Digital pathology enhances diagnostic accuracy by enabling high-resolution image analysis and AI-assisted pattern recognition, surpassing the limitations of traditional microscopy. It facilitates remote collaboration and data sharing, accelerating research and patient care workflows. This integration of digital tools improves efficiency, reproducibility, and scalability in biomedical diagnostics.
Table of Comparison
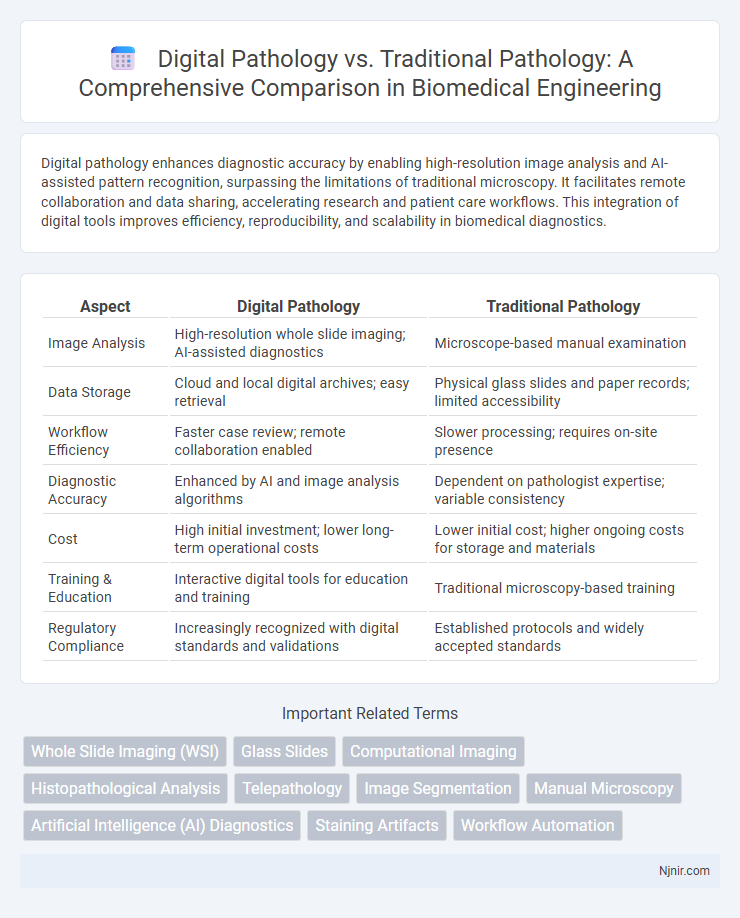
| Aspect | Digital Pathology | Traditional Pathology |
|---|---|---|
| Image Analysis | High-resolution whole slide imaging; AI-assisted diagnostics | Microscope-based manual examination |
| Data Storage | Cloud and local digital archives; easy retrieval | Physical glass slides and paper records; limited accessibility |
| Workflow Efficiency | Faster case review; remote collaboration enabled | Slower processing; requires on-site presence |
| Diagnostic Accuracy | Enhanced by AI and image analysis algorithms | Dependent on pathologist expertise; variable consistency |
| Cost | High initial investment; lower long-term operational costs | Lower initial cost; higher ongoing costs for storage and materials |
| Training & Education | Interactive digital tools for education and training | Traditional microscopy-based training |
| Regulatory Compliance | Increasingly recognized with digital standards and validations | Established protocols and widely accepted standards |
Introduction to Pathology: Digital vs Traditional
Digital pathology leverages high-resolution slide scanning and advanced image analysis software to enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline workflow compared to traditional pathology's reliance on manual microscope examination. Digital imaging allows for easy storage, remote consultations, and integration with AI algorithms, enabling faster and more consistent interpretations. Traditional pathology remains foundational for hands-on tissue assessment but faces limitations in scalability and data sharing, positioning digital pathology as a transformative innovation in modern diagnostic practices.
Evolution of Pathology Practices
Digital pathology has revolutionized traditional pathology by enabling high-resolution slide scanning, remote analysis, and AI-assisted diagnostics, significantly enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Unlike manual microscopic examination, digital pathology facilitates easier data storage, sharing, and integration with electronic health records, streamlining workflows for pathologists. This evolution supports faster diagnosis, improved patient outcomes, and advances in research through enhanced computational pathology tools.
Key Technologies in Digital Pathology
Digital pathology leverages advanced imaging technologies such as whole slide imaging (WSI), artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, and cloud computing to enhance diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency. Key technologies include high-resolution scanners that convert glass slides into digital images, machine learning models for automated image analysis, and secure data storage solutions enabling remote access and telepathology. These innovations significantly optimize pathology diagnostics compared to traditional microscopy-based methods by enabling faster case review and improved collaboration.
