Modular construction involves assembling entire building modules off-site, allowing for faster on-site installation and enhanced quality control compared to traditional methods. Prefabricated construction typically refers to manufacturing individual building components, such as walls or panels, which are transported and assembled on-site, offering flexibility in design but requiring longer assembly times. Both approaches improve efficiency and reduce waste, though modular construction delivers greater speed and integration for complex civil engineering projects.
Table of Comparison
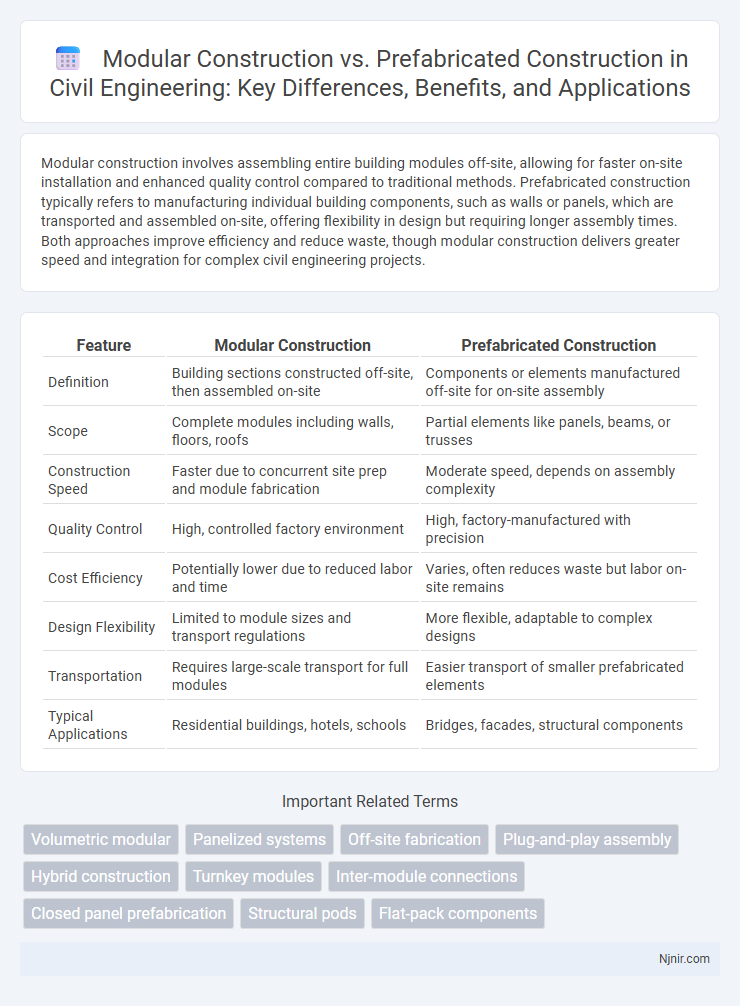
| Feature | Modular Construction | Prefabricated Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building sections constructed off-site, then assembled on-site | Components or elements manufactured off-site for on-site assembly |
| Scope | Complete modules including walls, floors, roofs | Partial elements like panels, beams, or trusses |
| Construction Speed | Faster due to concurrent site prep and module fabrication | Moderate speed, depends on assembly complexity |
| Quality Control | High, controlled factory environment | High, factory-manufactured with precision |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially lower due to reduced labor and time | Varies, often reduces waste but labor on-site remains |
| Design Flexibility | Limited to module sizes and transport regulations | More flexible, adaptable to complex designs |
| Transportation | Requires large-scale transport for full modules | Easier transport of smaller prefabricated elements |
| Typical Applications | Residential buildings, hotels, schools | Bridges, facades, structural components |
Introduction to Modular and Prefabricated Construction
Modular construction involves assembling sections of a building, called modules, off-site in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the construction site for installation. Prefabricated construction encompasses a broader range of factory-built components, including panels, trusses, and modules, that are produced off-site and assembled on-site. Both methods enhance construction efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality control compared to traditional building techniques.
Defining Modular Construction
Modular construction involves assembling building sections, or modules, manufactured off-site under controlled factory conditions before being transported and installed on-site. This method enhances quality control, reduces construction time, and minimizes waste compared to traditional building techniques. Prefabricated construction broadly refers to any building components made in factories, including modular units, panelized systems, and precast concrete elements, but modular construction is distinct for its complete, volumetric modules.
Understanding Prefabricated Construction
Prefabricated construction involves manufacturing building components in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the site for assembly, ensuring higher precision and reduced construction time. This method enhances quality control, minimizes waste, and improves overall project efficiency by streamlining the production process. Prefabricated construction is ideal for repetitive designs and large-scale developments, offering cost-effective scalability compared to traditional building techniques.
