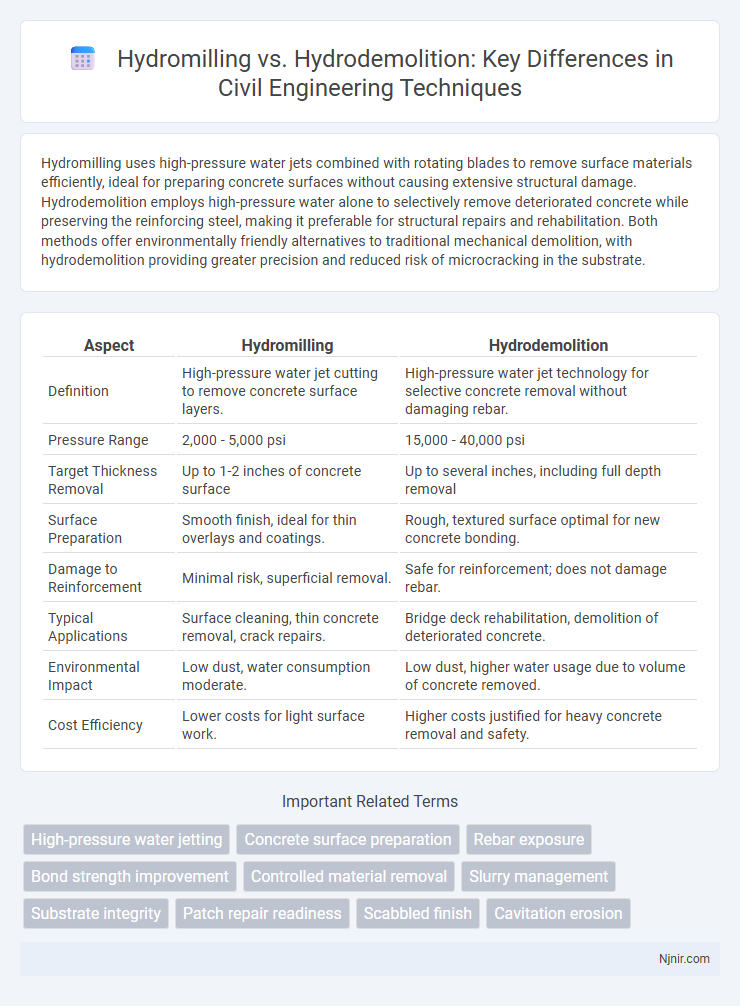
Hydromilling uses high-pressure water jets combined with rotating blades to remove surface materials efficiently, ideal for preparing concrete surfaces without causing extensive structural damage. Hydrodemolition employs high-pressure water alone to selectively remove deteriorated concrete while preserving the reinforcing steel, making it preferable for structural repairs and rehabilitation. Both methods offer environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional mechanical demolition, with hydrodemolition providing greater precision and reduced risk of microcracking in the substrate.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hydromilling | Hydrodemolition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-pressure water jet cutting to remove concrete surface layers. | High-pressure water jet technology for selective concrete removal without damaging rebar. |
| Pressure Range | 2,000 - 5,000 psi | 15,000 - 40,000 psi |
| Target Thickness Removal | Up to 1-2 inches of concrete surface | Up to several inches, including full depth removal |
| Surface Preparation | Smooth finish, ideal for thin overlays and coatings. | Rough, textured surface optimal for new concrete bonding. |
| Damage to Reinforcement | Minimal risk, superficial removal. | Safe for reinforcement; does not damage rebar. |
| Typical Applications | Surface cleaning, thin concrete removal, crack repairs. | Bridge deck rehabilitation, demolition of deteriorated concrete. |
| Environmental Impact | Low dust, water consumption moderate. | Low dust, higher water usage due to volume of concrete removed. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs for light surface work. | Higher costs justified for heavy concrete removal and safety. |
Introduction to Hydromilling and Hydrodemolition
Hydromilling and hydrodemolition are advanced concrete removal techniques utilizing high-pressure water jets to achieve precision surface preparation. Hydromilling involves controlled abrasion using water and abrasive materials to remove surface layers, making it ideal for delicate or detailed tasks. Hydrodemolition employs ultra-high-pressure water to selectively remove deteriorated concrete without damaging the underlying structure, ensuring structural integrity and enhanced bonding for repairs.
Fundamental Principles of Hydromilling
Hydromilling operates on the fundamental principle of using high-pressure water jets to precisely remove concrete or asphalt surfaces without damaging the underlying substrate. This process combines water with abrasive materials to optimize cutting efficiency and surface texture control. The technology ensures minimal dust production and environmental impact compared to traditional mechanical methods.
Core Methods of Hydrodemolition
Hydrodemolition utilizes high-pressure water jets, typically ranging from 15,000 to 40,000 psi, to selectively remove deteriorated or damaged concrete without harming the underlying structure. This method employs advanced robotic systems and specialized nozzles to precisely control the depth and pattern of concrete removal, ensuring optimal surface preparation for repairs. Core techniques in hydrodemolition include surface scaling, partial-depth removal, and full-depth removal, offering versatility in infrastructure rehabilitation and maintenance projects.
