Wye and Delta transformer configurations differ in their connection and application, with Wye providing a neutral connection ideal for grounding and load balancing, while Delta offers higher reliability and is resistant to phase loss. Wye transformers typically handle higher voltages and are preferred in transmission systems, whereas Delta transformers are common in distribution networks due to their ability to supply three-phase power without a neutral. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing power delivery and ensuring system stability in electrical engineering projects.
Table of Comparison
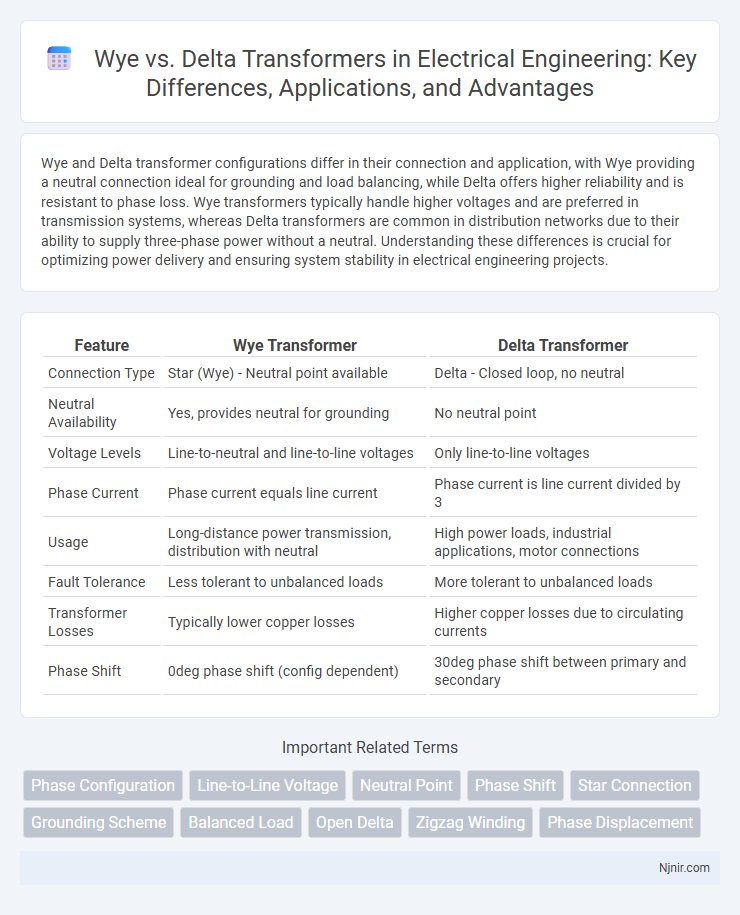
| Feature | Wye Transformer | Delta Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Star (Wye) - Neutral point available | Delta - Closed loop, no neutral |
| Neutral Availability | Yes, provides neutral for grounding | No neutral point |
| Voltage Levels | Line-to-neutral and line-to-line voltages | Only line-to-line voltages |
| Phase Current | Phase current equals line current | Phase current is line current divided by 3 |
| Usage | Long-distance power transmission, distribution with neutral | High power loads, industrial applications, motor connections |
| Fault Tolerance | Less tolerant to unbalanced loads | More tolerant to unbalanced loads |
| Transformer Losses | Typically lower copper losses | Higher copper losses due to circulating currents |
| Phase Shift | 0deg phase shift (config dependent) | 30deg phase shift between primary and secondary |
Introduction to Wye and Delta Transformer Configurations
Wye and Delta transformer configurations represent two fundamental methods for connecting transformer windings in three-phase systems, impacting voltage levels and phase relationships. The Wye (Y) configuration connects each winding to a common neutral point, enabling multiple voltage outputs and grounding options, whereas the Delta (D) configuration connects windings in a closed loop, allowing for circulating currents and better fault tolerance. These configurations influence system characteristics such as load balancing, fault detection, and phase shift, essential for designing efficient electrical power distribution networks.
Fundamental Differences: Wye vs Delta Connections
Wye transformers feature a star-shaped configuration with a neutral point allowing for multiple voltage levels and easier fault detection, while Delta transformers form a closed loop without a neutral, providing higher phase-to-phase voltage and better handling of unbalanced loads. Wye connections are typically used for transmitting power over long distances due to their ability to support neutral grounding and reduce insulation requirements. Delta connections offer robustness in industrial environments by providing phase shift and continuity of service during transformer failures.
Construction and Design Comparison
Wye and Delta transformers differ primarily in their winding configurations, where Wye transformers connect each phase winding to a common neutral point, forming a Y shape, while Delta transformers connect windings end-to-end in a closed loop, creating a triangular arrangement. The Wye design allows for a neutral wire, facilitating grounding and providing multiple voltage levels, whereas the Delta design eliminates the neutral, offering higher phase-to-phase voltage and better handling of unbalanced loads. Constructionally, Wye transformers often feature simpler insulation requirements due to lower phase voltages, while Delta transformers require robust insulation to manage the higher line-to-line voltages inherent in their triangular configuration.
