Incinerator systems in marine engineering efficiently reduce waste volume by burning solid waste at high temperatures, minimizing environmental impact through controlled emissions. Waste compactors compress waste to decrease space usage and facilitate easier storage and disposal but do not reduce waste mass or volume like incinerators. Choosing between incinerator systems and waste compactors depends on ship size, waste type, and environmental regulations governing marine operations.
Table of Comparison
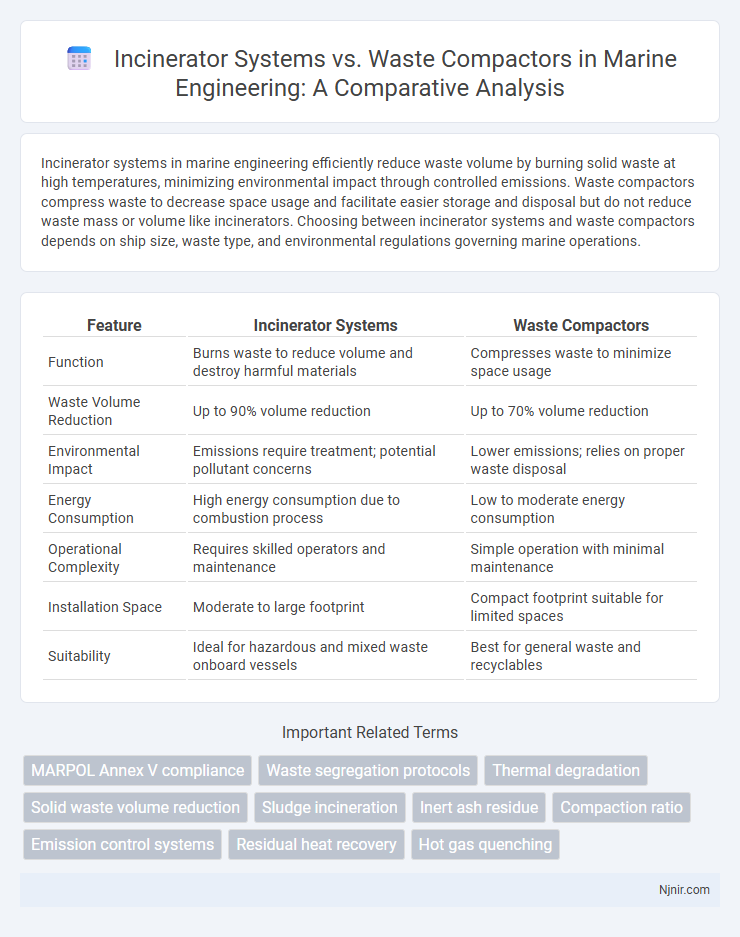
| Feature | Incinerator Systems | Waste Compactors |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Burns waste to reduce volume and destroy harmful materials | Compresses waste to minimize space usage |
| Waste Volume Reduction | Up to 90% volume reduction | Up to 70% volume reduction |
| Environmental Impact | Emissions require treatment; potential pollutant concerns | Lower emissions; relies on proper waste disposal |
| Energy Consumption | High energy consumption due to combustion process | Low to moderate energy consumption |
| Operational Complexity | Requires skilled operators and maintenance | Simple operation with minimal maintenance |
| Installation Space | Moderate to large footprint | Compact footprint suitable for limited spaces |
| Suitability | Ideal for hazardous and mixed waste onboard vessels | Best for general waste and recyclables |
Introduction to Waste Management in Marine Engineering
Incinerator systems in marine engineering effectively reduce waste volume by combusting solid refuse at high temperatures, minimizing environmental impact and onboard storage needs. Waste compactors compress solid waste into denser forms, optimizing limited ship space but requiring subsequent waste disposal or processing. Both systems are integral to sustainable waste management onboard vessels, with incinerators addressing organic and combustible waste and compactors managing non-combustible materials.
Overview of Incinerator Systems on Ships
Incinerator systems on ships are designed to efficiently burn solid waste, reducing volume and eliminating harmful substances through high-temperature combustion processes. These systems comply with IMO regulations, ensuring environmentally safe disposal of ship-generated waste by converting refuse into ash, gases, and heat. Incinerators are essential for managing waste on vessels operating in remote areas, minimizing environmental impact and maintaining vessel cleanliness.
Marine Waste Compactors: Function and Design
Marine waste compactors are engineered to reduce the volume of solid waste on vessels by compressing materials such as plastics, paper, and food packaging, optimizing onboard storage capacity. Their design incorporates corrosion-resistant materials and robust hydraulic mechanisms to withstand harsh marine environments, ensuring reliable performance during long voyages. Unlike incinerator systems that thermally treat waste, marine compactors emphasize efficient space management and ease of waste handling, aligning with maritime regulatory standards for waste disposal and environmental protection.
