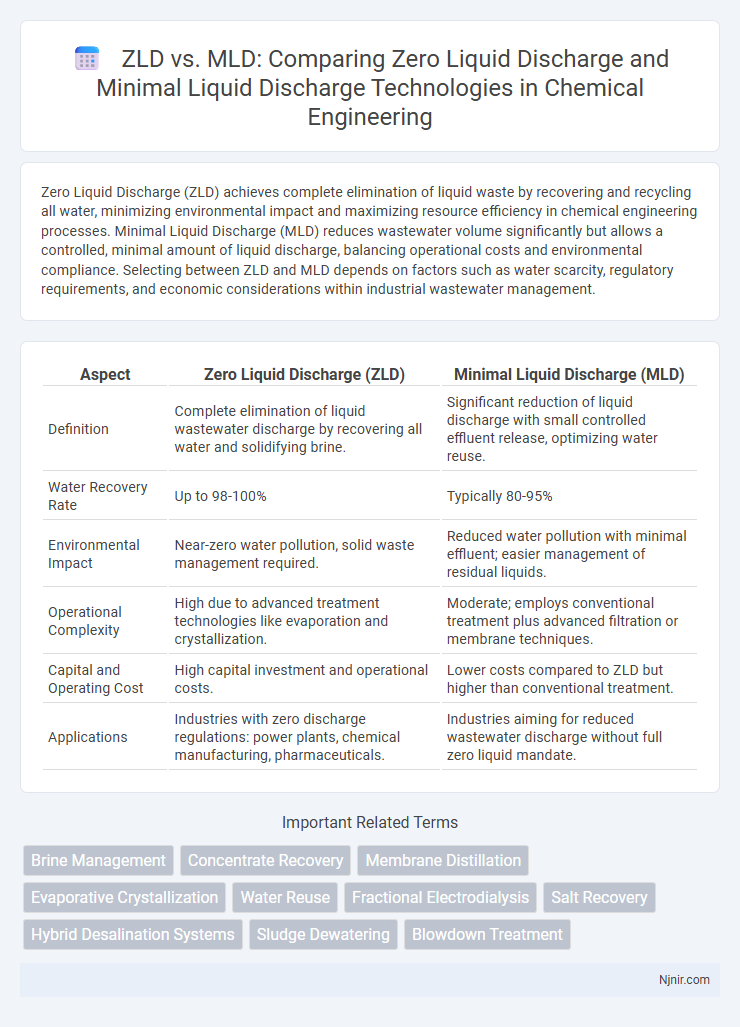
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) achieves complete elimination of liquid waste by recovering and recycling all water, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource efficiency in chemical engineering processes. Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) reduces wastewater volume significantly but allows a controlled, minimal amount of liquid discharge, balancing operational costs and environmental compliance. Selecting between ZLD and MLD depends on factors such as water scarcity, regulatory requirements, and economic considerations within industrial wastewater management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) | Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete elimination of liquid wastewater discharge by recovering all water and solidifying brine. | Significant reduction of liquid discharge with small controlled effluent release, optimizing water reuse. |
| Water Recovery Rate | Up to 98-100% | Typically 80-95% |
| Environmental Impact | Near-zero water pollution, solid waste management required. | Reduced water pollution with minimal effluent; easier management of residual liquids. |
| Operational Complexity | High due to advanced treatment technologies like evaporation and crystallization. | Moderate; employs conventional treatment plus advanced filtration or membrane techniques. |
| Capital and Operating Cost | High capital investment and operational costs. | Lower costs compared to ZLD but higher than conventional treatment. |
| Applications | Industries with zero discharge regulations: power plants, chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals. | Industries aiming for reduced wastewater discharge without full zero liquid mandate. |
Introduction to ZLD and MLD in Chemical Engineering
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) are advanced wastewater management strategies in chemical engineering aimed at minimizing environmental pollution and maximizing water recovery. ZLD systems achieve near-total elimination of liquid waste by employing technologies such as evaporation, crystallization, and membrane filtration to recover all water and leave behind solid residues. MLD focuses on significantly reducing liquid discharge by integrating conventional treatment with partial water reuse and brine management, offering a more cost-effective and adaptable approach for industrial effluent treatment.
Core Principles of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) operates on the core principle of recovering and recycling all wastewater to eliminate liquid waste discharge entirely, ensuring zero environmental contamination. This process involves advanced technologies such as membrane filtration, evaporation, and crystallization to extract maximum water and solid salts from industrial effluents. ZLD systems are essential in industries with stringent water reuse requirements and limited water resources, promoting sustainability by achieving complete water conservation and waste minimization.
Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD): Key Concepts
Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) aims to significantly reduce wastewater by maximizing water recovery and recycling within industrial processes, often targeting recovery rates above 95%. MLD systems integrate advanced treatment technologies such as membrane filtration, evaporation, and crystallization to minimize effluent volumes while managing concentrate disposal effectively. This approach offers a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD), balancing environmental compliance with operational feasibility and resource conservation.
Comparative Technologies Used in ZLD and MLD
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) employs advanced technologies such as multiple-effect evaporators, crystallizers, and membrane filtration to completely eliminate liquid waste by recovering nearly all water and producing solid residues. Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) utilizes membrane processes like ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, and occasionally forward osmosis to significantly reduce wastewater but allows a controlled volume of liquid effluent discharge. ZLD focuses on achieving zero effluent through energy-intensive thermal methods, while MLD balances cost and sustainability by integrating energy-efficient membrane technologies with partial evaporation.
