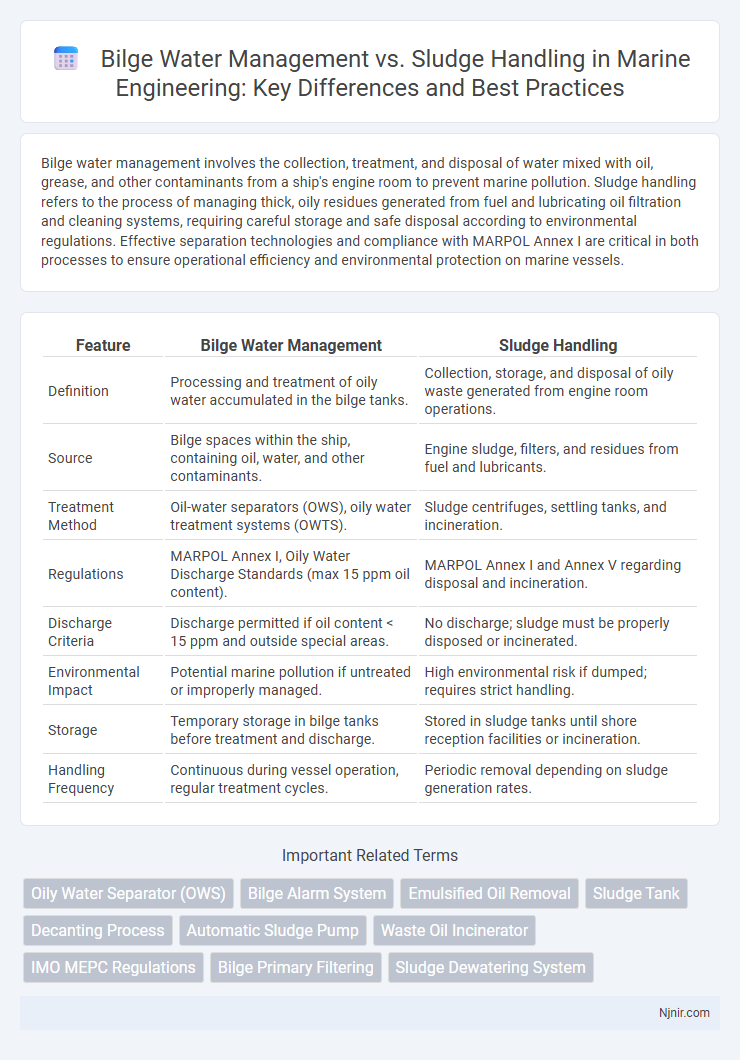
Bilge water management involves the collection, treatment, and disposal of water mixed with oil, grease, and other contaminants from a ship's engine room to prevent marine pollution. Sludge handling refers to the process of managing thick, oily residues generated from fuel and lubricating oil filtration and cleaning systems, requiring careful storage and safe disposal according to environmental regulations. Effective separation technologies and compliance with MARPOL Annex I are critical in both processes to ensure operational efficiency and environmental protection on marine vessels.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bilge Water Management | Sludge Handling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processing and treatment of oily water accumulated in the bilge tanks. | Collection, storage, and disposal of oily waste generated from engine room operations. |
| Source | Bilge spaces within the ship, containing oil, water, and other contaminants. | Engine sludge, filters, and residues from fuel and lubricants. |
| Treatment Method | Oil-water separators (OWS), oily water treatment systems (OWTS). | Sludge centrifuges, settling tanks, and incineration. |
| Regulations | MARPOL Annex I, Oily Water Discharge Standards (max 15 ppm oil content). | MARPOL Annex I and Annex V regarding disposal and incineration. |
| Discharge Criteria | Discharge permitted if oil content < 15 ppm and outside special areas. | No discharge; sludge must be properly disposed or incinerated. |
| Environmental Impact | Potential marine pollution if untreated or improperly managed. | High environmental risk if dumped; requires strict handling. |
| Storage | Temporary storage in bilge tanks before treatment and discharge. | Stored in sludge tanks until shore reception facilities or incineration. |
| Handling Frequency | Continuous during vessel operation, regular treatment cycles. | Periodic removal depending on sludge generation rates. |
Introduction to Bilge Water and Sludge in Marine Engineering
Bilge water in marine engineering refers to the mixture of water, oil, grease, and other contaminants collected from the lowest part of a ship's hull, requiring effective treatment before discharge to meet environmental regulations. Sludge comprises thick, semi-solid residues generated from engine room operations, including fuel oil residues and waste lubricants, demanding specialized handling to prevent marine pollution. Efficient bilge water management and sludge handling systems are critical for maintaining vessel compliance with international maritime environmental standards such as MARPOL Annex I and Annex V.
Regulatory Framework for Bilge Water and Sludge Management
The regulatory framework for bilge water management is primarily governed by the International Maritime Organization's MARPOL Annex I, which strictly limits oil content in discharged bilge water to 15 parts per million to prevent marine pollution. Sludge handling is regulated under MARPOL Annex V, mandating proper collection, storage, and discharge protocols to manage residues from oil filtering and sludge tank cleaning, ensuring environmental compliance. Both frameworks emphasize stringent monitoring, record-keeping, and the use of certified pollution prevention equipment to align with global environmental protection standards.