Operational Efficiency Comparison
Incinerator systems offer high operational efficiency by significantly reducing waste volume through combustion, which minimizes landfill dependency and generates energy recovery opportunities. Waste compactors improve efficiency by compressing waste into dense, manageable units, reducing transportation frequency and storage space requirements. Comparing both, incinerators provide more sustainable waste volume reduction and energy benefits, while compactors are cost-effective solutions for space optimization and waste handling logistics.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Residues
Incinerator systems generate emissions containing pollutants like dioxins, particulate matter, and heavy metals, which require advanced filtration to mitigate environmental harm, while producing ash residues that often require hazardous waste disposal. Waste compactors reduce landfill volume by compressing waste but do not alter its chemical composition, leading to prolonged decomposition and potential methane emissions if not managed properly. Evaluating environmental impact demands balancing emissions control from incineration against the long-term greenhouse gas release and leachate risks associated with compacted waste disposal.
Regulatory Compliance: IMO and MARPOL Standards
Incinerator systems on ships must comply with IMO Resolution MEPC.76(40) and MARPOL Annex VI, which regulate emissions and residue disposal to minimize environmental impact. Waste compactors, governed primarily under MARPOL Annex V, focus on reducing volume for efficient storage and disposal but do not address air pollution or hazardous gas emissions. Understanding these regulatory frameworks ensures that maritime operators implement systems adhering to international pollution prevention standards for sustainable waste management.
Space, Weight, and Installation Considerations
Incinerator systems require significantly more space and structural support due to the need for ventilation, combustion chambers, and ash collection units, making them heavier than waste compactors. Waste compactors are more compact and lighter, designed to minimize volume by compressing waste, allowing for easier installation in limited spaces. Installation of incinerators often involves complex permits and safety measures, whereas compactors have simpler setup requirements and reduced operational constraints.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Incinerator systems typically demand higher maintenance due to complex combustion components, including burners, flue gas treatment units, and ash handling systems, which require frequent inspections and specialized servicing to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Waste compactors feature simpler mechanical parts with lower maintenance needs, mainly involving routine checks of hydraulic systems and structural integrity, resulting in reduced operational downtime and lower maintenance expenses. Despite higher upfront costs, incinerators incur significant ongoing maintenance spending, whereas compactors offer cost efficiency through minimal upkeep and longer service intervals.
Crew Training and Safety Implications
Incinerator systems require specialized crew training to manage high-temperature combustion processes and handle hazardous emissions safely, emphasizing fire prevention, toxic gas monitoring, and emergency protocols. Waste compactors, while simpler to operate, demand thorough training on mechanical safety, pinch point awareness, and proper waste loading to prevent crush injuries and equipment malfunctions. Both systems necessitate comprehensive safety programs to minimize operational risks and ensure regulatory compliance in waste management environments.
Future Trends in Shipboard Waste Management Systems
Future trends in shipboard waste management systems emphasize the integration of advanced incinerator systems with improved emission controls and energy recovery technologies, reducing environmental impact while enhancing efficiency. Waste compactors are evolving with smart sensor technology for optimized volume reduction and real-time monitoring, promoting onboard space conservation and compliance with MARPOL Annex V regulations. Hybrid systems combining incineration and compaction are gaining traction, supporting sustainable maritime operations by balancing waste minimization with regulatory adherence and operational cost-effectiveness.
MARPOL Annex V compliance
Incinerator systems effectively reduce waste volume and destroy organic pollutants, ensuring MARPOL Annex V compliance by minimizing harmful discharge, whereas waste compactors primarily reduce waste size without eliminating hazardous substances.
Waste segregation protocols
Implementing strict waste segregation protocols enhances the efficiency of incinerator systems by reducing hazardous emissions, while waste compactors rely on pre-sorted recyclable and non-recyclable materials to optimize volume reduction and landfill diversion.
Thermal degradation
Incinerator systems utilize high-temperature thermal degradation to efficiently reduce waste volume and destroy hazardous materials, whereas waste compactors primarily mechanically compress waste without altering its chemical composition.
Solid waste volume reduction
Incinerator systems reduce solid waste volume by up to 90% through high-temperature combustion, while waste compactors typically achieve only 60-80% volume reduction by physically compressing the waste.
Sludge incineration
Sludge incineration systems efficiently reduce volume and destroy pathogens by thermally processing sludge, whereas waste compactors primarily minimize sludge volume through mechanical compression without thermal treatment or pathogen elimination.
Inert ash residue
Incinerator systems reduce waste volume by converting materials into inert ash residue, whereas waste compactors primarily compress waste without altering its chemical composition or generating inert ash.
Compaction ratio
Waste compactors achieve a higher compaction ratio of up to 10:1, significantly reducing waste volume compared to incinerator systems that primarily focus on waste combustion rather than volume reduction.
Emission control systems
Incinerator systems utilize advanced emission control technologies such as scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and activated carbon filters to significantly reduce toxic air pollutants compared to waste compactors, which produce minimal emissions but lack comprehensive emission control mechanisms.
Residual heat recovery
Incinerator systems offer efficient residual heat recovery by converting waste combustion heat into energy, whereas waste compactors lack this capability and primarily focus on volume reduction.
Hot gas quenching
Hot gas quenching in incinerator systems rapidly cools exhaust gases to minimize dioxin formation, offering a key advantage over waste compactors that lack this advanced emission control technology.
Incinerator systems vs waste compactor Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com