Variable frequency drives (VFDs) provide precise control over motor speed and torque by adjusting the power frequency, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing mechanical stress in marine applications. Soft starters gradually ramp up motor voltage, minimizing inrush current and avoiding electrical and mechanical shock during startup but lack continuous speed control. Choosing between a VFD and a soft starter depends on the need for variable speed operation versus simple starting current management in marine propulsion systems.
Table of Comparison
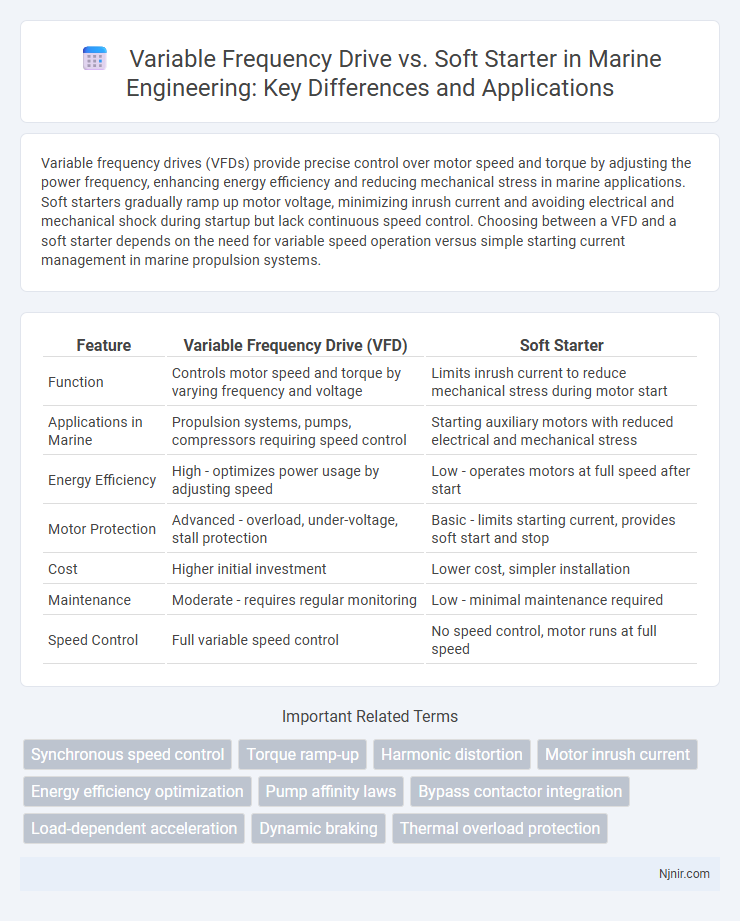
| Feature | Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | Soft Starter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Controls motor speed and torque by varying frequency and voltage | Limits inrush current to reduce mechanical stress during motor start |
| Applications in Marine | Propulsion systems, pumps, compressors requiring speed control | Starting auxiliary motors with reduced electrical and mechanical stress |
| Energy Efficiency | High - optimizes power usage by adjusting speed | Low - operates motors at full speed after start |
| Motor Protection | Advanced - overload, under-voltage, stall protection | Basic - limits starting current, provides soft start and stop |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost, simpler installation |
| Maintenance | Moderate - requires regular monitoring | Low - minimal maintenance required |
| Speed Control | Full variable speed control | No speed control, motor runs at full speed |
Introduction to Motor Control in Marine Engineering
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) and soft starters are essential motor control devices in marine engineering, optimizing the operation of electric motors aboard vessels. VFDs regulate motor speed and torque by adjusting frequency and voltage, enhancing energy efficiency and precise control during propulsion and auxiliary systems. Soft starters limit inrush current during motor startup, reducing mechanical stress and electrical demand, crucial for protecting marine equipment and ensuring smooth vessel operation.
Understanding Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) precisely control motor speed and torque by adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied to the electric motor, enhancing energy efficiency and process control. Unlike soft starters that only limit inrush current during startup, VFDs enable continuous speed variation for applications requiring variable speed operation. This capability reduces mechanical stress, lowers energy consumption, and optimizes performance in pumps, fans, and conveyor systems.
Overview of Soft Starters in Marine Applications
Soft starters in marine applications provide controlled acceleration and deceleration of electric motors, reducing mechanical stress on pumps, fans, and propulsion systems. These devices limit inrush current during startup, enhancing electrical system stability aboard ships and minimizing wear on motor components. Their compact design and ease of integration make soft starters ideal for improving the reliability and efficiency of marine motor control systems.
