Condition-based maintenance in marine engineering relies on real-time data from sensors to assess equipment health and predict failures, optimizing maintenance schedules and minimizing downtime. Time-based maintenance follows preset intervals regardless of equipment condition, which can lead to unnecessary servicing or unexpected breakdowns. Implementing condition-based maintenance enhances vessel reliability, reduces operational costs, and extends the lifespan of marine machinery.
Table of Comparison
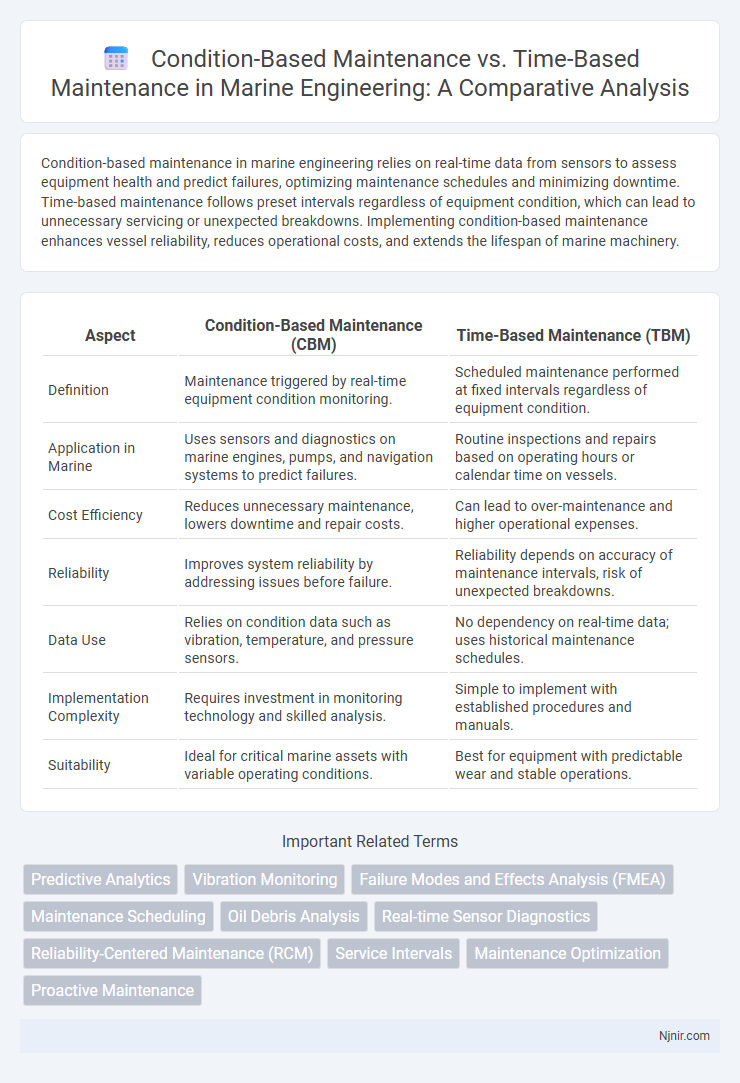
| Aspect | Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) | Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance triggered by real-time equipment condition monitoring. | Scheduled maintenance performed at fixed intervals regardless of equipment condition. |
| Application in Marine | Uses sensors and diagnostics on marine engines, pumps, and navigation systems to predict failures. | Routine inspections and repairs based on operating hours or calendar time on vessels. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces unnecessary maintenance, lowers downtime and repair costs. | Can lead to over-maintenance and higher operational expenses. |
| Reliability | Improves system reliability by addressing issues before failure. | Reliability depends on accuracy of maintenance intervals, risk of unexpected breakdowns. |
| Data Use | Relies on condition data such as vibration, temperature, and pressure sensors. | No dependency on real-time data; uses historical maintenance schedules. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires investment in monitoring technology and skilled analysis. | Simple to implement with established procedures and manuals. |
| Suitability | Ideal for critical marine assets with variable operating conditions. | Best for equipment with predictable wear and stable operations. |
Introduction to Maintenance Strategies in Marine Engineering
Condition-based maintenance in marine engineering relies on real-time data from equipment sensors to predict failures and optimize servicing intervals, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Time-based maintenance schedules regular inspections and repairs at fixed intervals regardless of equipment condition, ensuring consistent upkeep but potentially leading to unnecessary maintenance. Selecting between these strategies depends on factors such as vessel type, operational conditions, and cost-effectiveness, with condition-based methods increasingly favored for their efficiency and improved reliability.
Defining Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) is a proactive maintenance strategy that relies on real-time data and sensor monitoring to assess equipment health and performance. It triggers maintenance activities only when specific indicators, such as vibration levels, temperature, or pressure thresholds, signal potential failure or deterioration. CBM reduces unnecessary maintenance interventions compared to Time-Based Maintenance (TBM), which schedules tasks at fixed intervals regardless of actual equipment condition.
Defining Time-Based Maintenance (TBM)
Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) schedules maintenance activities at predetermined intervals regardless of equipment condition, relying on historical data and manufacturer recommendations to prevent failures. This method emphasizes routine inspections, parts replacement, or system overhauls after set operating hours or calendar periods to maintain reliability. While straightforward to implement, TBM may lead to unnecessary maintenance or unexpected breakdowns if equipment wear varies.