Equipment and Technology Comparison
Hydromilling utilizes rotating high-pressure water jets combined with abrasive media to remove concrete surfaces efficiently, relying on specialized rotating heads and slurry recovery systems. Hydrodemolition employs ultra-high-pressure water jets without abrasives, powered by robotic arms or hydraulic machines that precisely fracture and remove deteriorated concrete while preserving underlying rebar integrity. Both methods require advanced pump units capable of delivering pressures exceeding 20,000 psi, with hydrodemolition equipment emphasizing automation for controlled, selective demolition.
Applications in Civil Engineering Projects
Hydromilling and hydrodemolition are advanced water jet techniques used in civil engineering for surface preparation and concrete removal. Hydromilling is ideal for precise surface cleaning, concrete texturing, and paint removal on bridges, tunnels, and pavements, preserving structural integrity. Hydrodemolition excels in heavy-duty concrete removal for repairing damaged slabs, creating rough surfaces for overlays, and removing deteriorated concrete without microcracking, enhancing durability in infrastructure rehabilitation projects.
Advantages and Limitations of Hydromilling
Hydromilling offers precise surface removal with minimal structural impact, making it ideal for concrete surface preparation and repair without deep substrate damage. Its advantages include efficient removal of coatings, adhesives, and deteriorated concrete layers while preserving surrounding materials. Limitations involve slower removal rates compared to hydrodemolition and reduced effectiveness on heavily reinforced structures or very thick concrete slabs.
Benefits and Challenges of Hydrodemolition
Hydrodemolition offers precise concrete removal using high-pressure water jets, minimizing structural damage and reducing dust and vibration compared to traditional methods. Its benefits include enhanced surface preparation for repairs and improved bonding of new concrete layers, while challenges involve high equipment costs and the need for skilled operators. Despite these hurdles, hydrodemolition's environmental advantages and efficiency make it a preferred choice for infrastructure maintenance and rehabilitation projects.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Hydromilling and hydrodemolition both utilize high-pressure water jets but differ in safety and environmental impacts; hydromilling produces less vibration and noise, reducing worker fatigue and structural risks. Hydrodemolition generates significant water runoff containing concrete slurry, requiring effective containment systems to prevent environmental contamination. Proper PPE and water recycling systems are critical to minimizing health hazards and ecological effects in both processes.
Cost Analysis and Project Efficiency
Hydromilling typically offers lower initial costs compared to hydrodemolition due to less specialized equipment and reduced labor requirements, making it suitable for smaller-scale projects with budget constraints. Hydrodemolition provides higher project efficiency by delivering precise concrete removal with minimal surface damage, often reducing repair times and extending structural lifespan, which can result in long-term cost savings despite higher upfront expenses. Choosing between hydromilling and hydrodemolition depends on balancing immediate budget limitations against the potential for improved durability and faster project completion.
Future Trends in Concrete Removal Techniques
Hydromilling and hydrodemolition are advancing with the integration of AI-driven automation and enhanced water recycling systems, reducing environmental impact and operational costs. The future of concrete removal emphasizes precision cutting and selective material extraction to minimize structural damage and improve sustainability. Emerging technologies in sensor-based monitoring and robotic controls are set to revolutionize the efficiency and safety standards of these high-pressure water techniques.
High-pressure water jetting
Hydromilling uses high-pressure water jetting combined with abrasive materials for precise surface removal, while hydrodemolition relies solely on pure high-pressure water jets to efficiently remove concrete without damaging the substrate.
Concrete surface preparation
Hydrodemolition uses high-pressure water jets to precisely remove deteriorated concrete and prepare surfaces without damaging the underlying structure, whereas hydromilling grinds the concrete surface for smoother finishes but is less effective for structural repairs.
Rebar exposure
Hydrodemolition uses higher pressure water jets to expose rebar more precisely and thoroughly than hydromilling, which tends to be less effective in revealing clean rebar surfaces.
Bond strength improvement
Hydromilling enhances bond strength by providing a rougher concrete surface for better adhesion, while hydrodemolition achieves superior bond strength improvement through selective removal of weak concrete and exposing sound substrate with minimal microcracking.
Controlled material removal
Hydromilling offers precise, controlled material removal using high-pressure water jets ideal for delicate surface preparation, while hydrodemolition provides more aggressive, selective concrete removal with minimal structural damage.
Slurry management
Hydromilling produces a slurry with fine concrete particles requiring advanced filtration systems, while hydrodemolition creates coarser slurry demanding robust separation and containment strategies for effective slurry management.
Substrate integrity
Hydromilling preserves substrate integrity by removing concrete layers with minimal impact, whereas hydrodemolition employs high-pressure water jets that may cause microcracking and weaken the substrate structure.
Patch repair readiness
Hydromilling offers quicker patch repair readiness by creating a rough surface profile for optimal bonding, while hydrodemolition provides cleaner concrete removal with minimal microcracking, enhancing structural integrity before patch application.
Scabbled finish
Hydromilling produces a smoother surface with a scabbled finish ideal for concrete repair, while hydrodemolition creates a rougher, more textured scabbled finish that enhances adhesive bonding and structural soundness.
Cavitation erosion
Cavitation erosion significantly impacts hydromilling by accelerating surface degradation through high-pressure water jets, whereas hydrodemolition minimizes this effect by using controlled water flow to selectively remove concrete without excessive surface damage.
hydromilling vs hydrodemolition Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com