Workflow Differences: Traditional vs Digital Pathology
Digital pathology streamlines workflow by enabling slide digitization, remote analysis, and automated image analysis, significantly reducing manual handling and turnaround time compared to traditional pathology. Traditional pathology relies heavily on physical microscope examination, manual slide preparation, and face-to-face consultations, which can lead to slower diagnosis and increased risk of human error. Integration of digital pathology platforms enhances collaboration, data sharing, and storage efficiency, transforming diagnostic workflows into faster, more scalable processes.
Diagnostic Accuracy and Reliability
Digital pathology enhances diagnostic accuracy by utilizing high-resolution whole slide imaging and advanced AI algorithms that detect subtle cellular abnormalities often missed in traditional microscopy. Studies show digital systems reduce diagnostic variability and increase reliability through standardized image analysis and remote expert consultations. In contrast, traditional pathology relies heavily on subjective interpretation and is prone to inter-observer variability, impacting consistency and diagnostic confidence.
Impact on Pathologist Collaboration and Communication
Digital pathology enhances pathologist collaboration and communication by enabling real-time sharing of high-resolution whole slide images across remote locations, reducing turnaround times for diagnosis and consultations. Advanced annotation tools and integrated telepathology platforms facilitate precise case discussions and collective decision-making, improving diagnostic accuracy. In contrast, traditional pathology relies heavily on physical slide exchanges and in-person meetings, often causing delays and limiting collaborative opportunities among pathologists.
Data Management and Storage Solutions
Digital pathology leverages advanced data management systems and cloud storage solutions to handle vast amounts of high-resolution slide images, enabling efficient retrieval and collaborative analysis. Traditional pathology relies heavily on physical storage of glass slides and paper records, which limits scalability and poses risks of data loss or damage. Enhanced metadata tagging and AI-driven indexing in digital pathology streamline workflow and improve long-term data preservation compared to conventional methods.
Cost Analysis: Implementation and Maintenance
Digital pathology involves significant initial costs including high-resolution scanners, image storage solutions, and specialized software licenses, often exceeding traditional pathology's expenses for microscopes and slide preparation materials. Maintenance costs for digital systems include data management, software updates, and IT support, which can be substantial but enable remote consultations and faster diagnosis workflows. Traditional pathology's ongoing costs are primarily labor-intensive with physical storage of glass slides and reagents, making long-term cost savings in digital pathology notable despite the higher upfront investment.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Digital pathology introduces regulatory challenges such as compliance with FDA guidelines for software as a medical device (SaMD) and data privacy laws like HIPAA, requiring robust cybersecurity measures to protect patient information. Traditional pathology, governed by established protocols and manual record-keeping, often lacks digital traceability but benefits from clear ethical frameworks developed over decades. The shift to digital platforms demands new standards for validation, quality assurance, and informed consent, emphasizing transparency and accountability in diagnostic accuracy and data handling.
Future Trends in Digital and Traditional Pathology
Future trends in digital pathology emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence algorithms for enhanced diagnostic accuracy and predictive analytics, transforming disease detection and treatment planning. Traditional pathology is evolving with increased automation and improved imaging techniques but faces challenges in scalability and real-time data sharing compared to digital platforms. The convergence of cloud computing and advanced digital histology systems is set to revolutionize pathology workflows, enabling collaborative research and telepathology on a global scale.
Whole Slide Imaging (WSI)
Whole Slide Imaging (WSI) in digital pathology provides faster, more accurate diagnostics and remote collaboration compared to traditional pathology's reliance on physical glass slides and manual microscopy.
Glass Slides
Digital pathology enhances glass slide analysis by enabling high-resolution scanning, remote access, and advanced image analysis compared to traditional microscopy methods.
Computational Imaging
Computational imaging in digital pathology enhances diagnostic accuracy and efficiency by enabling advanced image analysis and automated detection of pathological features, surpassing the limitations of traditional microscopy.
Histopathological Analysis
Digital pathology enhances histopathological analysis by enabling high-resolution slide digitization, remote consultations, and AI-driven image quantification, offering faster and more precise diagnostic insights compared to traditional microscopy-based methods.
Telepathology
Telepathology enhances digital pathology by enabling remote diagnosis and consultation, improving accuracy and turnaround time compared to traditional pathology methods.
Image Segmentation
Digital pathology utilizes advanced image segmentation algorithms to enhance accuracy and efficiency compared to the manual, time-consuming segmentation methods in traditional pathology.
Manual Microscopy
Digital pathology enhances diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency by enabling high-resolution image analysis and remote consultation, surpassing the limitations of manual microscopy reliant on traditional glass slides and subjective visual assessments.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Diagnostics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) diagnostics in digital pathology enhances accuracy and efficiency by automating image analysis, outperforming traditional pathology's manual examination methods.
Staining Artifacts
Digital pathology reduces errors caused by staining artifacts through standardized image processing, whereas traditional pathology often struggles with inconsistent stain quality impacting diagnosis accuracy.
Workflow Automation
Digital pathology enhances workflow automation by enabling faster slide scanning, seamless image sharing, and AI-powered analysis compared to the manual, time-consuming processes of traditional pathology.
digital pathology vs traditional pathology Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com