Switch mode power supplies (SMPS) offer higher efficiency and smaller size compared to linear power supplies by converting electrical power using high-frequency switching techniques. Linear power supplies generate less electromagnetic interference and provide cleaner, more stable output voltage due to their simple design but are bulkier and dissipate more heat. The choice between SMPS and linear power supplies depends on application requirements such as efficiency, size constraints, cost, and noise sensitivity.
Table of Comparison
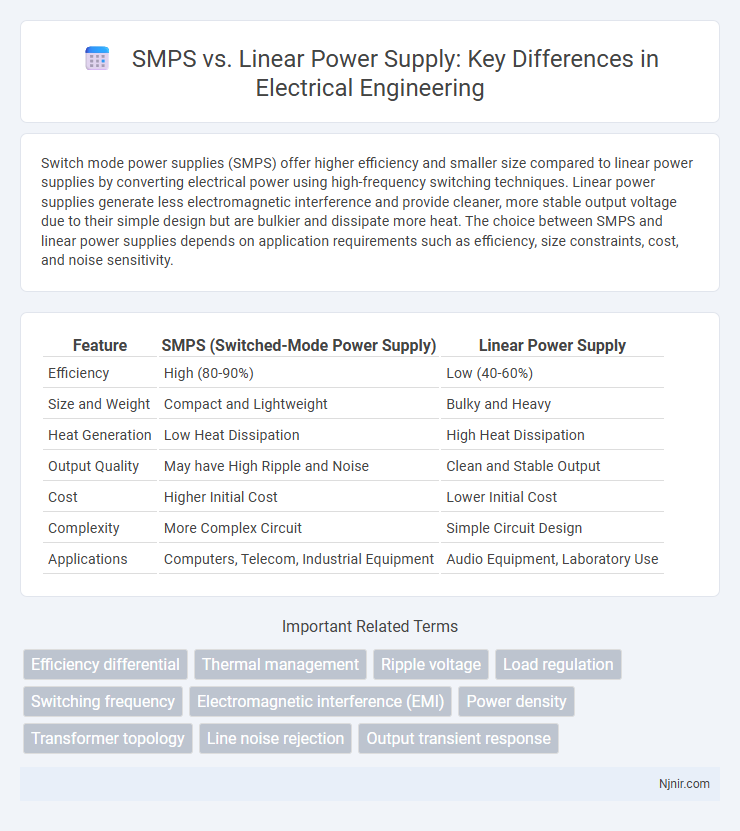
| Feature | SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) | Linear Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High (80-90%) | Low (40-60%) |
| Size and Weight | Compact and Lightweight | Bulky and Heavy |
| Heat Generation | Low Heat Dissipation | High Heat Dissipation |
| Output Quality | May have High Ripple and Noise | Clean and Stable Output |
| Cost | Higher Initial Cost | Lower Initial Cost |
| Complexity | More Complex Circuit | Simple Circuit Design |
| Applications | Computers, Telecom, Industrial Equipment | Audio Equipment, Laboratory Use |
Introduction to Power Supply Types
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) and Linear Power Supplies are two primary types of power supply units that convert electrical power to a usable form for electronic devices. SMPS efficiently regulate voltage through high-frequency switching components, resulting in reduced size and heat generation compared to the larger, heavier Linear Power Supplies, which rely on dissipative components like transformers and linear regulators. Understanding the voltage regulation mechanisms and efficiency differences between SMPS and Linear Power Supplies is essential for selecting the appropriate power supply for applications requiring stable and reliable power delivery.
Fundamental Working Principles
Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) operate by rapidly switching a transistor on and off to regulate voltage through high-frequency transformers and inductors, converting electrical power efficiently with minimal heat dissipation. Linear power supplies rely on linear regulation by dissipating excess voltage as heat using components like transformers, rectifiers, and linear voltage regulators to provide a stable output voltage. SMPS offer higher efficiency and compact design due to high-frequency operation, while linear power supplies provide low noise and simple design but consume more power and generate more heat.
Efficiency Comparison: SMPS vs Linear
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) typically achieve efficiency levels of 80-90%, significantly higher than Linear Power Supplies, which usually range between 40-60% efficiency. SMPS minimize energy loss by rapidly switching components on and off, reducing heat generation and overall power consumption. Linear power supplies dissipate excess voltage as heat, making them less efficient for high-voltage or high-current applications.
