SPICE specializes in simulating analog circuits at the transistor level, providing accurate modeling of electrical components and transient behavior. MATLAB offers a versatile environment for system-level analysis, algorithm development, and numerical computation, suitable for control systems and signal processing in electrical engineering. SPICE excels in circuit verification while MATLAB supports broader system design and optimization tasks.
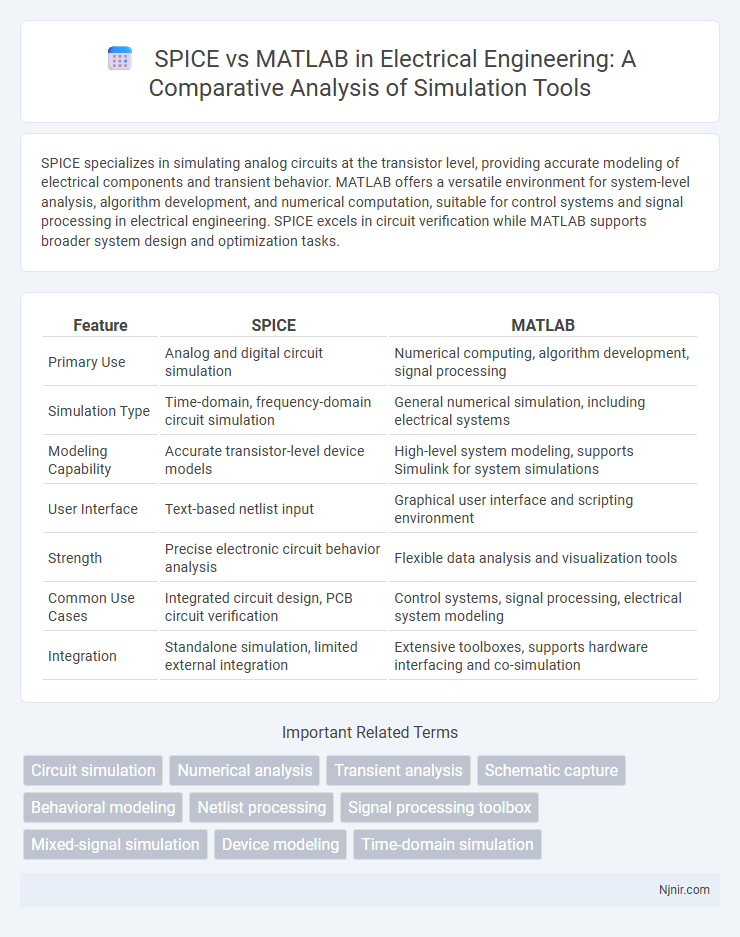
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SPICE | MATLAB |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Analog and digital circuit simulation | Numerical computing, algorithm development, signal processing |
| Simulation Type | Time-domain, frequency-domain circuit simulation | General numerical simulation, including electrical systems |
| Modeling Capability | Accurate transistor-level device models | High-level system modeling, supports Simulink for system simulations |
| User Interface | Text-based netlist input | Graphical user interface and scripting environment |
| Strength | Precise electronic circuit behavior analysis | Flexible data analysis and visualization tools |
| Common Use Cases | Integrated circuit design, PCB circuit verification | Control systems, signal processing, electrical system modeling |
| Integration | Standalone simulation, limited external integration | Extensive toolboxes, supports hardware interfacing and co-simulation |
Introduction to SPICE and MATLAB: Core Differences
SPICE is a specialized circuit simulation tool widely used for analyzing analog circuits with detailed transistor-level accuracy, whereas MATLAB serves as a versatile numerical computing environment optimized for algorithm development, data analysis, and system-level modeling. SPICE excels in simulating electrical behavior at the component level, enabling precise transient, AC, and DC analysis, while MATLAB provides extensive toolboxes for matrix computations, signal processing, and control system design. The core difference lies in their primary applications: SPICE focuses on electrical circuit simulation, and MATLAB supports broader engineering and scientific computations beyond circuit analysis.
Simulation Capabilities: Analog, Digital, and Mixed-Signal Analysis
SPICE excels in analog circuit simulation with detailed transistor-level modeling, enabling accurate analysis of small-signal, large-signal, and transient behaviors. MATLAB offers robust digital and mixed-signal simulation through Simulink and Simscape, supporting system-level modeling, algorithm development, and hardware-in-the-loop testing. Mixed-signal analysis benefits from MATLAB's integration of continuous-time and discrete-event simulations, whereas SPICE remains the standard for high-precision analog circuit verification.
User Interface and Ease of Learning
SPICE offers a text-based interface that requires familiarity with command syntax, making it less intuitive for beginners compared to MATLAB's graphical user interface with interactive toolboxes and built-in plotting capabilities. MATLAB provides extensive documentation and user-friendly features like drag-and-drop Simulink blocks, which significantly reduce the learning curve for new users. The integrated development environment (IDE) in MATLAB supports debugging and visualization, enhancing usability for complex simulations compared to SPICE's more technical environment.
