Incinerator waste in marine engineering involves the combustion of solid waste to reduce volume and eliminate hazardous materials, producing ash that requires proper disposal. Sewage treatment, on the other hand, focuses on processing wastewater to remove contaminants, ensuring that effluents meet environmental standards before discharge. Both methods are essential for maintaining marine vessel hygiene and complying with international maritime regulations, but they address different waste streams with distinct environmental impacts.
Table of Comparison
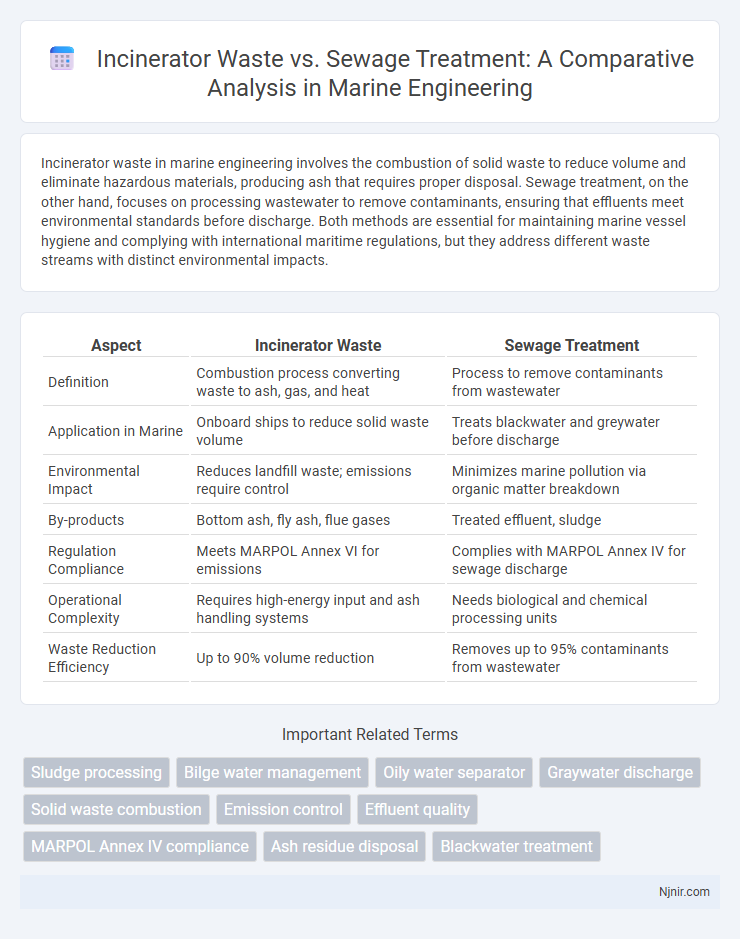
| Aspect | Incinerator Waste | Sewage Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combustion process converting waste to ash, gas, and heat | Process to remove contaminants from wastewater |
| Application in Marine | Onboard ships to reduce solid waste volume | Treats blackwater and greywater before discharge |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste; emissions require control | Minimizes marine pollution via organic matter breakdown |
| By-products | Bottom ash, fly ash, flue gases | Treated effluent, sludge |
| Regulation Compliance | Meets MARPOL Annex VI for emissions | Complies with MARPOL Annex IV for sewage discharge |
| Operational Complexity | Requires high-energy input and ash handling systems | Needs biological and chemical processing units |
| Waste Reduction Efficiency | Up to 90% volume reduction | Removes up to 95% contaminants from wastewater |
Introduction to Onboard Waste Management
Onboard waste management involves the effective handling and treatment of waste generated on ships, focusing on minimizing environmental impact. Incinerator waste systems thermally decompose solid and liquid waste, reducing volume and eliminating harmful pathogens, while sewage treatment uses biological and chemical processes to treat wastewater before discharge. Understanding the differences between these methods is crucial for compliance with maritime environmental regulations and sustainable ship operation.
Overview of Marine Incinerator Waste
Marine incinerator waste consists of hazardous byproducts generated from burning waste materials at sea, producing ash and emissions that require careful management to prevent environmental contamination. Unlike sewage treatment, which biologically processes and breaks down organic waste through primary, secondary, and tertiary stages to reduce pollutants, marine incineration primarily eliminates waste volume but can release toxic substances. Proper regulation and advanced pollution control technologies are critical in mitigating the impact of marine incinerator waste on marine ecosystems and water quality.
Understanding Marine Sewage Treatment Systems
Marine sewage treatment systems are designed to process and treat wastewater generated on ships or offshore platforms, ensuring compliance with international maritime regulations such as MARPOL Annex IV. These systems utilize biological, chemical, or mechanical methods to remove contaminants before discharge, minimizing the environmental impact on marine ecosystems. In contrast, incinerator waste involves burning solid waste at high temperatures to reduce volume and toxicity, a process that does not treat liquid sewage but can complement waste management on vessels.
