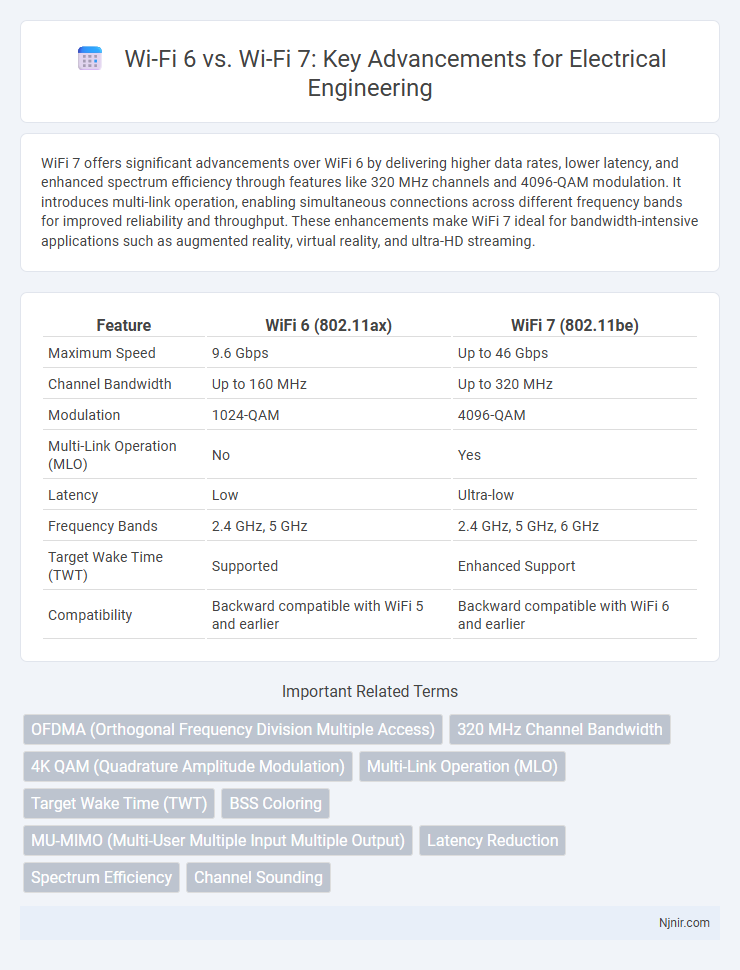
WiFi 7 offers significant advancements over WiFi 6 by delivering higher data rates, lower latency, and enhanced spectrum efficiency through features like 320 MHz channels and 4096-QAM modulation. It introduces multi-link operation, enabling simultaneous connections across different frequency bands for improved reliability and throughput. These enhancements make WiFi 7 ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and ultra-HD streaming.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | WiFi 6 (802.11ax) | WiFi 7 (802.11be) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Speed | 9.6 Gbps | Up to 46 Gbps |
| Channel Bandwidth | Up to 160 MHz | Up to 320 MHz |
| Modulation | 1024-QAM | 4096-QAM |
| Multi-Link Operation (MLO) | No | Yes |
| Latency | Low | Ultra-low |
| Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz |
| Target Wake Time (TWT) | Supported | Enhanced Support |
| Compatibility | Backward compatible with WiFi 5 and earlier | Backward compatible with WiFi 6 and earlier |
Introduction to WiFi 6 and WiFi 7
WiFi 6, also known as 802.11ax, offers improved data rates, increased capacity, and better performance in congested environments compared to its predecessor, WiFi 5. WiFi 7, based on the emerging 802.11be standard, promises even faster speeds exceeding 30 Gbps, lower latency, and enhanced efficiency through technologies like multi-link operation and wider channel bandwidths. Both standards aim to support the growing demand for high-bandwidth applications, but WiFi 7 introduces advanced features to meet the future needs of ultra-reliable connectivity and multi-device environments.
Key Technological Advancements
WiFi 7 introduces key technological advancements such as wider channel bandwidths up to 320 MHz, multi-link operation (MLO) for simultaneous data transmission over different bands, and enhanced modulation with 4096-QAM, significantly surpassing WiFi 6's 160 MHz channels and 1024-QAM. These innovations enable WiFi 7 to deliver ultra-high throughput, lower latency, and improved reliability vital for applications like VR, AR, and 8K streaming. The multi-link feature also optimizes spectrum efficiency and reduces interference, marking a substantial leap over WiFi 6's capabilities in dense environments.
Frequency Bands and Channel Widths
WiFi 6 operates primarily on the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands with maximum channel widths of 160 MHz, enabling improved speed and reduced latency compared to earlier standards. WiFi 7 expands onto the 6 GHz band in addition to 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, supporting channel widths up to 320 MHz, which doubles the maximum bandwidth and significantly boosts data throughput. The wider channel widths and additional frequency spectrum in WiFi 7 facilitate higher performance, lower latency, and enhanced capacity for dense network environments.
Data Rates and Throughput Capabilities
WiFi 7, based on the IEEE 802.11be standard, offers significantly higher data rates and throughput capabilities compared to WiFi 6 (802.11ax), reaching up to 46 Gbps versus WiFi 6's maximum of 9.6 Gbps. WiFi 7 achieves this through wider channel bandwidths of up to 320 MHz, higher modulation schemes such as 4096-QAM, and improved Multi-link Operation (MLO) for simultaneous data transmission across multiple frequency bands. These enhancements enable WiFi 7 to deliver lower latency and greater network efficiency, making it ideal for high-demand applications like 8K streaming, virtual reality, and large-scale IoT deployments.
