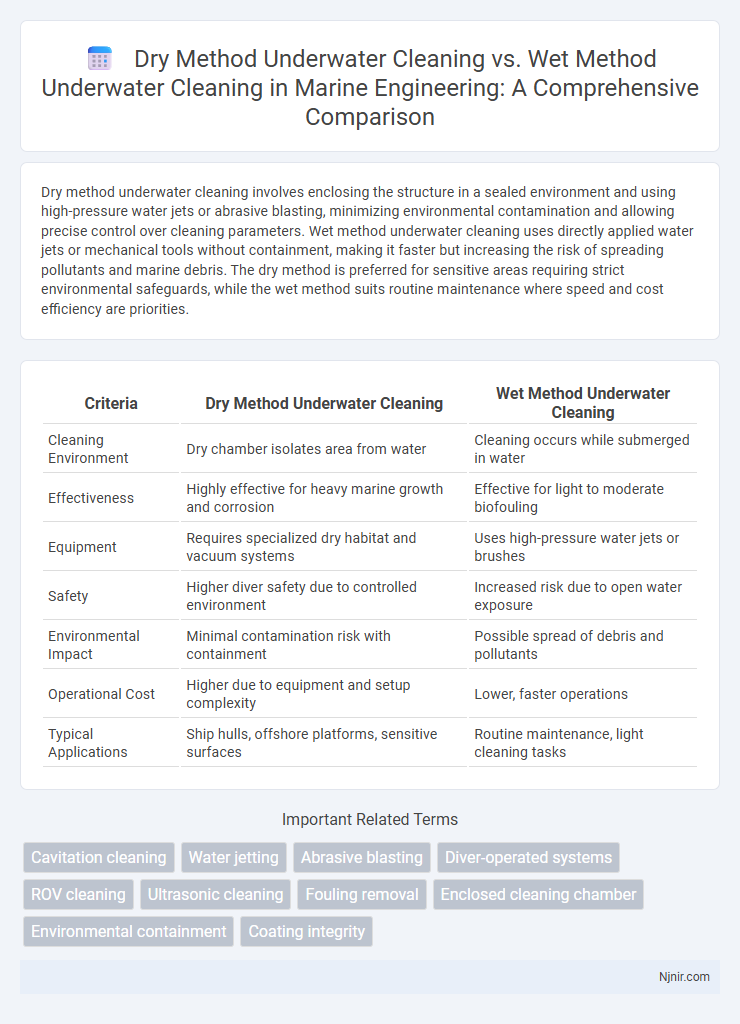
Dry method underwater cleaning involves enclosing the structure in a sealed environment and using high-pressure water jets or abrasive blasting, minimizing environmental contamination and allowing precise control over cleaning parameters. Wet method underwater cleaning uses directly applied water jets or mechanical tools without containment, making it faster but increasing the risk of spreading pollutants and marine debris. The dry method is preferred for sensitive areas requiring strict environmental safeguards, while the wet method suits routine maintenance where speed and cost efficiency are priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Dry Method Underwater Cleaning | Wet Method Underwater Cleaning |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning Environment | Dry chamber isolates area from water | Cleaning occurs while submerged in water |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective for heavy marine growth and corrosion | Effective for light to moderate biofouling |
| Equipment | Requires specialized dry habitat and vacuum systems | Uses high-pressure water jets or brushes |
| Safety | Higher diver safety due to controlled environment | Increased risk due to open water exposure |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal contamination risk with containment | Possible spread of debris and pollutants |
| Operational Cost | Higher due to equipment and setup complexity | Lower, faster operations |
| Typical Applications | Ship hulls, offshore platforms, sensitive surfaces | Routine maintenance, light cleaning tasks |
Introduction to Underwater Cleaning Methods in Marine Engineering
Dry method underwater cleaning in marine engineering involves deploying specialized cofferdams or enclosures to create a sealed, dry work environment around submerged structures, facilitating precise cleaning without water interference. Wet method underwater cleaning uses divers or remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) equipped with high-pressure jets or brushes directly in the aquatic environment, enabling quicker removal of biofouling and contaminants. Both methods address biofouling management in ship hull maintenance and offshore structures, balancing effectiveness, operational complexity, and environmental impact.
Overview of Dry Method Underwater Cleaning
The dry method underwater cleaning involves isolating the submerged structure from water using a cofferdam or a similar enclosure, enabling cleaning in a controlled, water-free environment. This technique provides superior precision for removing marine growth, corrosion, and contaminants, minimizing environmental impact and preventing debris dispersion. It is especially effective for sensitive surfaces and complex inspections, offering enhanced safety and operational efficiency compared to the wet method.
Overview of Wet Method Underwater Cleaning
Wet method underwater cleaning involves the direct application of cleaning agents and equipment while the structure remains submerged, enabling the removal of marine growth, sediments, and biofilms without the need for dewatering. This method uses high-pressure water jets, brushes, or scrapers operated by divers or remotely operated vehicles to efficiently clean ship hulls, offshore platforms, and underwater pipelines. The wet method reduces downtime and environmental impact by preventing the release of contaminants into surrounding waters through the use of containment systems and environmentally friendly cleaning agents.
Key Differences Between Dry and Wet Cleaning Techniques
Dry method underwater cleaning involves the use of enclosed, controlled environments such as hyperbaric chambers or cofferdams to isolate the work area from water, allowing for precise cleaning without water interference. In contrast, wet method underwater cleaning is performed directly in the water using high-pressure jets, brushes, or abrasive tools, making it faster and more cost-effective but less controlled. Key differences include the dry method's ability to provide a cleaner, drier surface suitable for inspections and repairs, while the wet method excels in routine maintenance and biofouling removal with simpler setups.
