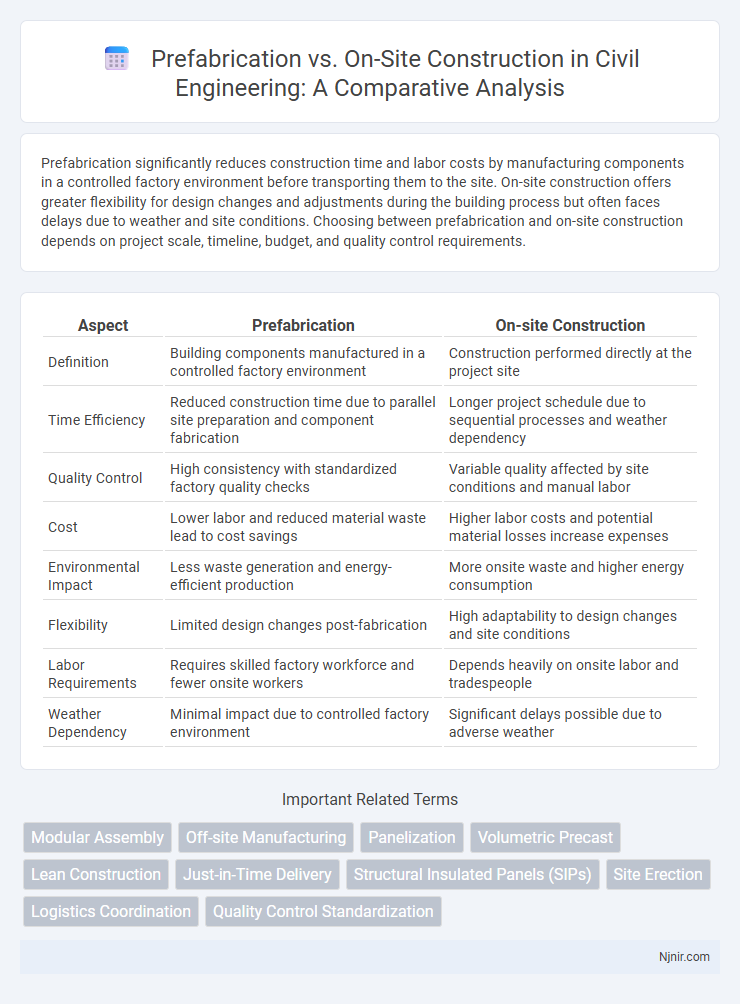
Prefabrication significantly reduces construction time and labor costs by manufacturing components in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the site. On-site construction offers greater flexibility for design changes and adjustments during the building process but often faces delays due to weather and site conditions. Choosing between prefabrication and on-site construction depends on project scale, timeline, budget, and quality control requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Prefabrication | On-site Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building components manufactured in a controlled factory environment | Construction performed directly at the project site |
| Time Efficiency | Reduced construction time due to parallel site preparation and component fabrication | Longer project schedule due to sequential processes and weather dependency |
| Quality Control | High consistency with standardized factory quality checks | Variable quality affected by site conditions and manual labor |
| Cost | Lower labor and reduced material waste lead to cost savings | Higher labor costs and potential material losses increase expenses |
| Environmental Impact | Less waste generation and energy-efficient production | More onsite waste and higher energy consumption |
| Flexibility | Limited design changes post-fabrication | High adaptability to design changes and site conditions |
| Labor Requirements | Requires skilled factory workforce and fewer onsite workers | Depends heavily on onsite labor and tradespeople |
| Weather Dependency | Minimal impact due to controlled factory environment | Significant delays possible due to adverse weather |
Introduction to Prefabrication and On-site Construction
Prefabrication involves manufacturing building components in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the construction site for assembly, enhancing precision and reducing waste. On-site construction refers to the traditional method where all building activities, from foundation laying to finishing, occur directly at the site, offering flexibility to adapt designs during the process. Comparing these approaches highlights differences in project timelines, cost efficiency, and quality control, influencing construction strategies worldwide.
Comparative Overview: Definitions and Core Principles
Prefabrication involves manufacturing building components in a controlled factory environment before transporting them to the construction site for assembly, enhancing precision and reducing waste. On-site construction entails erecting structures entirely at the location, offering greater flexibility but often leading to longer timelines and increased labor costs. Core principles of prefabrication emphasize standardization, modularity, and efficiency, whereas on-site construction prioritizes adaptability and customization to the specific site conditions.
Speed and Efficiency: Project Timelines
Prefabrication significantly reduces project timelines by enabling simultaneous off-site module construction and on-site preparation, accelerating overall completion. Factory-controlled environments minimize weather delays and improve quality control, contributing to fewer reworks and faster assembly on-site. On-site construction often faces disruptions from weather and logistical challenges, extending project durations compared to the streamlined workflow of prefabrication.
