DDR5 memory offers significant improvements over DDR4 by providing higher data transfer rates and increased bandwidth, enhancing overall system performance for demanding applications. It also delivers greater power efficiency through lower voltage requirements, allowing for reduced energy consumption and improved thermal management. Enhanced reliability features such as on-die ECC further differentiate DDR5, making it a superior choice for next-generation computing tasks.
Table of Comparison
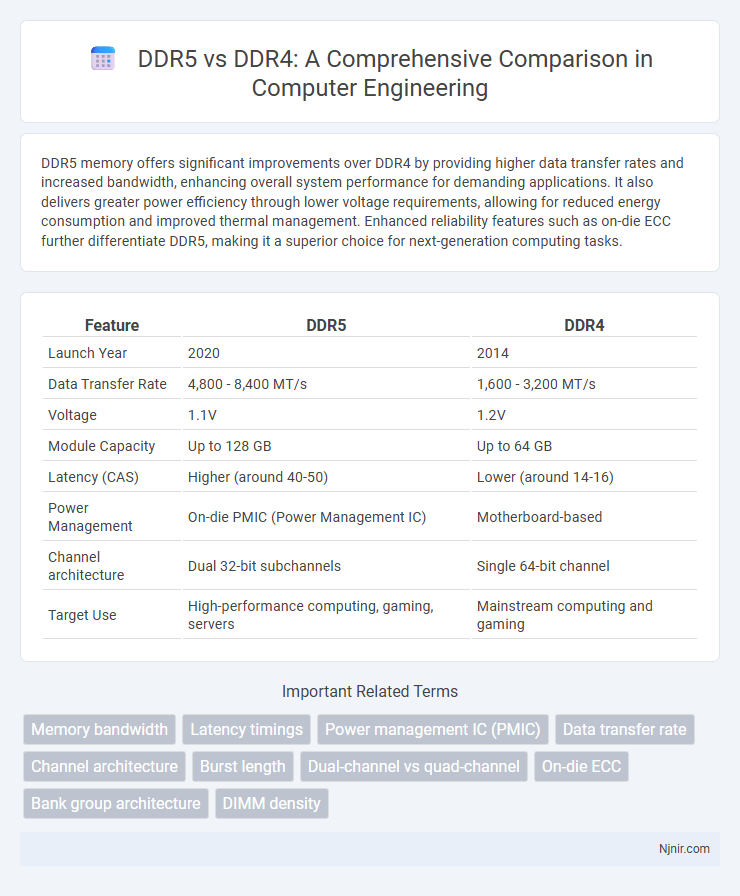
| Feature | DDR5 | DDR4 |
|---|---|---|
| Launch Year | 2020 | 2014 |
| Data Transfer Rate | 4,800 - 8,400 MT/s | 1,600 - 3,200 MT/s |
| Voltage | 1.1V | 1.2V |
| Module Capacity | Up to 128 GB | Up to 64 GB |
| Latency (CAS) | Higher (around 40-50) | Lower (around 14-16) |
| Power Management | On-die PMIC (Power Management IC) | Motherboard-based |
| Channel architecture | Dual 32-bit subchannels | Single 64-bit channel |
| Target Use | High-performance computing, gaming, servers | Mainstream computing and gaming |
Introduction to DDR4 and DDR5 Memory
DDR4 memory, introduced in 2014, offers speeds ranging from 1600 MHz to 3200 MHz and features a 1.2V power consumption, improving efficiency over its predecessor DDR3. DDR5 memory, launched in 2020, doubles the maximum data rate starting at 4800 MHz and supports voltage scaling down to 1.1V, enhancing speed and power efficiency for next-generation computing. Both DDR4 and DDR5 utilize different channel architectures and improved error correction mechanisms, with DDR5 designed to meet higher bandwidth demands and future scalability.
Key Architectural Differences
DDR5 memory features doubled burst length and increased bank groups compared to DDR4, enabling higher data rates and improved efficiency. It incorporates on-die ECC for enhanced reliability and integrates power management directly on the module, reducing motherboard power delivery requirements. The architecture supports higher channel counts and operates at lower voltage levels, resulting in better overall performance and energy efficiency.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Bandwidth
DDR5 memory offers significantly higher speeds and bandwidth compared to DDR4, with data rates starting at 4800 MT/s and scaling beyond 8400 MT/s, whereas DDR4 typically maxes out around 3200 MT/s. The increased bandwidth in DDR5, reaching up to 51.2 GB/s per module, enhances data transfer efficiency, making it ideal for high-performance computing and gaming applications. DDR5 also features improved channel architecture, which allows better parallelism and overall system responsiveness compared to the single 64-bit channel in DDR4.
