In vitro diagnostics (IVD) provide highly accurate laboratory-based testing essential for complex analyses, while point-of-care testing (POCT) delivers rapid results at or near the patient, enabling immediate clinical decisions. IVD systems typically require specialized equipment and trained personnel, whereas POCT devices are designed for ease of use and portability. The integration of both approaches enhances diagnostic efficiency, improving patient outcomes through timely and precise medical interventions.
Table of Comparison
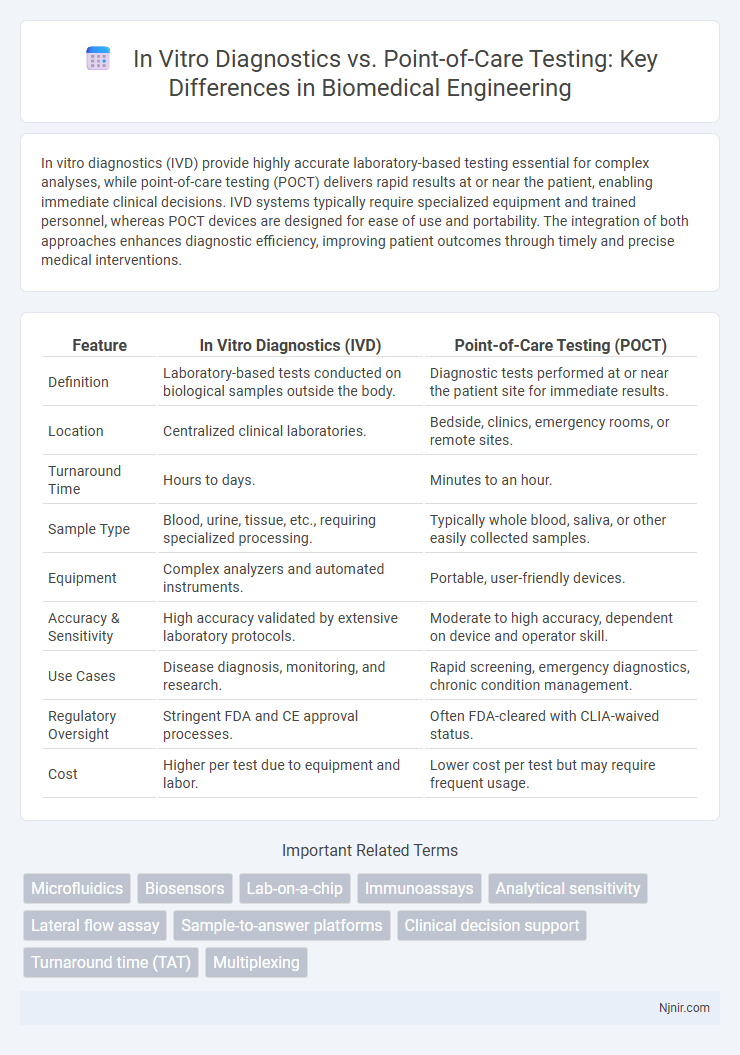
| Feature | In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) | Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laboratory-based tests conducted on biological samples outside the body. | Diagnostic tests performed at or near the patient site for immediate results. |
| Location | Centralized clinical laboratories. | Bedside, clinics, emergency rooms, or remote sites. |
| Turnaround Time | Hours to days. | Minutes to an hour. |
| Sample Type | Blood, urine, tissue, etc., requiring specialized processing. | Typically whole blood, saliva, or other easily collected samples. |
| Equipment | Complex analyzers and automated instruments. | Portable, user-friendly devices. |
| Accuracy & Sensitivity | High accuracy validated by extensive laboratory protocols. | Moderate to high accuracy, dependent on device and operator skill. |
| Use Cases | Disease diagnosis, monitoring, and research. | Rapid screening, emergency diagnostics, chronic condition management. |
| Regulatory Oversight | Stringent FDA and CE approval processes. | Often FDA-cleared with CLIA-waived status. |
| Cost | Higher per test due to equipment and labor. | Lower cost per test but may require frequent usage. |
Introduction to In Vitro Diagnostics and Point-of-Care Testing
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) involves performing tests on samples such as blood, urine, or tissue outside the human body to detect diseases or monitor health conditions with high accuracy and reliability. Point-of-care testing (POCT) enables rapid diagnostic results near the patient, facilitating immediate clinical decision-making without the need for centralized laboratory facilities. Both IVD and POCT are integral to modern healthcare, offering complementary benefits in diagnostics, with IVD providing comprehensive laboratory analysis and POCT delivering swift, on-site results.
Defining In Vitro Diagnostics: Technologies and Applications
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) encompass a broad range of laboratory technologies designed to analyze samples such as blood, urine, or tissue outside the human body to detect diseases, monitor health conditions, and guide treatment decisions. These technologies include immunoassays, molecular diagnostics, and clinical chemistry, employed in centralized labs for high-throughput, precise analysis. Unlike point-of-care testing, which provides rapid results at or near the patient site, IVD relies on sophisticated instruments and standardized protocols to ensure accuracy and comprehensive data for clinical diagnostics.
Understanding Point-of-Care Testing: Scope and Evolution
Point-of-care testing (POCT) delivers rapid diagnostic results at or near the patient site, enabling immediate clinical decisions that improve patient outcomes. Unlike traditional in vitro diagnostics (IVD), which require centralized laboratory settings and longer turnaround times, POCT utilizes portable devices and simple procedures to expand accessibility in diverse environments. The evolution of POCT reflects advances in microfluidics, biosensors, and connectivity, broadening its scope from glucose monitoring to multiplex pathogen detection across healthcare and remote settings.