Cost Implications and Budget Control
Prefabrication significantly reduces labor costs and material waste by manufacturing components in controlled factory settings, enabling precise budget control compared to unpredictable on-site construction expenses. On-site construction often incurs higher costs due to variable weather conditions, delays, and unforeseen site challenges that can lead to budget overruns. Implementing prefabrication streamlines project timelines and fixed costs, providing stakeholders with better financial predictability and minimizing cost escalation risks.
Quality Assurance and Consistency
Prefabrication enhances quality assurance by manufacturing components in controlled factory environments, minimizing variability and reducing errors compared to on-site construction. Consistency is achieved through standardized processes and inspections that ensure uniformity across all prefabricated units, resulting in fewer defects and higher durability. On-site construction often faces challenges like weather conditions and variable craftsmanship, leading to inconsistent quality outcomes throughout the building process.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Prefabrication significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing material waste and optimizing resource use through controlled factory settings, leading to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional on-site construction. The process allows for efficient energy consumption and less noise pollution, enhancing sustainability in urban environments. On-site construction typically generates more waste and emissions due to variable work conditions and redundant material handling, posing greater challenges for sustainable building practices.
Labor Requirements and Site Safety
Prefabrication significantly reduces labor requirements on-site by shifting much of the construction process to controlled factory environments, where skilled workers utilize automated tools and assembly lines. This controlled setting enhances site safety by minimizing exposure to weather hazards, heavy equipment, and high-risk tasks typically encountered during on-site construction. In contrast, on-site construction demands a larger, more diverse labor force working under variable conditions, increasing the potential for accidents and safety challenges.
Flexibility in Design and Customization
Prefabrication offers limited flexibility in design and customization due to factory constraints and standardized components, making it less adaptable to unique architectural features. On-site construction provides greater design freedom, allowing adjustments and personalized elements to be incorporated throughout the building process. Architects and clients seeking bespoke designs often prefer on-site methods for enhanced customization and adaptability.
Case Studies: Real-world Applications
Case studies reveal prefabrication's effectiveness in reducing construction time by up to 50% compared to traditional on-site methods, as seen in projects like the Marriott International hotel in Las Vegas. Real-world applications demonstrate significant cost savings and improved quality control, evidenced by the Broad Group's rapid assembly of a 57-story skyscraper in China within 19 days. On-site construction remains preferred for highly customized projects, but prefabrication excels in modular housing and disaster relief structures, highlighting its growing role in modern construction strategies.
Future Trends in Civil Engineering Construction Methods
Prefabrication in civil engineering is rapidly evolving with advancements in modular design, automation, and sustainable materials, leading to faster project completion and reduced labor costs compared to traditional on-site construction. Emerging technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and 3D printing are further enhancing precision and customization in prefabricated components, promoting efficiency and waste reduction. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards hybrid construction methods that integrate prefabrication's speed and quality control with the flexibility of on-site assembly to meet complex project demands.
Modular Assembly
Modular assembly in prefabrication accelerates construction timelines, reduces labor costs, and enhances quality control compared to traditional on-site construction methods.
Off-site Manufacturing
Off-site manufacturing in prefabrication enhances construction efficiency by reducing on-site labor, minimizing weather delays, and improving quality control compared to traditional on-site construction.
Panelization
Panelization in prefabrication reduces construction time by up to 50% and improves quality control compared to traditional on-site construction methods.
Volumetric Precast
Volumetric precast construction accelerates project timelines by assembling fully finished 3D modules off-site with precise quality control, reducing on-site labor and minimizing material waste compared to traditional on-site construction.
Lean Construction
Prefabrication enhances Lean Construction by minimizing waste, reducing on-site labor, and accelerating project timelines compared to traditional on-site construction methods.
Just-in-Time Delivery
Just-in-time delivery in prefabrication minimizes material storage and delays compared to on-site construction by synchronizing component arrival with assembly schedules.
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs)
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) in prefabrication offer superior thermal performance, faster assembly, and reduced waste compared to traditional on-site construction methods.
Site Erection
Site erection in prefabrication significantly reduces construction time, enhances safety, and improves quality control compared to traditional on-site construction methods.
Logistics Coordination
Prefabrication streamlines logistics coordination by centralizing component production and reducing on-site material handling, contrasting with on-site construction that demands complex scheduling of diverse deliveries and workforce management.
Quality Control Standardization
Prefabrication enhances quality control and standardization by manufacturing components in controlled factory environments, reducing variability and defects compared to on-site construction.
Prefabrication vs On-site Construction Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com