Key Differences Between VFDs and Soft Starters
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) regulate motor speed by adjusting voltage and frequency, enabling precise control over acceleration, deceleration, and energy consumption. Soft starters limit initial inrush current by gradually increasing voltage but do not control motor speed once started. VFDs offer enhanced energy efficiency and operational flexibility compared to soft starters, which primarily focus on reducing mechanical stress during motor startup.
Energy Efficiency: VFD vs Soft Starter
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) optimize energy efficiency by continuously adjusting motor speed to match load requirements, significantly reducing power consumption during partial load conditions. Soft starters provide smooth motor acceleration but operate at full voltage once running, resulting in minimal energy savings compared to VFDs. In industrial applications where variable speed control and energy reduction are critical, VFDs offer superior efficiency benefits over soft starters.
Impact on Marine Motor Lifespan
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) offer precise motor speed control and reduce mechanical stress by gradually ramping current, significantly extending marine motor lifespan through smoother startups and reduced thermal overload. Soft starters limit inrush current and minimize mechanical shock during startup but lack the continuous speed control that VFDs provide, resulting in less overall motor life enhancement. Implementing VFDs in marine applications enhances energy efficiency and reduces wear, making them superior to soft starters for preserving long-term motor durability.
Application Scenarios in Marine Systems
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) are ideal for marine propulsion systems requiring precise speed control and energy efficiency, such as thrusters and pumps in dynamic positioning systems. Soft starters are better suited for applications with high starting torque demands but constant speed operation, like large marine compressors and cargo winches, where smooth acceleration reduces mechanical stress. Selecting VFDs enhances fuel savings and operational flexibility, while soft starters extend equipment lifespan by minimizing electrical and mechanical stresses during startup.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) require more complex installation involving proper grounding, electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters, and thermal management compared to soft starters, which have simpler wiring and straightforward setup. Maintenance for VFDs includes regular inspection of cooling fans, capacitors, and firmware updates, whereas soft starters demand less frequent upkeep primarily focused on contactor health and coil integrity. Both devices benefit from a clean, dry environment, but VFDs necessitate stricter adherence to manufacturer guidelines to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operating Costs
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) typically have a higher initial investment compared to soft starters due to their complex technology and advanced control features. However, VFDs can offer significant operating cost savings by reducing energy consumption through precise motor speed control and improving process efficiency. Soft starters provide a lower upfront cost solution with simpler motor protection but lack the energy-saving benefits, leading to potentially higher long-term operating expenses.
Choosing the Right Solution for Marine Vessels
Variable frequency drives (VFDs) provide precise speed control and energy efficiency for marine vessels, enhancing propulsion system performance and reducing operational costs. Soft starters limit inrush current and protect mechanical components during engine startup, ideal for applications requiring gentle acceleration without speed variation. Selecting between VFDs and soft starters depends on vessel operational demands, with VFDs favored for variable-speed applications and soft starters preferred for simple, cost-effective motor protection.
Synchronous speed control
Variable frequency drives provide precise synchronous speed control by continuously adjusting motor frequency, whereas soft starters only enable smooth starting without speed regulation.
Torque ramp-up
Variable frequency drives offer precise torque ramp-up control by adjusting motor speed smoothly, whereas soft starters provide limited torque control primarily during the initial startup phase.
Harmonic distortion
Variable frequency drives significantly increase harmonic distortion in electrical systems compared to soft starters, which produce minimal harmonics and better maintain power quality.
Motor inrush current
Variable frequency drives reduce motor inrush current by gradually ramping voltage and frequency, whereas soft starters limit inrush current only during startup without controlling motor speed.
Energy efficiency optimization
Variable frequency drives optimize energy efficiency by precisely controlling motor speed and torque, whereas soft starters primarily reduce initial inrush current without continuous energy savings.
Pump affinity laws
Variable frequency drives optimize pump performance by adjusting motor speed according to affinity laws, while soft starters provide only reduced starting torque without influencing flow or power characteristics.
Bypass contactor integration
Variable frequency drives with integrated bypass contactors enable seamless motor start-up and operation control, while soft starters with bypass contactors provide smooth motor acceleration followed by direct line connection to minimize energy loss and component wear.
Load-dependent acceleration
Variable frequency drives provide precise load-dependent acceleration by continuously adjusting motor speed, while soft starters offer limited load-dependent control through initial voltage ramp-up.
Dynamic braking
Variable frequency drives provide precise dynamic braking control by adjusting motor speed and torque, whereas soft starters offer limited or no dynamic braking capabilities.
Thermal overload protection
Variable frequency drives provide precise thermal overload protection by continuously monitoring motor current and adjusting voltage, whereas soft starters offer limited thermal protection by controlling initial inrush current without continuous current regulation.
Variable frequency drive vs Soft starter Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com