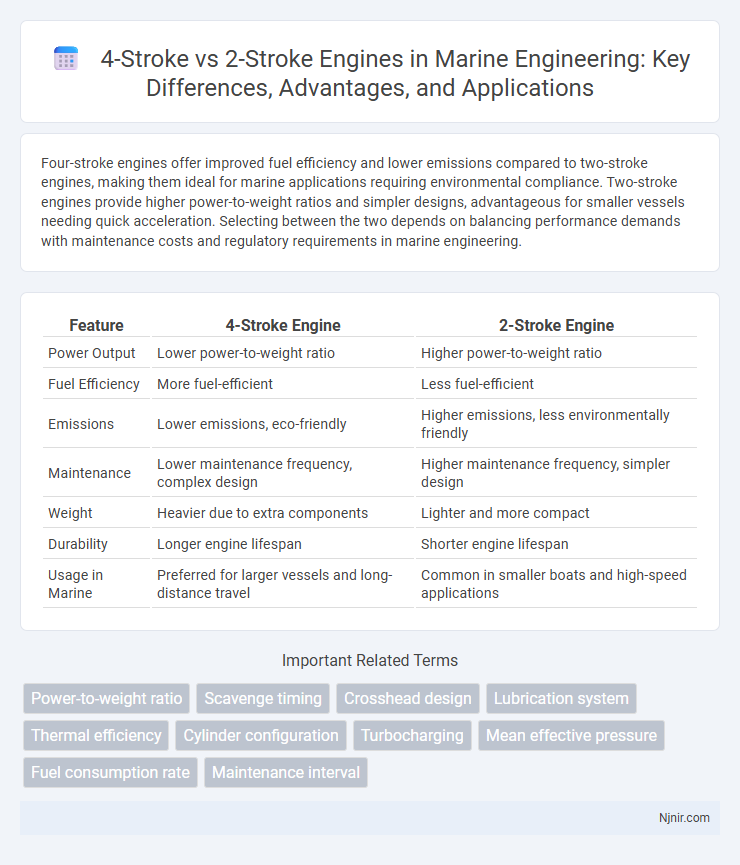
Four-stroke engines offer improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions compared to two-stroke engines, making them ideal for marine applications requiring environmental compliance. Two-stroke engines provide higher power-to-weight ratios and simpler designs, advantageous for smaller vessels needing quick acceleration. Selecting between the two depends on balancing performance demands with maintenance costs and regulatory requirements in marine engineering.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 4-Stroke Engine | 2-Stroke Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Lower power-to-weight ratio | Higher power-to-weight ratio |
| Fuel Efficiency | More fuel-efficient | Less fuel-efficient |
| Emissions | Lower emissions, eco-friendly | Higher emissions, less environmentally friendly |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance frequency, complex design | Higher maintenance frequency, simpler design |
| Weight | Heavier due to extra components | Lighter and more compact |
| Durability | Longer engine lifespan | Shorter engine lifespan |
| Usage in Marine | Preferred for larger vessels and long-distance travel | Common in smaller boats and high-speed applications |
Overview of 4-Stroke and 2-Stroke Marine Engines
4-stroke marine engines operate through four distinct piston strokes--intake, compression, power, and exhaust--providing efficient fuel combustion and lower emissions. In contrast, 2-stroke marine engines complete a power cycle in just two strokes, offering higher power-to-weight ratios and simpler design but increased fuel consumption and emissions. These fundamental operational differences influence their applications, with 4-stroke engines favored for fuel efficiency and environmental compliance, while 2-stroke engines suit high-power marine vessels requiring robust performance.
Core Operating Principles
A 4-stroke engine operates through four distinct phases: intake, compression, power, and exhaust, optimizing fuel efficiency and emissions by completing one power cycle per two revolutions. In contrast, a 2-stroke engine combines these phases into two strokes, delivering a power stroke every revolution for higher power density but with increased fuel consumption and emissions. The fundamental difference lies in the timing and overlap of intake and exhaust processes, impacting engine performance, efficiency, and environmental impact.
Power Output and Efficiency Comparison
Four-stroke engines typically deliver higher fuel efficiency and produce cleaner emissions due to separate intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes, resulting in more complete combustion. Two-stroke engines generate greater power output relative to their size and weight by firing once every revolution, but often sacrifice fuel efficiency and emit higher levels of pollutants. The power-to-weight ratio of two-stroke engines makes them suitable for applications requiring high power in compact designs, while four-stroke engines excel in energy efficiency and durability.
Fuel Consumption Differences
4-stroke engines generally exhibit lower fuel consumption compared to 2-stroke engines due to their more efficient combustion process and better fuel-air mixture control. While 2-stroke engines complete a power cycle in two strokes, leading to higher fuel burn and loss through exhaust, 4-stroke engines complete it in four strokes, which reduces unburned fuel escape and improves fuel efficiency. Consequently, 4-stroke engines are preferred in applications requiring better fuel economy and lower emissions.