Key Differences Between CBM and TBM
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) relies on real-time data from sensors to monitor equipment health and trigger maintenance only when specific indicators show deterioration, enhancing efficiency and reducing unnecessary work. Time-based maintenance (TBM) schedules maintenance activities at fixed intervals regardless of equipment condition, which can lead to either premature servicing or increased risk of unexpected failures. Key differences include CBM's reliance on predictive analytics and sensor data versus TBM's reliance on historical usage patterns and fixed time schedules.
Advantages of Condition-Based Maintenance in Marine Applications
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) in marine applications offers significant advantages by enabling real-time monitoring of equipment health, which reduces unplanned downtime and extends the lifespan of critical components such as engines and propulsion systems. Unlike time-based maintenance that relies on fixed schedules, CBM uses sensor data and predictive analytics to perform maintenance only when necessary, improving operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. This proactive approach enhances safety by preventing catastrophic failures and optimizing resource allocation within marine vessels.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Time-Based Maintenance
Time-based maintenance (TBM) often leads to unnecessary servicing and increased operational costs due to fixed schedules that do not consider actual equipment condition. This approach can result in premature part replacements or unexpected failures between intervals, reducing overall asset reliability. TBM lacks flexibility and fails to optimize maintenance resources compared to condition-based maintenance (CBM), which uses real-time data for predictive decision-making.
Implementation Challenges for CBM in Marine Vessels
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) implementation in marine vessels faces challenges such as the integration of advanced sensor systems and real-time data analytics in harsh marine environments, which often requires significant upfront investment and specialized technical expertise. Data reliability and the complexity of interpreting sensor outputs to predict equipment failures accurately complicate the transition from traditional time-based maintenance schedules. Limited crew training and resistance to change further hinder the effective adoption of CBM, impacting operational efficiency and maintenance cost savings.
Cost Efficiency: CBM vs TBM in Marine Operations
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) significantly reduces operational costs in marine operations by minimizing unnecessary maintenance activities and preventing equipment failures through real-time monitoring and predictive analytics. Time-based maintenance (TBM) often incurs higher expenses due to scheduled, routine servicing regardless of actual equipment condition, leading to potential over-maintenance or unexpected downtime. The integration of CBM systems enhances cost efficiency by optimizing maintenance intervals, reducing labor costs, and extending the lifespan of marine machinery.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications in the Marine Industry
Case studies highlight that condition-based maintenance (CBM) in the marine industry significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs by leveraging real-time sensor data to monitor engine performance and hull integrity. Time-based maintenance (TBM), though widely used for scheduled tasks like oil changes and inspections, often leads to unnecessary part replacements and unplanned failures due to fixed intervals. Comparative analyses from shipping companies demonstrate that CBM enhances operational reliability and prolongs equipment life by predicting faults before they occur, making it a preferred strategy for modern fleet management.
Future Trends and Innovations in Marine Maintenance
Condition-based maintenance leverages real-time sensor data and predictive analytics to optimize vessel performance and reduce downtime, emerging as the future standard in marine maintenance. Advances in IoT integration, AI-powered diagnostics, and digital twins enable proactive repairs and smarter asset management, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and safety. Time-based maintenance, while still prevalent, faces gradual replacement by these intelligent systems that minimize unnecessary servicing and extend equipment lifespan.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics enhances condition-based maintenance by using real-time sensor data and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures, reducing downtime compared to the fixed schedules of time-based maintenance.
Vibration Monitoring
Vibration monitoring enables condition-based maintenance by accurately detecting mechanical anomalies in real-time, reducing unnecessary downtime and maintenance costs compared to fixed-interval time-based maintenance schedules.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Condition-based maintenance enhances Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) by providing real-time data to detect failure modes early, improving risk prioritization compared to the periodic, less adaptive approach of time-based maintenance.
Maintenance Scheduling
Condition-based maintenance schedules optimize maintenance timing using real-time equipment data, reducing downtime compared to fixed-interval time-based maintenance schedules.
Oil Debris Analysis
Oil Debris Analysis in condition-based maintenance detects machinery wear and prevents failures more effectively than scheduled inspections in time-based maintenance.
Real-time Sensor Diagnostics
Real-time sensor diagnostics in condition-based maintenance enable precise equipment monitoring and predictive failure detection, surpassing the fixed scheduling limitations of time-based maintenance.
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) prioritizes condition-based maintenance by using real-time data and asset performance indicators to optimize maintenance schedules, unlike time-based maintenance which relies on fixed intervals regardless of equipment condition.
Service Intervals
Condition-based maintenance optimizes service intervals by monitoring equipment performance in real-time, reducing unnecessary maintenance compared to fixed time-based schedules.
Maintenance Optimization
Condition-based maintenance leverages real-time equipment data to optimize maintenance schedules, reducing downtime and costs compared to the fixed intervals used in time-based maintenance.
Proactive Maintenance
Condition-based maintenance reduces unexpected failures and optimizes equipment uptime by monitoring real-time asset health, making it a more proactive approach compared to the scheduled intervals of time-based maintenance.
Condition-based maintenance vs Time-based maintenance Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com