SaaS solutions offer greater scalability and reduced maintenance overhead compared to self-hosted software, allowing businesses to deploy updates seamlessly in the cloud. Self-hosted options provide enhanced control over data security and customization, making them ideal for organizations with strict compliance requirements. Choosing between SaaS and self-hosted depends on factors like budget, IT infrastructure, and long-term scalability needs.
Table of Comparison
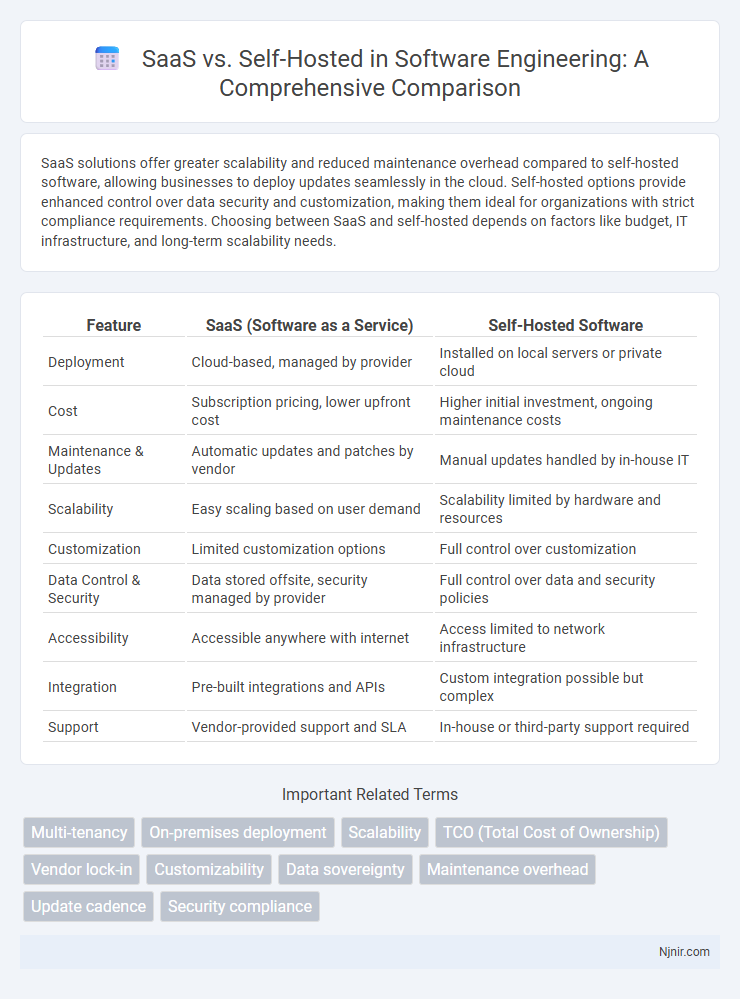
| Feature | SaaS (Software as a Service) | Self-Hosted Software |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Cloud-based, managed by provider | Installed on local servers or private cloud |
| Cost | Subscription pricing, lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment, ongoing maintenance costs |
| Maintenance & Updates | Automatic updates and patches by vendor | Manual updates handled by in-house IT |
| Scalability | Easy scaling based on user demand | Scalability limited by hardware and resources |
| Customization | Limited customization options | Full control over customization |
| Data Control & Security | Data stored offsite, security managed by provider | Full control over data and security policies |
| Accessibility | Accessible anywhere with internet | Access limited to network infrastructure |
| Integration | Pre-built integrations and APIs | Custom integration possible but complex |
| Support | Vendor-provided support and SLA | In-house or third-party support required |
Introduction to SaaS and Self-Hosted Solutions
SaaS (Software as a Service) solutions deliver software applications via the internet, enabling access without local installation and minimizing IT maintenance tasks. Self-hosted solutions require organizations to install and manage software on their own servers, providing greater control, customization, and data security. Choosing between SaaS and self-hosted depends on factors like budget, scalability, compliance, and technical expertise.
Key Differences: SaaS vs Self-Hosted Architectures
SaaS architecture relies on cloud-hosted infrastructure managed by service providers, enabling rapid deployment, automatic updates, and scalable resources without user maintenance. Self-hosted architecture requires on-premises or private server installations, granting organizations full control over data security, customization, and hardware management but demanding dedicated IT resources. Key differences include SaaS's subscription-based pricing versus upfront licensing costs in self-hosted setups, and the trade-off between convenience and control in deployment models.
Cost Analysis: Total Cost of Ownership
SaaS solutions typically involve predictable subscription fees covering infrastructure, maintenance, and updates, reducing upfront capital expenditure compared to self-hosted systems that require significant initial hardware investment and ongoing IT personnel costs. Self-hosted deployments often incur hidden expenses such as server maintenance, software licensing, scalability upgrades, and security compliance management, increasing the total cost of ownership over time. Evaluating long-term operational costs, including downtime risks and resource allocation for system management, is crucial for an accurate cost comparison between SaaS and self-hosted options.