Emissions and Environmental Impact
4-stroke engines produce significantly lower emissions compared to 2-stroke engines due to more efficient fuel combustion and separate lubrication systems, reducing unburned hydrocarbons and particulate matter released into the atmosphere. 2-stroke engines often emit higher levels of pollutants, including carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, because they mix oil with fuel, resulting in incomplete combustion and increased environmental impact. Regulatory agencies favor 4-stroke engines for their compliance with stricter emission standards and better fuel economy, making them more eco-friendly for both recreational and commercial use.
Maintenance and Durability
4-stroke engines generally require less frequent maintenance due to their more efficient lubrication system and separate compartments for fuel and oil, which reduces wear and extends engine life. In contrast, 2-stroke engines mix oil with fuel, leading to higher engine deposits and more frequent maintenance intervals to prevent fouling and wear. Durability in 4-stroke engines is typically superior, supported by robust components and lower operating temperatures compared to the simpler, lighter 2-stroke design.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Operational
A 2-stroke engine typically incurs lower initial costs due to its simpler design and fewer components, making it more affordable for entry-level applications. Operational expenses for 2-stroke engines are generally higher because of increased fuel consumption and more frequent maintenance requirements caused by faster wear and oil mixing. In contrast, 4-stroke engines, though costlier upfront, offer improved fuel efficiency and longevity, resulting in reduced long-term maintenance and fuel expenses.
Suitability for Different Vessel Types
4-stroke engines offer superior fuel efficiency and lower emissions, making them ideal for larger vessels such as yachts and commercial boats that require sustained power and fuel economy. In contrast, 2-stroke engines provide higher power-to-weight ratios and simpler maintenance, suiting smaller vessels like outboard motorboats and personal watercraft where weight and compactness are critical. Each engine type aligns with specific maritime needs, balancing performance, efficiency, and operational demands.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in 4-stroke engines include direct fuel injection and variable valve timing, enhancing fuel efficiency and emissions control compared to traditional designs. Modern 2-stroke engines benefit from innovations like electronic fuel injection and improved lubrication systems, reducing pollution and increasing power output. These developments have significantly narrowed the performance and environmental gaps between 4-stroke and 2-stroke engines in applications such as motorcycles and small machinery.
Future Trends in Marine Propulsion Systems
Future trends in marine propulsion systems emphasize the shift from traditional 2-stroke engines to advanced 4-stroke engines due to stricter environmental regulations and the need for improved fuel efficiency. Innovations in 4-stroke marine engines integrate hybrid technology, alternative fuels such as LNG and hydrogen, and enhanced emissions control systems to comply with IMO Tier III standards. The transition supports reduced NOx and particulate matter emissions, aligning with global efforts to decarbonize the maritime industry and promote sustainable shipping practices.
Power-to-weight ratio
A 2-stroke engine typically offers a higher power-to-weight ratio than a 4-stroke engine due to its simpler design and ability to complete a power cycle in two strokes.
Scavenge timing
The scavenge timing in a 2-stroke engine is precisely timed for rapid exhaust and intake within each crankshaft revolution, while a 4-stroke engine completes scavenging during separate exhaust and intake strokes, optimizing efficiency and reducing emissions.
Crosshead design
Crosshead design in 4-stroke engines enhances durability and efficient piston movement by separating the piston rod forces from the crankshaft, unlike 2-stroke engines which typically lack crossheads, resulting in simpler but less robust mechanisms.
Lubrication system
4-stroke engines use a separate lubrication system with an oil reservoir and pump to circulate oil, while 2-stroke engines rely on a premixed fuel and oil blend for lubrication.
Thermal efficiency
A 4-stroke engine generally exhibits higher thermal efficiency than a 2-stroke engine due to improved fuel combustion and reduced heat loss during its intake and exhaust cycles.
Cylinder configuration
Four-stroke engines typically have more complex cylinder configurations with separate intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes, while two-stroke engines use simpler configurations where each cylinder completes a power cycle in just two strokes for faster power delivery.
Turbocharging
Turbocharging significantly enhances the efficiency and power output of 4-stroke engines by improving air intake and combustion, whereas its application in 2-stroke engines is more complex due to their simpler design and reliance on crankcase scavenging.
Mean effective pressure
Four-stroke engines typically exhibit higher mean effective pressure (MEP) compared to two-stroke engines due to more efficient combustion cycles and better volumetric efficiency.
Fuel consumption rate
A 4-stroke engine typically has a lower fuel consumption rate compared to a 2-stroke engine due to its more efficient combustion cycle and better fuel economy.
Maintenance interval
4-stroke engines require longer maintenance intervals due to separate lubrication systems, while 2-stroke engines need more frequent servicing because of their oil-fuel mixture combustion.
4-stroke engine vs 2-stroke engine Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com