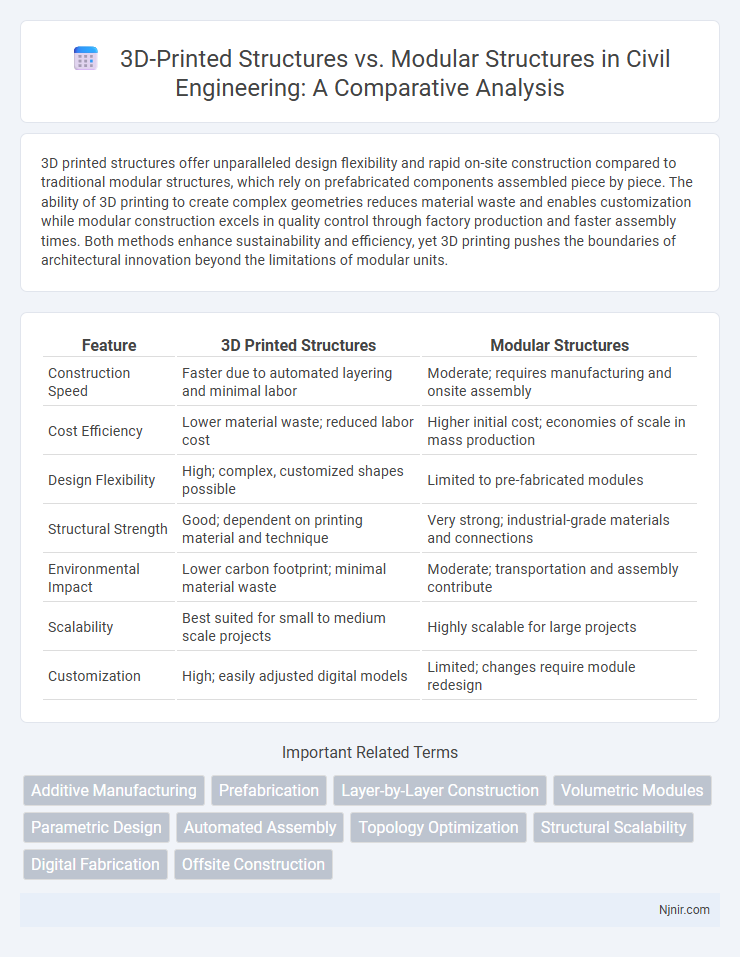
3D printed structures offer unparalleled design flexibility and rapid on-site construction compared to traditional modular structures, which rely on prefabricated components assembled piece by piece. The ability of 3D printing to create complex geometries reduces material waste and enables customization while modular construction excels in quality control through factory production and faster assembly times. Both methods enhance sustainability and efficiency, yet 3D printing pushes the boundaries of architectural innovation beyond the limitations of modular units.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printed Structures | Modular Structures |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Speed | Faster due to automated layering and minimal labor | Moderate; requires manufacturing and onsite assembly |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower material waste; reduced labor cost | Higher initial cost; economies of scale in mass production |
| Design Flexibility | High; complex, customized shapes possible | Limited to pre-fabricated modules |
| Structural Strength | Good; dependent on printing material and technique | Very strong; industrial-grade materials and connections |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint; minimal material waste | Moderate; transportation and assembly contribute |
| Scalability | Best suited for small to medium scale projects | Highly scalable for large projects |
| Customization | High; easily adjusted digital models | Limited; changes require module redesign |
Introduction to 3D Printed and Modular Structures
3D printed structures utilize additive manufacturing technology, building components layer by layer from materials like concrete, polymers, or metals, enabling complex geometries and rapid construction. Modular structures consist of prefabricated units manufactured off-site, which are then transported and assembled on-site, offering scalability and reduced construction time. Both methods revolutionize construction processes by enhancing efficiency, minimizing waste, and allowing customization.
Evolution of Construction Techniques
3D printed structures have revolutionized construction by enabling rapid fabrication of complex geometries using additive manufacturing technology, reducing material waste and labor costs compared to traditional methods. Modular structures, developed through prefabrication and assembly of standardized components, offer enhanced quality control and accelerated project timelines by allowing parallel off-site construction. The evolution from modular to 3D printed techniques highlights a shift towards automation, sustainability, and greater design flexibility in modern building practices.
Materials Used in 3D Printing vs Modular Construction
3D printed structures utilize advanced materials such as concrete composites, thermoplastics, and bio-based polymers that allow for precise layering and customization in construction. Modular construction primarily relies on traditional materials like steel, concrete panels, and wood frames prefabricated offsite for quick assembly. The material versatility in 3D printing enables complex shapes and waste reduction, while modular construction benefits from the strength and reliability of conventional building components.