Efficiency and Water Recovery Rates
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems achieve near 100% water recovery by completely eliminating liquid waste through advanced treatment and evaporation technologies, maximizing resource efficiency and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) focuses on reducing wastewater volume significantly but allows for small amounts of liquid discharge, often resulting in water recovery rates of 70-90%, balancing operational costs and environmental impact. Both methods enhance sustainable water management, with ZLD preferred in regions with zero wastewater discharge policies and MLD suitable for less restrictive environments prioritizing cost-efficiency.
Energy and Operational Costs: ZLD vs MLD
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems typically require higher energy input due to extensive evaporation and crystallization processes, resulting in significantly increased operational costs compared to Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) systems. MLD technologies reduce energy consumption by allowing a controlled volume of liquid discharge, minimizing the need for intensive treatments and associated expenses. Consequently, MLD offers a cost-effective balance between environmental compliance and operational efficiency, while ZLD provides maximum waste minimization at a premium energy and cost investment.
Environmental Impact and Regulatory Compliance
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems eliminate all wastewater discharge by recovering and recycling all water, significantly reducing environmental contamination and meeting stringent regulatory standards for wastewater management. Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) systems reduce wastewater volume to a small extent, allowing limited discharge under regulated conditions, which may still pose some environmental risks but generally complies with moderate regulatory requirements. ZLD offers superior environmental protection by preventing pollutant release, making it ideal for industries facing strict compliance mandates, whereas MLD provides a balance between treatment cost and regulatory adherence in less sensitive areas.
Challenges in Implementation and Scale-Up
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) face significant challenges in implementation and scale-up, including high capital and operational costs, complex treatment technologies, and energy-intensive processes. ZLD systems require advanced membrane filtration, evaporation, and crystallization units that are difficult to design and operate efficiently at large scales. MLD presents fewer technical hurdles but struggles with achieving consistent performance and regulatory compliance while balancing water recovery and brine disposal constraints.
Industrial Applications and Case Studies
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) technologies play crucial roles in industrial wastewater management, particularly in sectors like power plants, chemical manufacturing, and textiles. ZLD systems eliminate wastewater discharge by recovering nearly all water through advanced treatment methods such as reverse osmosis and evaporation, enabling complete reuse and minimizing environmental impact, as demonstrated in power plant case studies that achieve water recycling rates above 95%. MLD strategies reduce effluent volumes substantially while allowing controlled discharge of minimal concentrated brine, offering cost-effective compliance solutions in industries with moderate water reuse demands, exemplified by textile facilities optimizing water usage with 70-80% recycling efficiency.
Future Trends in Liquid Discharge Management
Future trends in liquid discharge management emphasize the integration of advanced membrane technologies and AI-driven monitoring systems to enhance Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) efficiency. Innovations in ZLD focus on achieving near-complete water reuse with minimal environmental impact, driven by tightening regulatory standards and water scarcity challenges. MLD systems are evolving to balance cost-effectiveness with sustainability, using hybrid treatment processes to reduce liquid waste volume while optimizing resource recovery.
Brine Management
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) achieves complete brine management by recovering all water and converting brine into solid waste, whereas Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) reduces brine volume significantly but allows controlled liquid discharge to minimize environmental impact.
Concentrate Recovery
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems achieve nearly 100% concentrate recovery by completely eliminating liquid waste through advanced evaporation and crystallization processes, whereas Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) systems recover a significant portion of concentrate but still produce some liquid effluent, balancing operational cost with partial concentrate reuse.
Membrane Distillation
Membrane Distillation technology enhances Zero Liquid Discharge systems by efficiently recovering pure water from brine, reducing waste volume compared to Minimal Liquid Discharge processes.
Evaporative Crystallization
Evaporative crystallization in Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems completely eliminates liquid waste by converting all brine into solid salts, whereas Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) reduces waste volume but still produces some concentrated liquid effluent.
Water Reuse
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) achieves 100% water reuse by eliminating liquid waste entirely through advanced treatment and evaporation, whereas Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) reduces wastewater volume significantly but still discharges a minimal amount of treated liquid, enabling high yet partial water reuse.
Fractional Electrodialysis
Fractional Electrodialysis enhances Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems by selectively separating and recovering valuable salts and water, achieving higher resource efficiency compared to Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) processes.
Salt Recovery
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems achieve nearly 100% salt recovery by completely eliminating liquid waste, while Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) systems prioritize reducing liquid waste volume and recovering a significant but lower percentage of salts to optimize operational costs.
Hybrid Desalination Systems
Hybrid desalination systems combining Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) and Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) technologies optimize water recovery and minimize brine volume by integrating advanced membrane filtration and thermal processes for sustainable, cost-effective wastewater management.
Sludge Dewatering
ZLD systems achieve higher sludge dewatering efficiency than MLD by recovering nearly 100% water from wastewater, resulting in minimal liquid discharge and more concentrated sludge solids.
Blowdown Treatment
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) achieves complete blowdown treatment by recycling and evaporating all wastewater to eliminate liquid effluent, whereas Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) significantly reduces blowdown volume but allows limited discharge after advanced treatment.
ZLD vs MLD (Zero Liquid Discharge vs Minimal Liquid Discharge) Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com