Security Considerations for SaaS and Self-Hosting
SaaS platforms offer robust, vendor-managed security protocols including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular vulnerability assessments, reducing the burden on in-house IT teams. Self-hosted solutions provide greater control over security configurations and data privacy but require dedicated resources to manage patching, firewall settings, and threat detection effectively. Organizations must weigh the trade-offs between outsourced cloud security expertise and the risks linked to potential misconfigurations in self-hosted environments.
Customization and Flexibility: Which Offers More Control?
Self-hosted solutions provide greater customization and flexibility by allowing full access to the source code and server environment, enabling tailored feature development and integration specific to organizational needs. SaaS platforms offer limited customization within predefined parameters and rely on vendor updates, which can restrict control over functionality and timing. Enterprises seeking deep control and unique adaptations often prefer self-hosted deployments despite the increased maintenance and infrastructure responsibilities.
Deployment and Maintenance Efforts
SaaS solutions offer streamlined deployment with minimal setup, as providers manage hosting, updates, and infrastructure, significantly reducing in-house maintenance efforts. Self-hosted software requires substantial initial installation, configuration, and continuous maintenance, including hardware management, security patches, and software upgrades. Organizations must balance the scalability and ease of SaaS deployment against the control and customization offered by self-hosted environments.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
SaaS platforms offer seamless scalability through cloud infrastructure, automatically adjusting resources to handle fluctuating workloads and user demands without downtime. Self-hosted solutions require manual resource allocation and hardware upgrades, often leading to potential performance bottlenecks during traffic spikes. Cloud-based SaaS typically delivers optimized performance with global data centers and advanced load balancing, whereas self-hosted systems depend heavily on local hardware capacity and network configuration.
Compliance and Data Privacy Implications
SaaS solutions often include built-in compliance certifications such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, reducing the burden on organizations to maintain data privacy standards independently. Self-hosted deployments provide greater control over data storage and security policies, enabling tailored compliance measures but requiring significant internal resources and expertise. Evaluating the trade-offs between SaaS's standardized compliance frameworks and the customizable, yet complex, self-hosted approach is critical for ensuring robust data privacy management.
Use Cases: When to Choose SaaS or Self-Hosting
SaaS solutions are ideal for businesses seeking quick deployment, minimal IT maintenance, and scalable features, particularly suitable for startups and remote teams requiring seamless updates and cloud accessibility. Self-hosted options fit organizations with stringent data security needs, extensive customization requirements, or regulatory compliance mandates, commonly favored by enterprises managing sensitive information or requiring full infrastructure control. Evaluating use cases such as budget constraints, technical expertise, and long-term scalability guides the decision between SaaS convenience and self-hosted autonomy.
Future Trends in Software Delivery Models
Future trends in software delivery models indicate a growing preference for SaaS due to its scalability, automatic updates, and reduced infrastructure costs. Advances in cloud computing and edge technologies accelerate SaaS adoption, enhancing real-time collaboration and security. Meanwhile, self-hosted solutions continue evolving with hybrid cloud integration and increased customization for industries with strict compliance requirements.
Multi-tenancy
Multi-tenancy in SaaS enables cost-effective resource sharing and streamlined updates across users, whereas self-hosted environments require isolated infrastructure management for each tenant.
On-premises deployment
On-premises deployment of self-hosted software offers greater data control, enhanced security, and customization flexibility compared to SaaS solutions that rely on external cloud infrastructure.
Scalability
SaaS platforms offer seamless scalability with minimal infrastructure management, while self-hosted solutions require significant resources and expertise to scale effectively.
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
SaaS solutions typically have a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to reduced upfront infrastructure expenses and maintenance costs compared to self-hosted alternatives that require significant hardware investment and ongoing IT support.
Vendor lock-in
SaaS solutions often impose vendor lock-in by restricting data portability and customization, whereas self-hosted platforms offer greater control and freedom from vendor dependency.
Customizability
Self-hosted solutions offer greater customizability than SaaS platforms by allowing full control over software modifications and configurations.
Data sovereignty
Choosing SaaS often limits data sovereignty due to third-party data storage, whereas self-hosted solutions provide full control over data location and compliance with local regulations.
Maintenance overhead
SaaS solutions minimize maintenance overhead by outsourcing updates and infrastructure management, whereas self-hosted systems require dedicated resources for ongoing software maintenance, security patches, and hardware upkeep.
Update cadence
SaaS platforms offer automatic, frequent update cadence ensuring immediate access to the latest features and security patches, while self-hosted solutions require manual updates with variable timing impacting system stability and security.
Security compliance
SaaS platforms often provide robust security compliance certifications like SOC 2 and GDPR by default, while self-hosted solutions require organizations to independently implement and continuously manage security controls to meet regulatory standards.
SaaS vs self-hosted Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com