Key Differences Between In Vitro Diagnostics and Point-of-Care Testing
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) primarily involve laboratory-based testing of biological samples using sophisticated instruments, providing high accuracy and comprehensive data analysis. Point-of-care testing (POCT) delivers rapid diagnostic results at or near the patient site, emphasizing speed and convenience over extensive data detail. The key differences lie in the testing environment, turnaround time, and complexity of equipment used, with IVD favoring centralized labs and POCT supporting decentralized, immediate clinical decision-making.
Workflow and Turnaround Time Comparison
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) typically involve complex laboratory workflows with centralized processing, which can extend turnaround times to several hours or days depending on sample transportation and batching. Point-of-care testing (POCT) streamlines the workflow by enabling immediate sample analysis at or near the patient site, significantly reducing turnaround times to minutes. This rapid result delivery in POCT facilitates quicker clinical decision-making and improves patient management compared to the more time-intensive IVD processes.
Analytical Performance: Sensitivity and Specificity
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) typically offer higher sensitivity and specificity due to controlled laboratory conditions and advanced instrumentation, enabling precise detection of low analyte concentrations. Point-of-care testing (POCT) provides rapid results near the patient but may exhibit slightly lower analytical performance, with sensitivity and specificity influenced by simplified assay formats and environmental variables. Balancing speed and accuracy is crucial, as enhanced sensitivity reduces false negatives while high specificity minimizes false positives in both diagnostic approaches.
Impact on Clinical Decision-Making and Patient Outcomes
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) provide comprehensive laboratory-based analysis with high accuracy, supporting detailed clinical decision-making through extensive data. Point-of-care testing (POCT) delivers rapid results at or near the patient site, enabling immediate clinical interventions and enhancing patient outcomes by reducing diagnostic delays. Integration of POCT with IVD data optimizes treatment strategies, improves workflow efficiency, and facilitates personalized medicine in various healthcare settings.
Integration with Digital Health and Data Management
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) systems offer comprehensive data integration capabilities through centralized laboratory information management systems, facilitating robust data analytics and long-term patient monitoring. Point-of-care testing (POCT) devices emphasize real-time data capture and immediate digital health integration via cloud-based platforms and mobile applications, enabling rapid clinical decision-making at the patient's side. Both approaches leverage interoperability standards like HL7 and FHIR to ensure seamless data exchange and enhance overall healthcare data management efficiency.
Regulatory and Quality Assurance Considerations
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) require stringent regulatory approval from agencies such as the FDA or EMA, emphasizing comprehensive validation and quality management system compliance under ISO 13485 standards. Point-of-care testing (POCT) devices face unique regulatory challenges due to their decentralized usage, necessitating robust quality assurance protocols to ensure accuracy and operator competency outside traditional laboratory settings. Both IVD and POCT must adhere to post-market surveillance and risk management procedures in accordance with ISO 14971 to maintain safety and reliability throughout their lifecycle.
Future Trends and Innovations in Diagnostic Testing
Future trends in diagnostic testing emphasize the integration of advanced biosensors and artificial intelligence to enhance the accuracy and speed of both in vitro diagnostics (IVD) and point-of-care testing (POCT). Innovations such as microfluidics and wearable diagnostic devices are driving the shift towards more accessible, real-time health monitoring outside traditional laboratory settings. The convergence of digital health technologies with diagnostics is poised to revolutionize personalized medicine through improved data analytics and connectivity.
Microfluidics
Microfluidics enhances both in vitro diagnostics and point-of-care testing by enabling rapid, accurate analysis of small sample volumes, accelerating disease detection and monitoring.
Biosensors
Biosensors enhance point-of-care testing by providing rapid, accurate, and portable in vitro diagnostics for real-time patient monitoring and immediate clinical decision-making.
Lab-on-a-chip
Lab-on-a-chip technology revolutionizes in vitro diagnostics and point-of-care testing by integrating multiple laboratory functions on a single microfluidic chip, enabling rapid, accurate, and portable analysis at the patient's bedside.
Immunoassays
Immunoassays in in vitro diagnostics offer highly sensitive laboratory-based analysis, while point-of-care testing emphasizes rapid, bedside immunoassay results for immediate clinical decision-making.
Analytical sensitivity
In vitro diagnostics generally offer higher analytical sensitivity than point-of-care testing, enabling more precise detection of low-abundance biomarkers in clinical samples.
Lateral flow assay
Lateral flow assays in point-of-care testing provide rapid, user-friendly diagnostic results compared to the laboratory-based, highly sensitive, but time-consuming in vitro diagnostics.
Sample-to-answer platforms
Sample-to-answer platforms in vitro diagnostics offer centralized, high-throughput testing with extensive biomarker panels, while point-of-care testing delivers rapid, user-friendly results at or near the patient location, optimizing diagnostic turnaround time and clinical decision-making.
Clinical decision support
Point-of-care testing enables rapid clinical decision support by providing immediate diagnostic results at the bedside, whereas in vitro diagnostics typically require centralized laboratory analysis, potentially delaying treatment decisions.
Turnaround time (TAT)
Point-of-care testing delivers significantly faster turnaround times than traditional in vitro diagnostics by providing immediate results at the bedside or clinic without the need for centralized laboratory processing.
Multiplexing
In vitro diagnostics offer high-throughput multiplexing capabilities for simultaneous analysis of multiple biomarkers, whereas point-of-care testing provides rapid, on-site multiplexed assays with simplified workflows suitable for immediate clinical decision-making.
in vitro diagnostics vs point-of-care testing Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com