Speed of Construction: A Comparative Analysis
3D printed structures significantly reduce construction time by enabling rapid, automated layer-by-layer fabrication directly on-site, often completing projects in days instead of weeks or months required by modular structures. Modular construction involves prefabricating building components off-site and assembling them on-site, which speeds up the process compared to traditional methods but still faces logistical delays in transportation and on-site integration. Overall, 3D printing offers superior speed efficiency by eliminating the need for large-scale assembly and minimizing dependency on external factors.
Structural Integrity and Durability
3D printed structures offer enhanced customization and complex geometries that improve stress distribution, resulting in increased structural integrity compared to traditional modular structures. Materials used in 3D printing, such as advanced polymers and concrete composites, exhibit superior durability and resistance to environmental factors like corrosion and weathering. Modular structures rely on pre-fabricated components assembled on-site, which can introduce weak points at joints, potentially affecting long-term durability and structural performance under dynamic loads.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
3D printed structures significantly reduce material waste by using precise additive manufacturing techniques, lowering the carbon footprint compared to traditional modular constructions that often involve off-site fabrication and transportation emissions. These structures enable the use of sustainable materials such as recycled plastics and bio-based composites, enhancing resource efficiency. Modular structures offer the advantage of reusability and adaptability, but their assembly processes can generate considerable waste and energy consumption, making 3D printing a more environmentally friendly alternative in sustainable building practices.
Cost Efficiency and Budget Considerations
3D printed structures significantly reduce labor costs and material waste through automated precision, leading to lower overall budget requirements compared to traditional modular construction. Modular structures benefit from economies of scale and shorter on-site assembly times, which can decrease indirect costs and expedite project timelines. Cost efficiency in 3D printing is rapidly improving with advancements in technology and material innovation, making it increasingly competitive against established modular construction methods for various budget-conscious projects.
Design Flexibility and Architectural Innovation
3D printed structures offer unparalleled design flexibility by enabling complex geometries and customized components that traditional modular structures cannot easily achieve. This technology allows architects to push the boundaries of innovation with organic shapes, intricate detail, and rapid prototyping, redefining structural aesthetics and functionality. In contrast, modular structures prioritize efficiency and scalability but often face limitations in design complexity due to standardized, prefabricated units.
Applications in Modern Civil Engineering Projects
3D printed structures in modern civil engineering enable rapid construction of complex, customized components with reduced material waste and labor costs, ideal for innovative housing, bridges, and infrastructure projects. Modular structures facilitate efficient assembly through prefabricated units, significantly accelerating project timelines and improving quality control in residential buildings, commercial complexes, and healthcare facilities. Both technologies enhance sustainability and design flexibility, with 3D printing excelling in intricate geometries and modular construction excelling in scalability and repeatability.
Future Trends in 3D Printed and Modular Structures
Future trends in 3D printed structures emphasize advanced materials like carbon fiber composites and bio-based polymers, enabling lightweight, durable, and sustainable construction. Modular structures are evolving with smart technology integration, allowing for rapid assembly, customization, and efficient resource use. Innovations in 3D printing and modular design collectively drive the construction industry's shift towards eco-friendly, cost-effective, and resilient building solutions.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing enables 3D printed structures with complex geometries and material efficiency, surpassing traditional modular structures in customization and speed.
Prefabrication
3D printed structures reduce construction time and waste by fabricating complex components onsite, while modular structures rely on offsite prefabrication of standardized units for faster assembly and consistent quality control.
Layer-by-Layer Construction
3D printed structures utilize precision layer-by-layer construction for complex geometric designs, while modular structures rely on assembling pre-fabricated units, impacting customization and construction speed.
Volumetric Modules
Volumetric modules in modular structures offer faster construction and consistent quality compared to 3D printed structures, which excel in design flexibility and complex geometries.
Parametric Design
Parametric design enhances 3D printed structures by enabling precise, customizable geometries that optimize material efficiency and structural performance compared to traditional modular structures.
Automated Assembly
Automated assembly in 3D printed structures offers precise layer-by-layer fabrication reducing labor costs, whereas modular structures rely on mechanized joining of prefabricated units enabling faster on-site construction with standardized components.
Topology Optimization
Topology optimization enables 3D printed structures to achieve superior material efficiency and complex geometries compared to modular structures, enhancing strength-to-weight ratios and customization possibilities.
Structural Scalability
3D printed structures offer greater structural scalability by enabling complex, customized designs with reduced material waste and faster production compared to traditional modular structures.
Digital Fabrication
Digital fabrication in 3D printed structures enables highly customizable, complex geometries with reduced material waste compared to the standardized, prefabricated components typical of modular structures.
Offsite Construction
3D printed structures revolutionize offsite construction by enabling rapid, customizable builds with reduced material waste compared to the faster assembly and standardized quality control of modular structures.
3D Printed Structures vs Modular Structures Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com