Equipment and Technology Used in Each Method
Dry method underwater cleaning relies on specially designed cofferdams or enclosures that create a sealed, water-free environment around the structure, allowing divers or remote-operated vehicles (ROVs) to perform high-precision cleaning using high-pressure water jets, scrapers, or abrasive blasting equipment without water interference. This technique employs advanced sealing technologies and air supply systems to maintain dryness, along with monitoring sensors to ensure structural integrity during the operation. In contrast, the wet method utilizes submersible pumps, underwater brushes, and hydroblasters directly in the aquatic environment, often supplemented by remotely operated cleaning robots equipped with cameras and hydraulic tools optimized for underwater use, providing a flexible yet lower precision cleaning solution for large surface areas.
Impact on Hull Performance and Fuel Efficiency
Dry method underwater cleaning eliminates biofouling more effectively by allowing thorough cleaning of the hull surface without water interference, resulting in improved hull smoothness and reduced drag. This method significantly enhances hull performance and fuel efficiency by restoring optimal hydrodynamic conditions, leading to lower fuel consumption and decreased emissions. Wet method cleaning, while less disruptive, often leaves residual fouling and can cause uneven surface conditions, negatively impacting fuel efficiency and increasing operational costs.
Environmental Considerations and Regulations
Dry method underwater cleaning significantly reduces the release of harmful contaminants and suspended sediments into the surrounding water, minimizing ecological disruption and complying with stringent environmental regulations such as those enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the International Maritime Organization (IMO). Wet method underwater cleaning often results in the dispersal of pollutants, including invasive species and toxic biofilm residues, posing risks to marine habitats and requiring stricter monitoring under environmental protection laws. Compliance with local and international environmental standards favors the dry method for its superior containment capabilities and mitigation of underwater pollution.
Cost Comparison: Dry vs Wet Underwater Cleaning
Dry method underwater cleaning generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized dry habitats and equipment needed to create a sealed environment for divers. Wet method underwater cleaning is often more cost-effective for routine maintenance, utilizing standard diving gear without complex setups. Over time, dry cleaning can reduce repair expenses by providing more thorough cleaning, but wet cleaning remains preferred for budget-conscious operations with less critical cleaning requirements.
Safety Concerns and Risk Management
Dry method underwater cleaning significantly reduces safety risks by eliminating direct human exposure to underwater currents, contaminants, and marine life during operations. Wet method underwater cleaning poses higher safety concerns due to prolonged diver exposure to pressurized environments, increasing the risk of decompression sickness and underwater hazards. Effective risk management in dry method cleaning involves controlled, enclosed environments, while wet methods require stringent diver safety protocols and emergency preparedness.
Best Practices and Future Trends in Underwater Cleaning
Dry method underwater cleaning involves isolating the structure from water using cofferdams or enclosures, enabling controlled and contaminant-free cleaning environments ideal for delicate marine infrastructures. Wet method underwater cleaning employs diver-operated tools or remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) to clean surfaces directly underwater, offering efficiency and cost-effectiveness for routine maintenance of offshore platforms and ship hulls. Emerging trends emphasize advanced robotics, AI-driven cleaning systems, and environmentally sustainable techniques to enhance precision, reduce ecological impact, and improve safety standards in underwater maintenance operations.
Cavitation cleaning
Dry method underwater cleaning using cavitation generates higher-pressure microbubbles, resulting in more effective biofouling removal compared to the wet method's lower cavitation intensity.
Water jetting
Dry method underwater cleaning uses controlled water jetting to minimize environmental contamination, while wet method underwater cleaning relies on direct water jetting causing higher dispersion of sediment and pollutants.
Abrasive blasting
Dry method underwater cleaning using abrasive blasting offers superior control and reduced environmental impact compared to the wet method, which often disperses contaminants and abrasive materials into the surrounding water.
Diver-operated systems
Diver-operated dry method underwater cleaning uses sealed habitats to protect divers from water, enabling precise cleaning of sensitive surfaces, while wet method involves direct exposure to water, offering simplicity but less control over debris and surface damage.
ROV cleaning
ROV dry method underwater cleaning uses high-pressure air or abrasive blasting to remove marine growth without water dilution, enhancing visibility and cleaning precision compared to the wet method, which relies on direct water jets that can cause turbidity and reduced sensor effectiveness.
Ultrasonic cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaning using the dry method underwater offers superior contaminant removal and corrosion prevention compared to the traditional wet method by employing high-frequency sound waves in a controlled, residue-free environment.
Fouling removal
Dry method underwater cleaning removes fouling more effectively by preventing immediate reattachment and avoiding chemical dilution compared to the wet method.
Enclosed cleaning chamber
The dry method underwater cleaning utilizes an enclosed cleaning chamber to isolate the structure from water, enabling precise cleaning without contamination, unlike the wet method which relies on direct water exposure for cleaning.
Environmental containment
Dry method underwater cleaning ensures superior environmental containment by preventing pollutant dispersal, whereas wet method underwater cleaning risks contaminant spread into surrounding aquatic ecosystems.
Coating integrity
Dry method underwater cleaning preserves coating integrity by minimizing abrasive water exposure, whereas wet method cleaning often risks coating damage due to continuous water immersion and mechanical scrubbing.
Dry method underwater cleaning vs wet method underwater cleaning Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com