard endoscopy, which typically relies on delayed image analysis.
Minimal sedation
Tethered capsule endoscopy requires minimal sedation compared to standard endoscopy, enhancing patient comfort and reducing procedural risks.
Tethered capsule endoscopy vs Standard endoscopy Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com