Voltage and Current Characteristics
Wye transformers provide a line-to-neutral voltage that is lower than the line-to-line voltage by a factor of 3, enabling easier grounding and balanced load distribution. Delta transformers deliver the same voltage across all three phases with no neutral, allowing higher phase currents and greater fault tolerance in unbalanced loads. The current in a Wye configuration is lower by 3 in each phase compared to line current, while Delta currents circulate within the winding, providing inherent harmonics reduction and enhanced stability.
Applications in Power Distribution Systems
Wye transformers are commonly used in power distribution systems for stepping down high voltage transmission lines to medium voltage levels, providing a neutral point for grounding and balanced load distribution. Delta transformers are preferred in industrial settings where three-phase power is required without a neutral, offering robustness against phase loss and harmonic currents. Both configurations are integral for optimizing voltage regulation, enhancing system reliability, and catering to specific load demands in electric power networks.
Advantages of Wye Transformers
Wye transformers offer significant advantages such as providing a neutral point, which allows for grounding and enhances system safety by stabilizing voltage during unbalanced loads. They enable easier connection to single-phase loads and facilitate multiple voltage levels from the same transformer, increasing flexibility in power distribution. The inherent design reduces insulation requirements on the phase windings, potentially lowering equipment costs and improving overall system reliability.
Advantages of Delta Transformers
Delta transformers offer significant advantages in power distribution systems, including the ability to provide a stable and balanced three-phase power output even under unbalanced load conditions. Their design enables the handling of higher surge currents, enhancing system reliability during transient faults and short circuits. Additionally, delta transformers do not require a neutral wire, simplifying wiring and reducing installation costs in industrial and commercial applications.
Common Faults and Troubleshooting
Common faults in Wye transformers often include grounding issues due to their neutral point connection, resulting in phase-to-ground faults and unbalanced currents. Delta transformers typically face phase-to-phase faults and circulating currents caused by insulation failures and winding shorts. Troubleshooting involves checking insulation resistance, verifying winding continuity, and analyzing fault current paths using specialized diagnostic tools to identify and rectify the specific malfunction.
Selection Criteria for Wye or Delta Transformers
Selection criteria for Wye or Delta transformers depend on load type, system grounding, and fault tolerance requirements. Wye transformers are preferred for distributing power in systems needing a neutral point for grounding and single-phase loads, offering better overvoltage protection. Delta transformers are chosen for their ability to handle unbalanced loads, provide phase voltage stability, and reduce third harmonics, making them ideal for industrial applications with heavy motor loads.
Summary and Future Trends in Transformer Configurations
Wye and Delta transformer configurations each offer distinct advantages; Wye connections provide a neutral point enabling grounding and line-to-neutral loads, while Delta connections facilitate phase voltage stability and handle unbalanced loads effectively. Future trends emphasize hybrid transformer designs integrating both configurations to optimize efficiency, minimize harmonic distortion, and improve fault tolerance in smart grid applications. Advances in solid-state transformers and real-time monitoring technologies are driving adaptive configuration shifts, enhancing grid reliability and energy distribution flexibility.
Phase Configuration
Wye transformers connect windings in a star configuration offering neutral grounding, while Delta transformers connect windings in a closed loop providing phase-to-phase voltage without a neutral point.
Line-to-Line Voltage
In Wye transformers, the line-to-line voltage is 3 times the line-to-neutral voltage, whereas in Delta transformers, the line-to-line voltage equals the phase voltage.
Neutral Point
The Wye transformer provides a neutral point for grounding and load balancing, while the Delta transformer lacks a true neutral point, impacting fault detection and system stability.
Phase Shift
Wye-Delta transformers introduce a 30-degree phase shift between primary and secondary windings, altering the phase angle to facilitate load balancing and system protection.
Star Connection
A Wye (Star) transformer connection features a neutral point allowing for multiple voltage levels and improved fault detection compared to Delta connections, which lack a neutral and are primarily used for balanced loads.
Grounding Scheme
Wye transformers provide a neutral grounding point allowing effective fault current return paths, while delta transformers typically rely on grounding through grounding transformers or external methods to manage unbalanced loads and grounding faults.
Balanced Load
Balanced loads in Wye transformers provide neutral grounding and allow phase voltage measurement, whereas Delta transformers distribute phase currents evenly without a neutral point, enhancing fault tolerance.
Open Delta
Open Delta transformer connections provide a cost-effective and reliable solution for three-phase power supply using only two transformers instead of three in a Delta system.
Zigzag Winding
Zigzag winding in transformers offers enhanced grounding and harmonic suppression compared to standard Wye and Delta configurations, improving stability and power quality in three-phase systems.
Phase Displacement
Phase displacement in Wye-Delta transformers typically measures 30 degrees, affecting vector group classification and load balancing.
Wye vs Delta Transformer Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com