Size and Weight Differences
Switching Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are significantly smaller and lighter compared to linear power supplies due to their high-frequency operation and use of smaller inductors and transformers. The compact design of SMPS reduces the overall volume and weight, making them ideal for portable and space-constrained applications. In contrast, linear power supplies require larger, heavier transformers and heat sinks, resulting in bulkier and heavier units.
Heat Dissipation and Thermal Management
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) generates significantly less heat compared to linear power supplies due to its higher efficiency, often exceeding 80-90%, which reduces power loss and heat dissipation. Linear power supplies dissipate excess voltage as heat through resistive elements, causing substantial thermal buildup requiring larger heat sinks and cooling solutions. Effective thermal management in SMPS involves compact heat sinks and strategic airflow, whereas linear power supplies demand robust heat dissipation mechanisms to maintain safe operating temperatures.
Output Voltage Regulation and Ripple
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) offer superior output voltage regulation compared to Linear Power Supplies due to their high-frequency switching mechanism, maintaining stable voltage under varying load conditions. SMPS typically exhibit higher ripple and noise levels, often ranging from tens to hundreds of millivolts, while Linear Power Supplies provide cleaner output with ripple usually below a few millivolts. Careful filtering in SMPS designs can reduce ripple, but Linear Power Supplies inherently deliver lower ripple and noise, making them preferable for sensitive analog circuits.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Considerations
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) generate higher levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to high-frequency switching, requiring extensive filtering and shielding to meet regulatory standards. Linear power supplies produce minimal EMI as they operate at lower frequencies and use simpler transformer and regulation components, making them preferable for sensitive electronic applications. Effective EMI management in SMPS involves using ferrite beads, EMI filters, and PCB layout optimization to mitigate noise emissions and ensure compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) offers lower production costs and higher efficiency compared to Linear power supplies, making it a cost-effective option for mass-market applications. Linear power supplies have simpler designs but consume more energy and generate heat, leading to higher operational costs despite lower initial prices. SMPS dominates the market due to widespread availability, compact size, and better performance in modern electronic devices.
Typical Applications in Electronics
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are widely used in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and computing devices due to their high efficiency and compact size, making them ideal for battery-operated and portable gadgets. Linear power supplies are preferred in audio equipment, laboratory instruments, and precision measurement devices where low noise and stable voltage are critical, despite their lower efficiency and larger size. SMPS excels in applications requiring variable voltage and high power density, while linear supplies dominate scenarios demanding minimal electromagnetic interference and clean output signals.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Project
Selecting the right power supply depends on factors such as efficiency, voltage regulation, size, and noise tolerance. Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) offer higher efficiency, compact size, and lighter weight but can introduce electrical noise, making them suitable for energy-sensitive designs. Linear power supplies deliver clean, low-noise output with excellent voltage regulation but are bulkier and less efficient, ideal for noise-sensitive analog or audio projects.
Efficiency differential
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) typically achieve 80-90% efficiency compared to 40-60% efficiency in linear power supplies due to reduced energy loss in heat dissipation.
Thermal management
SMPS offers superior thermal management with higher efficiency and less heat generation compared to the bulky heat dissipation and lower efficiency of linear power supplies.
Ripple voltage
SMPS offers significantly lower ripple voltage compared to linear power supplies, enhancing efficiency and reducing noise in electronic circuits.
Load regulation
SMPS offers superior load regulation with efficiency exceeding 80%, maintaining stable output voltage despite varying loads, unlike linear power supplies which exhibit poorer load regulation and higher energy loss.
Switching frequency
Switching Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) operate at high switching frequencies ranging from 20 kHz to several MHz, enabling smaller components and higher efficiency compared to Linear Power Supplies, which do not utilize switching frequencies and rely on continuous regulation with larger, less efficient components.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Switching Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) generate higher electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to high-frequency switching compared to Linear Power Supplies, which produce minimal EMI because of their continuous, low-frequency operation.
Power density
Switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) offer significantly higher power density than linear power supplies due to their efficient high-frequency operation and compact transformer design.
Transformer topology
Switch-mode power supplies use high-frequency transformer topology for compactness and efficiency, while linear power supplies rely on large, low-frequency transformers for voltage regulation and simplicity.
Line noise rejection
Switch mode power supplies (SMPS) generally provide superior line noise rejection compared to linear power supplies due to their high-frequency switching regulation and integrated filtering components.
Output transient response
SMPS exhibits faster output transient response than linear power supplies due to its high-frequency switching and feedback control, enabling quick voltage recovery during load changes.
SMPS vs Linear power supply Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com