Latency Improvements and Real-Time Applications
WiFi 7 introduces enhanced latency reductions compared to WiFi 6 through technologies like Multi-Link Operation (MLO) and improved Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), enabling real-time applications such as augmented reality and online gaming to perform with minimal delay. The lower latency in WiFi 7 supports ultra-responsive connections, critical for interactive video conferencing and virtual reality experiences. WiFi 7's advanced modulation schemes and simultaneous multi-band transmission optimize real-time data processing far beyond the capabilities of WiFi 6.
Enhanced Network Capacity and Device Density
WiFi 7 significantly improves enhanced network capacity by utilizing wider channels up to 320 MHz and 4096-QAM modulation, compared to WiFi 6's maximum 160 MHz channels and 1024-QAM, enabling faster data throughput and lower latency. The new multi-link operation (MLO) feature in WiFi 7 allows simultaneous connection across multiple frequency bands, dramatically increasing device density support and reducing interference in crowded environments. These advancements make WiFi 7 ideal for ultra-dense settings such as stadiums, offices, and smart cities, where large numbers of devices demand reliable and high-speed connections.
Power Efficiency and IoT Integration
WiFi 7 offers significant improvements in power efficiency over WiFi 6 by utilizing advanced Target Wake Time (TWT) protocols, reducing energy consumption for connected IoT devices. Enhanced multi-link operation (MLO) in WiFi 7 optimizes channel usage, enabling faster data transmission while minimizing power drain, crucial for battery-operated IoT sensors. This integration supports more robust and scalable IoT ecosystems, facilitating seamless connectivity with lower latency and extended device battery life.
Security Features Comparison
WiFi 6 employs WPA3 encryption, enhancing password protection and safeguarding against brute-force attacks, while WiFi 7 advances security with improved encryption protocols and enhanced protection against replay attacks. WiFi 7 integrates more robust support for simultaneous data streams, reducing latency and improving overall network security by minimizing vulnerabilities during high traffic loads. Enhanced security features in WiFi 7 also include better management of orphaned packets and improved authentication processes, ensuring stronger protection in complex network environments.
Backward Compatibility and Transition Challenges
WiFi 7 maintains backward compatibility with WiFi 6 and earlier standards, ensuring seamless connectivity for existing devices while delivering higher speeds and lower latency. Transition challenges include the need for updated hardware supporting wider channels and advanced modulation, which may delay widespread adoption. Network infrastructure upgrades and device firmware updates are crucial to fully leverage WiFi 7's enhanced performance without disrupting current WiFi 6 deployments.
Impact on Industrial and Commercial Electrical Systems
WiFi 7 offers significantly higher data speeds and reduced latency compared to WiFi 6, enabling more efficient real-time monitoring and control of industrial and commercial electrical systems. Its improved multi-link operation enhances network reliability and capacity, supporting numerous IoT devices and smart grid applications with minimal interference. Enhanced spectral efficiency and advanced modulation techniques in WiFi 7 optimize power consumption and data throughput, leading to more robust and scalable electrical infrastructure management.
OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)
WiFi 7 enhances OFDMA technology by increasing subcarrier granularity and multi-link operation, enabling higher capacity and reduced latency compared to WiFi 6.
320 MHz Channel Bandwidth
WiFi 7 supports up to 320 MHz channel bandwidth, doubling the 160 MHz maximum of WiFi 6, enabling significantly higher data rates and improved network capacity.
4K QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation)
WiFi 7 enhances data throughput and network efficiency by supporting 4K QAM modulation, doubling the symbol density compared to WiFi 6's 1K QAM, resulting in faster and more reliable wireless connections.
Multi-Link Operation (MLO)
WiFi 7's Multi-Link Operation (MLO) enhances network performance by enabling simultaneous data transmission across multiple frequency bands, surpassing WiFi 6's single-link limitations for lower latency and higher throughput.
Target Wake Time (TWT)
WiFi 7 enhances Target Wake Time (TWT) by enabling more precise scheduling and longer sleep intervals compared to WiFi 6, significantly improving power efficiency and reducing battery consumption in connected devices.
BSS Coloring
WiFi 7 enhances BSS Coloring technology compared to WiFi 6 by supporting up to 336 unique BSS colors, significantly reducing co-channel interference and improving spatial reuse in dense network environments.
MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output)
WiFi 7 significantly enhances MU-MIMO capabilities by supporting up to 16 simultaneous data streams per user compared to WiFi 6's 8 streams, enabling higher throughput and improved multi-device performance.
Latency Reduction
WiFi 7 reduces latency by up to 50% compared to WiFi 6 through features like Multi-Link Operation (MLO) and enhanced Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA).
Spectrum Efficiency
WiFi 7 enhances spectrum efficiency over WiFi 6 by utilizing wider channels up to 320 MHz and supporting Multi-Link Operation, enabling simultaneous data transmission across multiple frequency bands for increased throughput and reduced latency.
Channel Sounding
WiFi 7 enhances channel sounding by utilizing multi-link operation and increased subcarrier granularity compared to WiFi 6, resulting in more accurate channel state information and improved spatial multiplexing efficiency.
WiFi 6 vs WiFi 7 Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com