Composition and Sources of Bilge Water vs. Sludge
Bilge water primarily consists of a mixture of seawater, oil residues, grease, detergents, and miscellaneous shipboard waste fluids, originating from machinery spaces, engine rooms, and deck runoff. Sludge, on the other hand, is a thick, semi-solid waste generated primarily from the treatment of fuel and lubricating oils, as well as from oily water separators and bilge water processing systems. While bilge water contains emulsified oils and water, sludge has a higher concentration of hydrocarbons, sediments, and heavy metals due to its concentrated and treated nature.
Bilge Water Treatment Methods and Technologies
Bilge water treatment methods employ advanced technologies such as oily water separators (OWS), centrifuges, and chemical dosing systems to efficiently remove oil pollutants and meet MARPOL regulations. Membrane filtration and bioremediation techniques are increasingly integrated to enhance the separation of hydrocarbons and biodegrade contaminants in bilge water. In contrast to sludge handling, which focuses on solid waste dewatering and thermal treatment, bilge water management prioritizes liquid phase separation and purification to prevent marine pollution.
Sludge Handling and Disposal Procedures
Sludge handling involves the collection, treatment, and disposal of waste solids generated from ship operations, requiring specialized equipment such as sludge tanks, centrifuges, and incinerators to ensure environmental compliance. Proper disposal procedures mandate safe transfer to shore reception facilities or compliant incineration onboard, preventing marine pollution under MARPOL Annex I and V regulations. Effective sludge management minimizes hazardous waste buildup, safeguarding marine ecosystems and adhering to international maritime environmental standards.
Environmental Impacts of Bilge Water Discharge
Bilge water discharge contains hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and other toxic substances, posing significant risks to marine ecosystems through contamination and bioaccumulation. Effective bilge water management systems utilize oil-water separators and filtration technologies to reduce environmental pollution and comply with MARPOL regulations. In contrast, sludge handling involves the treatment and disposal of solid waste, with less direct impact on water quality but requiring careful management to prevent soil and air contamination.
Pollution Prevention: Best Practices in Sludge Management
Effective sludge handling is crucial for pollution prevention by minimizing the release of harmful contaminants into marine environments, unlike bilge water management which primarily targets oily water separation. Best practices in sludge management include proper containment, regular monitoring, and the use of advanced treatment technologies such as dewatering and thermal drying to reduce volume and toxicity. Adopting these measures prevents the discharge of hazardous substances, ensuring compliance with MARPOL Annex I and IV regulations for marine pollution control.
Operational Challenges in Bilge Water Management
Bilge water management faces significant operational challenges such as the separation of oil from water to meet strict environmental regulations and prevent marine pollution. Equipment fouling and maintenance issues due to sludge buildup complicate continuous treatment processes, leading to increased downtime and operational costs. In contrast, sludge handling primarily deals with the safe storage, dewatering, and disposal of solid residues, with less complexity in real-time processing compared to bilge water treatment.
Innovations in Bilge and Sludge Management Systems
Innovations in bilge water management have introduced advanced separation technologies and real-time monitoring systems that enhance pollutant removal efficiency and compliance with IMO regulations. Sludge handling systems now integrate automated dewatering and thermal treatment processes, reducing volume and improving waste disposal sustainability onboard vessels. Both systems leverage IoT and AI to optimize operational workflows, minimize environmental impact, and ensure regulatory adherence.
Future Trends and Sustainable Solutions in Marine Waste Handling
Emerging future trends in bilge water management emphasize advanced separation technologies and bio-remediation to minimize environmental impact and comply with stricter IMO regulations. Sludge handling is shifting towards energy recovery methods such as anaerobic digestion and thermal hydrolysis, promoting circular economy principles within marine waste management. Integrating AI-driven monitoring systems enhances operational efficiency and sustainability, aligning with global maritime environmental goals.
Oily Water Separator (OWS)
Oily Water Separator (OWS) is essential in bilge water management for efficiently separating oil from water to meet environmental regulations, whereas sludge handling involves managing thicker, heavier waste residues requiring different treatment methods.
Bilge Alarm System
Bilge Alarm Systems optimize bilge water management by detecting hazardous liquid levels to prevent environmental pollution and regulatory fines, whereas sludge handling primarily focuses on solid waste processing for disposal or recycling.
Emulsified Oil Removal
Emulsified oil removal in bilge water management employs advanced separation technologies such as ultrafiltration and chemical demulsifiers, whereas sludge handling primarily focuses on the dewatering and disposal of solid waste with limited oil-water separation efficacy.
Sludge Tank
Sludge tank systems in sludge handling efficiently separate and store oily residues and solid waste from bilge water, enhancing environmental compliance and operational safety.
Decanting Process
The decanting process in bilge water management efficiently separates oil from water to meet environmental discharge standards, whereas in sludge handling, it primarily reduces solids content to facilitate safer disposal or further treatment.
Automatic Sludge Pump
Automatic sludge pumps enhance bilge water management by efficiently removing sludge, reducing manual labor, and preventing contamination in marine waste systems.
Waste Oil Incinerator
Efficient bilge water management and sludge handling optimize Waste Oil Incinerator performance by reducing hazardous waste volume and enhancing combustion efficiency.
IMO MEPC Regulations
IMO MEPC regulations mandate stringent bilge water management standards to prevent marine pollution, while sludge handling protocols emphasize safe storage, treatment, and disposal in compliance with MARPOL Annex I requirements.
Bilge Primary Filtering
Bilge primary filtering efficiently separates oil and contaminants from ship bilge water, reducing environmental impact and improving compliance compared to traditional sludge handling methods.
Sludge Dewatering System
Sludge dewatering systems enhance bilge water management by efficiently reducing sludge volume and moisture content for easier handling and disposal.
Bilge water management vs Sludge handling Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com