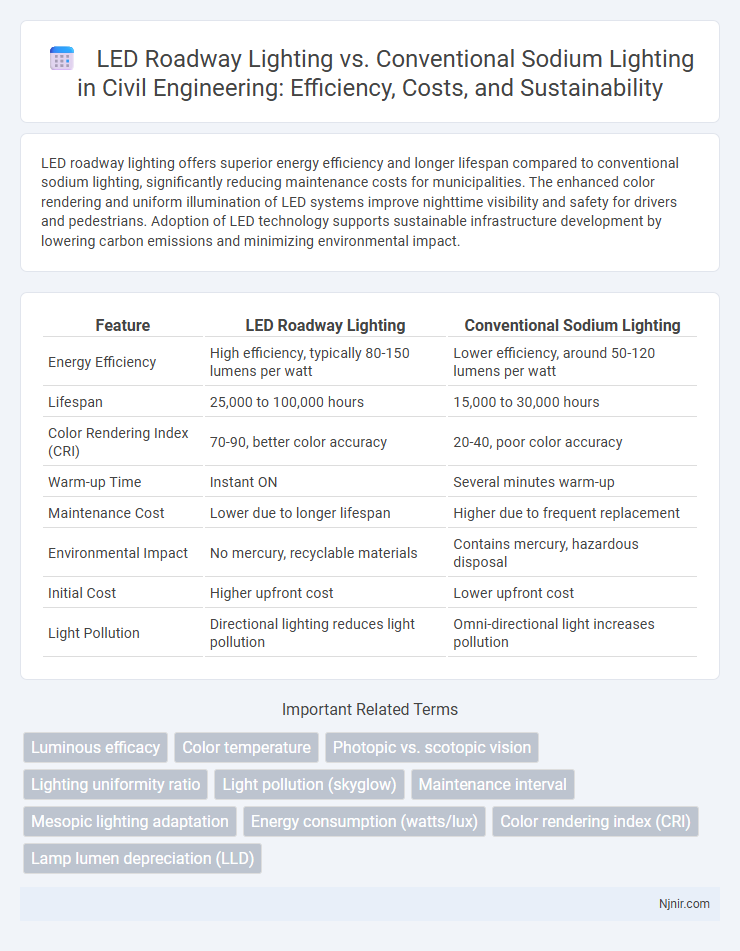
LED roadway lighting offers superior energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to conventional sodium lighting, significantly reducing maintenance costs for municipalities. The enhanced color rendering and uniform illumination of LED systems improve nighttime visibility and safety for drivers and pedestrians. Adoption of LED technology supports sustainable infrastructure development by lowering carbon emissions and minimizing environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | LED Roadway Lighting | Conventional Sodium Lighting |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency, typically 80-150 lumens per watt | Lower efficiency, around 50-120 lumens per watt |
| Lifespan | 25,000 to 100,000 hours | 15,000 to 30,000 hours |
| Color Rendering Index (CRI) | 70-90, better color accuracy | 20-40, poor color accuracy |
| Warm-up Time | Instant ON | Several minutes warm-up |
| Maintenance Cost | Lower due to longer lifespan | Higher due to frequent replacement |
| Environmental Impact | No mercury, recyclable materials | Contains mercury, hazardous disposal |
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Light Pollution | Directional lighting reduces light pollution | Omni-directional light increases pollution |
Introduction to Roadway Lighting Technologies
LED roadway lighting offers superior energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to conventional sodium lighting, reducing maintenance costs and environmental impact. High-pressure sodium (HPS) lamps, traditionally used for roadway illumination, produce a warm yellow glow with lower color rendering index (CRI), which can affect visibility and safety. Advances in LED technology provide enhanced uniformity, better color rendering, and adaptive control capabilities, making LED lighting the preferred choice for modern urban and highway roadways.
Overview of LED Roadway Lighting
LED roadway lighting provides superior energy efficiency, consuming up to 50-70% less power than conventional sodium lighting while delivering brighter, more uniform illumination. The longer lifespan of LEDs, often exceeding 50,000 hours, significantly reduces maintenance costs compared to the 15,000 to 24,000 hours typical of high-pressure sodium lamps. LED technology also offers enhanced color rendering index (CRI), improving visibility and safety by producing clearer, more natural light for drivers and pedestrians.
Overview of Conventional Sodium Lighting
Conventional sodium lighting, primarily high-pressure sodium (HPS) lamps, has been widely used in roadway lighting due to its high luminous efficacy and long operational life, typically ranging from 24,000 to 30,000 hours. These lamps emit a characteristic yellow-orange light with a color rendering index (CRI) around 22-40, which can reduce color perception and visibility at night. Despite being energy-efficient compared to older technologies, conventional sodium lighting generally consumes more power and requires more maintenance than modern LED alternatives.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
LED roadway lighting consumes up to 50-70% less energy compared to conventional sodium lighting due to higher luminous efficacy, typically ranging between 80-130 lumens per watt versus 60-100 lumens per watt for sodium lamps. LEDs offer directional light distribution, reducing wasted light and improving uniformity, which contributes significantly to overall energy savings. Moreover, LED systems have a longer operational lifespan of around 50,000 hours, resulting in lower maintenance costs and further enhancing energy efficiency over time.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
LED roadway lighting offers a significantly longer lifespan, typically exceeding 50,000 hours, compared to conventional sodium lighting which averages around 24,000 hours. The reduced failure rate of LED fixtures minimizes maintenance frequency, leading to lower labor and replacement costs over time. Infrastructures using LED technology benefit from decreased downtime and improved reliability, enhancing overall operational efficiency in public lighting systems.