Key Differences Between Modular and Prefabricated Methods
Modular construction involves assembling entire building sections or modules off-site, which are then transported and integrated on-site, ensuring faster completion and higher quality control compared to traditional methods. Prefabricated construction refers to manufacturing individual building components such as panels, trusses, or frames off-site for later assembly, offering flexibility but often requiring more on-site labor. Key differences include the scale of off-site fabrication, with modular focusing on complete volumetric units and prefabricated emphasizing discrete parts, impacting project timelines, cost efficiency, and structural precision.
Advantages of Modular Construction in Civil Engineering
Modular construction offers significant advantages in civil engineering by enabling faster project completion through simultaneous off-site fabrication and on-site preparation, reducing overall construction timelines by up to 50%. It enhances quality control with factory settings that minimize errors and defects, ensuring consistent structural integrity and durability. Cost efficiency is improved by reducing labor expenses and material waste, while promoting sustainability through better resource management and decreased environmental impact.
Benefits of Prefabricated Construction Techniques
Prefabricated construction techniques offer significant benefits including faster project completion due to off-site fabrication, which reduces on-site labor and weather-related delays. This method enhances quality control as components are produced in a controlled factory environment, ensuring consistent materials and structural precision. Cost savings arise from minimized waste, efficient material use, and streamlined logistics, making prefabricated construction a sustainable and economical choice compared to traditional modular building approaches.
Cost Comparison: Modular vs. Prefabricated Building
Modular construction typically offers cost advantages over prefabricated building due to streamlined factory production and reduced on-site labor expenses, often lowering overall project costs by 15-20%. Prefabricated construction involves manufacturing building components off-site but may require more complex on-site assembly, potentially increasing labor costs and extending timelines. Comparing both, modular construction achieves greater cost efficiency through standardized processes and economies of scale, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Modular construction reduces waste by manufacturing components in controlled factory settings, achieving up to 90% waste diversion compared to traditional methods. Prefabricated construction often utilizes sustainable materials and enables precise resource management, lowering overall carbon emissions by 40%. Both methods contribute to energy efficiency during assembly, minimizing site disturbance and promoting greener building practices.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Modular construction faces challenges such as transportation restrictions due to module size, limited design flexibility, and the need for precise coordination between factory production and on-site assembly. Prefabricated construction struggles with issues like inconsistent quality control across different manufacturing sites, higher initial setup costs, and difficulties integrating customized architectural features. Both methods require advanced logistics management and upfront planning to mitigate delays and cost overruns during project execution.
Future Trends in Modular and Prefabricated Construction
Future trends in modular and prefabricated construction emphasize increased integration of smart technologies and sustainable materials to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Advancements in digital design tools, such as BIM (Building Information Modeling), enable precise customization and faster assembly compared to traditional construction methods. Growing urbanization and labor shortages are driving demand for scalable, cost-effective modular solutions that streamline construction timelines and improve quality control.
Volumetric modular
Volumetric modular construction delivers fully finished, three-dimensional building modules off-site, offering faster assembly and higher quality control compared to traditional prefabricated flat-panel methods.
Panelized systems
Panelized systems in modular construction offer enhanced on-site assembly speed and customization compared to traditional prefabricated construction by delivering factory-built wall, floor, and roof panels that optimize material efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Off-site fabrication
Off-site fabrication in modular construction enables faster assembly and higher precision by producing fully finished building modules in controlled factory environments compared to traditional prefabricated construction components.
Plug-and-play assembly
Modular construction enables efficient plug-and-play assembly by delivering fully finished, pre-installed building sections that streamline on-site integration compared to traditional prefabricated construction methods.
Hybrid construction
Hybrid construction combines modular and prefabricated techniques to optimize building efficiency, reduce waste, and shorten project timelines by leveraging off-site assembly alongside on-site customization.
Turnkey modules
Turnkey modules in modular construction offer faster on-site assembly and higher customization compared to traditional prefabricated construction methods, reducing overall project timelines and costs.
Inter-module connections
Inter-module connections in modular construction prioritize permanent, robust integration with on-site assembly, whereas prefabricated construction often features detachable or semi-permanent connections for flexible installation and adaptation.
Closed panel prefabrication
Closed panel prefabrication in modular construction offers enhanced insulation, faster assembly, and improved quality control compared to traditional prefabricated methods.
Structural pods
Modular construction utilizes structural pods to streamline assembly and improve quality control, offering greater flexibility and faster on-site installation compared to traditional prefabricated construction methods.
Flat-pack components
Flat-pack components in modular construction offer enhanced on-site assembly efficiency and customization compared to traditional prefabricated construction methods.
modular construction vs prefabricated construction Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com