Breadth of Electrical Component Libraries
SPICE offers an extensive range of electrical component libraries with detailed transistor models, passive elements, and semiconductor devices essential for accurate analog circuit simulation. MATLAB, while primarily a numerical computing environment, incorporates Simulink and Simscape libraries providing modular electrical components suitable for system-level and multiphysics simulations. SPICE is preferred for deep transistor-level analysis, whereas MATLAB delivers broader coverage for system integration and control design within electrical engineering.
Customization, Scripting, and Programming Flexibility
SPICE offers extensive customization through its netlist-based approach, enabling detailed circuit simulations with user-defined device models, while MATLAB provides powerful scripting capabilities with a high-level programming language ideal for algorithm development and data analysis. MATLAB's flexibility allows integration of custom scripts, functions, and toolboxes, supporting complex system-level modeling beyond circuit simulation. SPICE excels in precise analog circuit behavior analysis, whereas MATLAB's programming environment favors versatile computational tasks, making each suitable for different aspects of electronic design and system simulation.
Circuit Visualization and Output Interpretation
SPICE excels in detailed circuit visualization with waveforms and node voltages, enabling precise analysis of analog circuits at the transistor level. MATLAB provides advanced output interpretation using customizable plots, data processing, and integration with control system toolboxes, ideal for complex simulations and algorithm development. Visualization in SPICE focuses on real-time circuit behavior, while MATLAB emphasizes flexible data manipulation and comprehensive result presentation.
Accuracy and Reliability in Circuit Simulation
SPICE offers high accuracy in circuit simulation through detailed transistor-level modeling and iterative numerical methods, making it reliable for analog and mixed-signal designs. MATLAB provides flexible simulation environments with built-in toolboxes for system-level analysis but may sacrifice some transistor-level precision compared to SPICE. For designs demanding precise transistor behavior and robust convergence, SPICE remains the industry standard in accuracy and reliability.
Integration with Hardware and Other Software Tools
SPICE offers robust integration with various hardware simulators and electronic design automation (EDA) tools, enabling seamless circuit simulation and hardware testing workflows. MATLAB excels in hardware interfacing through built-in support for data acquisition devices and real-time systems, as well as extensive toolboxes for communication with microcontrollers and FPGA boards. Combining SPICE's detailed circuit-level analysis with MATLAB's high-level algorithm development creates a powerful environment for comprehensive hardware-software co-design and prototyping.
Application Areas: Academia, Research, and Industry
SPICE excels in circuit simulation and verification, widely used in academia and research for electronic design automation and testing analog circuits. MATLAB dominates in numerical computing and algorithm development, serving diverse applications in academia, research, and industry, including signal processing, control systems, and data analysis. Both tools complement each other, with SPICE preferred for detailed electronic component simulation and MATLAB favored for mathematical modeling and system-level analysis.
Cost, Licensing, and Community Support
SPICE offers open-source versions like NGSPICE with free access, while commercial variants may require licensing fees, making it cost-effective for academic and hobbyist use. MATLAB requires a paid license with significant costs, though various toolboxes enhance its capabilities for engineering simulations. The MATLAB community is extensive with robust support, tutorials, and user forums, whereas SPICE benefits from a dedicated niche community focused on circuit simulation and electronic design.
Circuit simulation
SPICE provides detailed transistor-level circuit simulation with high accuracy in analog behavior, while MATLAB excels in system-level modeling and numerical analysis but offers less specialized circuit simulation capabilities.
Numerical analysis
SPICE excels in circuit-level simulation using device models for accurate transient and frequency response analysis, while MATLAB provides advanced numerical analysis tools and customizable algorithms for comprehensive mathematical modeling and data processing.
Transient analysis
SPICE offers highly accurate transient analysis for detailed circuit simulations at the transistor level, while MATLAB excels in flexible, high-level transient signal processing and system modeling for large-scale simulations.
Schematic capture
SPICE offers precise analog circuit simulation with basic schematic capture, while MATLAB excels in algorithm development and data visualization but lacks integrated schematic capture tools.
Behavioral modeling
SPICE excels in circuit-level behavioral modeling with detailed transistor-level simulation, while MATLAB offers high-level algorithmic behavioral modeling optimized for system-level design and analysis.
Netlist processing
SPICE efficiently processes analog circuit netlists with detailed transistor-level simulation, while MATLAB excels in algorithmic manipulation and customized analysis of netlist data for system-level modeling and control design.
Signal processing toolbox
MATLAB's Signal Processing Toolbox offers advanced built-in functions and real-time interactive tools for designing, analyzing, and simulating signals, while SPICE primarily focuses on circuit-level simulation without specialized signal processing capabilities.
Mixed-signal simulation
SPICE offers highly accurate transistor-level mixed-signal simulation ideal for detailed analog circuit analysis, while MATLAB provides powerful system-level mixed-signal modeling with advanced algorithm development and data visualization capabilities.
Device modeling
SPICE offers detailed transistor-level device modeling with extensive semiconductor physics accuracy, while MATLAB emphasizes device behavior simulation through customizable mathematical models and system-level integration.
Time-domain simulation
SPICE excels in accurate transistor-level time-domain simulations for analog circuits, while MATLAB offers flexible, high-level time-domain modeling and analysis suited for system-level and algorithmic simulations.
SPICE vs MATLAB Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com