Light Quality and Visibility
LED roadway lighting offers superior light quality with higher color rendering index (CRI) values typically above 70, enhancing visibility and color discrimination compared to conventional sodium lighting, which has CRI values around 20. The whiter, more uniform light spectrum of LEDs reduces glare and improves contrast, allowing drivers and pedestrians to detect hazards and objects more effectively. Sodium lamps emit a yellow-orange hue with limited spectral output, resulting in poorer visibility and slower reaction times under nighttime driving conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
LED roadway lighting significantly reduces energy consumption by up to 50-70% compared to conventional sodium lighting, leading to lower carbon emissions and decreased dependency on fossil fuels. Its longer lifespan minimizes waste generation and reduces the frequency of replacements, contributing to sustainable urban infrastructure. Furthermore, LEDs eliminate hazardous substances like mercury found in sodium lamps, enhancing environmental safety and promoting eco-friendly disposal practices.
Installation and Retrofit Considerations
LED roadway lighting offers significant advantages in installation and retrofit over conventional sodium lighting, primarily due to its modular design and compatibility with various mounting heights and pole types. Retrofit projects benefit from LED fixtures' lower weight and more compact size, reducing labor costs and infrastructure modifications compared to bulky sodium lamps. Furthermore, LED systems integrate easily with smart controls and adaptive lighting technologies, enhancing operational flexibility and energy efficiency during and after installation.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-term Savings
LED roadway lighting requires a higher initial investment compared to conventional sodium lighting due to the advanced technology and components involved. However, LED systems offer significant long-term savings through reduced energy consumption, lower maintenance costs, and longer lifespan, often resulting in up to 50-70% energy cost reduction. The total cost of ownership over a 10-15 year period favors LED technology, making it a more economically viable option despite the upfront expense.
Case Studies and Real-world Applications
Case studies highlight LED roadway lighting's superior energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to conventional sodium lighting, reducing operational costs by up to 50% in urban environments. Real-world applications report improved visibility and safety with LED technology due to better color rendering and uniform light distribution. Municipalities adopting LED systems experience reduced maintenance frequency and lower carbon emissions, contributing to sustainable urban infrastructure.
Luminous efficacy
LED roadway lighting offers significantly higher luminous efficacy, typically between 100-160 lumens per watt, compared to conventional sodium lighting which ranges from 60-120 lumens per watt, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Color temperature
LED roadway lighting offers adjustable color temperatures typically ranging from 3000K to 6000K for improved visibility and color rendering, while conventional sodium lighting emits a fixed warm yellow-orange glow around 2000K to 2200K with poor color accuracy.
Photopic vs. scotopic vision
LED roadway lighting enhances scotopic vision by providing higher blue-rich light levels that improve nighttime visibility compared to conventional sodium lighting, which primarily stimulates photopic vision with yellow-orange hues.
Lighting uniformity ratio
LED roadway lighting provides a superior lighting uniformity ratio, typically achieving values below 3:1, compared to conventional sodium lighting's higher ratios often exceeding 5:1, resulting in more consistent and safer illumination on roadways.
Light pollution (skyglow)
LED roadway lighting reduces skyglow significantly compared to conventional sodium lighting due to its targeted beam control and lower blue light emissions, minimizing light pollution in urban environments.
Maintenance interval
LED roadway lighting offers significantly longer maintenance intervals, often exceeding 50,000 hours, compared to conventional sodium lighting which typically requires maintenance every 15,000 to 24,000 hours.
Mesopic lighting adaptation
LED roadway lighting enhances mesopic vision adaptation by providing higher spectral efficiency and improved color rendering compared to conventional sodium lighting, resulting in better visibility and safety during low-light conditions.
Energy consumption (watts/lux)
LED roadway lighting consumes approximately 30-50% less watts per lux compared to conventional sodium lighting, significantly reducing energy consumption while maintaining equivalent luminance levels.
Color rendering index (CRI)
LED roadway lighting offers a higher Color Rendering Index (CRI) of typically 70-90 compared to conventional sodium lighting's CRI of around 20-25, resulting in improved color accuracy and visibility for drivers.
Lamp lumen depreciation (LLD)
LED roadway lighting exhibits significantly lower lamp lumen depreciation (LLD), maintaining up to 70-85% lumen output over 50,000 hours compared to conventional sodium lighting, which typically degrades to 60-70% lumen output within 24,000 hours.
LED roadway lighting vs Conventional sodium lighting Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com