Power Efficiency and Voltage Requirements
DDR5 memory operates at a lower voltage of 1.1V compared to DDR4's standard 1.2V, significantly improving power efficiency for high-performance computing. Enhanced power management features in DDR5, such as on-die ECC and independent power channels per module, reduce energy consumption and heat generation. These advancements make DDR5 more suitable for energy-conscious applications like mobile devices and data centers.
Capacity and Scalability Enhancements
DDR5 memory modules offer significantly higher capacity per DIMM compared to DDR4, with support for up to 128GB modules versus DDR4's typical maximum of 32GB. This increased capacity allows for enhanced scalability in servers and high-performance computing systems, enabling more memory-intensive applications and workloads. The improved density and efficiency of DDR5 also facilitate better future-proofing for expanding data requirements.
Latency and Real-World Application Impact
DDR5 offers higher bandwidth and improved power efficiency compared to DDR4, but it typically has slightly higher latency due to increased CAS latency timings. In real-world applications such as gaming or productivity tasks, the difference in latency is often negligible, with DDR5's increased bandwidth providing more noticeable performance gains in memory-intensive workloads. Users focused on tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, or handling large datasets benefit more from DDR5's overall speed improvements despite its latency trade-offs.
Compatibility with Motherboards and Chipsets
DDR5 memory modules require motherboards with compatible DDR5 slots and chipsets designed to support its higher speeds and enhanced features, making them incompatible with DDR4 slots. Most current motherboards for Intel 12th and 13th Gen processors and AMD Ryzen 7000 Series officially support DDR5, while earlier chipsets are limited to DDR4. Ensuring compatibility involves checking motherboard specifications for DDR5 support, as mixing DDR4 and DDR5 memory across platforms is technically impossible due to differences in voltage, signaling, and physical layout.
Cost Analysis: DDR4 vs DDR5 Pricing
DDR4 memory offers a significantly lower price per gigabyte compared to DDR5, making it a more cost-effective option for budget-conscious users. DDR5 pricing currently remains higher due to newer manufacturing technology and lower market availability, with premium models costing up to 50-70% more than DDR4 equivalents. Over time, DDR5 prices are expected to decrease as production scales and adoption increases, reducing the cost gap between the two generations.
Future-Proofing and Adoption Trends
DDR5 memory offers significantly higher bandwidth and improved power efficiency compared to DDR4, making it a more future-proof choice for high-performance computing and gaming systems. Industry adoption trends show DDR5 becoming the standard in new motherboards and laptops, driven by support from leading CPU manufacturers like Intel and AMD. Early adoption may come at a premium, but the expanding ecosystem ensures increasing availability and compatibility for mainstream users.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Memory for Your Needs
DDR5 memory offers higher bandwidth and improved power efficiency compared to DDR4, making it ideal for demanding applications like gaming, content creation, and future-proofing high-performance systems. DDR4 remains a cost-effective choice with solid performance for everyday computing and budget builds. Selecting between DDR5 and DDR4 depends on your specific workload requirements, budget constraints, and motherboard compatibility.
Memory bandwidth
DDR5 offers up to 50% higher memory bandwidth than DDR4, reaching speeds of 6400 MT/s compared to DDR4's maximum of 3200 MT/s, significantly improving data transfer rates in high-performance computing.
Latency timings
DDR5 memory features higher latency timings compared to DDR4, but its increased bandwidth and improved architecture compensate for the higher latency, resulting in better overall performance.
Power management IC (PMIC)
DDR5 integrates an advanced Power Management IC (PMIC) on the memory module, enabling efficient voltage regulation and improved power efficiency compared to DDR4's motherboard-based power management system.
Data transfer rate
DDR5 memory offers data transfer rates starting at 4,800 MT/s, significantly outperforming DDR4's maximum of 3,200 MT/s, enabling faster and more efficient data processing in modern computing systems.
Channel architecture
DDR5 features dual independent 32-bit channels per memory module, improving parallelism and efficiency compared to DDR4's single 64-bit channel architecture.
Burst length
DDR5 memory features a doubled burst length of 16 compared to DDR4's 8, enabling more efficient data transfer and improved overall performance in high-speed computing tasks.
Dual-channel vs quad-channel
DDR5 memory offers enhanced bandwidth and efficiency compared to DDR4, enabling better performance in quad-channel configurations, while DDR4 primarily supports dual-channel setups with lower data transfer rates.
On-die ECC
DDR5 memory features on-die ECC to enhance data integrity by automatically correcting errors within the chip, unlike DDR4 which lacks this built-in error correction capability.
Bank group architecture
DDR5 memory enhances performance over DDR4 by increasing the number of bank groups from 4 to 8, enabling higher parallelism and improved data access efficiency.
DIMM density
DDR5 DIMMs offer significantly higher maximum density, reaching up to 128GB per module, compared to DDR4 DIMMs which typically max out at 64GB.
DDR5 vs DDR4 Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com