Regulatory Standards: MARPOL Annex IV & V
Incinerator waste management must comply with MARPOL Annex V, which regulates the disposal of garbage from ships, ensuring that incinerator residues do not pollute marine environments. Sewage treatment on vessels falls under MARPOL Annex IV, mandating strict standards for the discharge of sewage effluents to prevent waterborne contamination and protect marine ecosystems. Compliance with these regulations is critical for maritime operators to avoid penalties and promote sustainable ocean practices.
Key Differences: Incinerator Waste vs Sewage
Incinerator waste primarily consists of solid residues produced from the combustion of various materials, whereas sewage treatment deals with the processing of liquid wastewater containing organic and inorganic pollutants. Incinerator waste requires thermal destruction and ash management, while sewage treatment involves biological, chemical, and physical processes to remove contaminants and produce clean effluent. The environmental impact differs significantly, with incinerator waste generating airborne emissions and ash disposal challenges, while sewage treatment focuses on preventing water pollution and managing sludge.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Incinerator waste treatment reduces landfill volume and decreases methane emissions but releases pollutants like dioxins and heavy metals into the air, posing air quality concerns. Sewage treatment processes primarily focus on removing organic matter and pathogens from wastewater, improving water quality and reducing eutrophication risks in aquatic ecosystems. While incineration offers volume reduction benefits, sewage treatment provides critical nutrient removal, making each method's environmental impact dependent on waste type and local ecological priorities.
Operational Challenges and Safety Concerns
Incinerator waste management faces operational challenges such as high energy consumption and the need for continuous emissions monitoring to control toxic byproducts like dioxins and heavy metals. Sewage treatment plants contend with variable influent quality affecting biological process stability and require stringent measures to prevent pathogen release and chemical exposure risks. Both systems demand rigorous safety protocols to protect workers from hazardous substances and ensure environmental compliance under evolving regulatory standards.
Waste Disposal Procedures at Sea
Incinerator waste disposal at sea involves burning waste materials to reduce volume and toxicity before discharge, whereas sewage treatment focuses on removing contaminants from wastewater through biological and chemical processes prior to release. International maritime regulations, such as MARPOL Annex IV and V, govern acceptable discharge levels and methods to minimize marine pollution from both incinerated waste and treated sewage. Effective waste disposal procedures at sea prioritize environmental protection by ensuring that incineration residues and treated effluents meet stringent quality standards to prevent harm to aquatic ecosystems.
Technological Advancements in Marine Waste Processing
Technological advancements in marine waste processing have significantly enhanced both incinerator waste treatment and sewage treatment methods, focusing on minimizing environmental impact and maximizing efficiency. Modern incinerators utilize high-temperature combustion and advanced emission control systems to safely reduce hazardous marine waste volume and toxic pollutants. Sewage treatment technologies incorporate biological nutrient removal, membrane bioreactors, and real-time monitoring to effectively treat marine wastewater, ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Future Trends in Sustainable Shipboard Waste Management
Future trends in sustainable shipboard waste management emphasize advanced incinerator technology and enhanced sewage treatment systems to minimize environmental impact. Innovations include energy-efficient incinerators with reduced emissions and biological sewage treatment methods that promote nutrient recovery and water reuse. Integrating digital monitoring and automation improves operational efficiency, ensuring compliance with stricter international maritime environmental regulations.
Sludge processing
Incinerator waste sludge processing reduces volume by up to 90% through thermal destruction, while sewage treatment sludge undergoes dewatering and anaerobic digestion to stabilize organic content and reduce pathogens.
Bilge water management
Efficient bilge water management prioritizes sewage treatment methods over incinerator waste disposal due to lower environmental impact and enhanced pollutant removal efficiency.
Oily water separator
Oily water separators in incinerator waste management effectively remove hydrocarbons and heavy oils, while in sewage treatment they primarily target emulsified oils and grease for improved effluent quality.
Graywater discharge
Graywater discharge from sewage treatment undergoes biological filtration to reduce contaminants, whereas incinerator waste produces ash requiring specialized disposal without graywater generation.
Solid waste combustion
Solid waste combustion in incinerators effectively reduces volume and hazardous components of waste compared to sewage treatment, which primarily focuses on liquid waste purification and sludge stabilization.
Emission control
Incinerator waste systems achieve higher emission control efficiency by significantly reducing airborne pollutants like dioxins and particulate matter compared to conventional sewage treatment plants.
Effluent quality
Incinerator waste produces minimal liquid effluent with low contaminant levels, whereas sewage treatment generates significant effluent requiring extensive biological and chemical processes to meet discharge quality standards.
MARPOL Annex IV compliance
Incinerator waste management and sewage treatment differ significantly in MARPOL Annex IV compliance, with sewage treatment plants required to meet stringent effluent discharge standards to prevent marine pollution, while incinerator ash disposal must adhere to solid waste regulations under the convention.
Ash residue disposal
Incinerator waste produces ash residue requiring specialized hazardous waste landfills, whereas sewage treatment generates biosolids that are commonly stabilized and safely applied as agricultural fertilizer.
Blackwater treatment
Incinerator waste treatment reduces volume by combustion, while sewage treatment for blackwater focuses on biological processes to remove pathogens and organic matter, ensuring safe disposal and potential resource recovery.
Incinerator waste vs Sewage treatment Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com