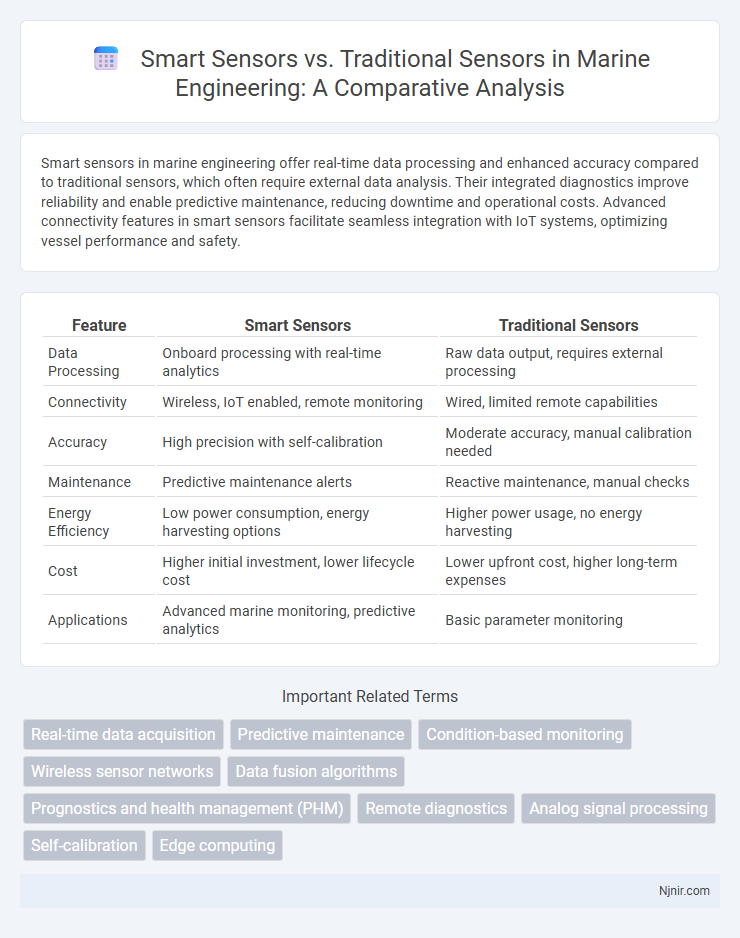
Smart sensors in marine engineering offer real-time data processing and enhanced accuracy compared to traditional sensors, which often require external data analysis. Their integrated diagnostics improve reliability and enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Advanced connectivity features in smart sensors facilitate seamless integration with IoT systems, optimizing vessel performance and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Sensors | Traditional Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing | Onboard processing with real-time analytics | Raw data output, requires external processing |
| Connectivity | Wireless, IoT enabled, remote monitoring | Wired, limited remote capabilities |
| Accuracy | High precision with self-calibration | Moderate accuracy, manual calibration needed |
| Maintenance | Predictive maintenance alerts | Reactive maintenance, manual checks |
| Energy Efficiency | Low power consumption, energy harvesting options | Higher power usage, no energy harvesting |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower lifecycle cost | Lower upfront cost, higher long-term expenses |
| Applications | Advanced marine monitoring, predictive analytics | Basic parameter monitoring |
Overview of Sensor Technologies in Marine Engineering
Smart sensors in marine engineering incorporate integrated microprocessors that enable real-time data processing, self-calibration, and wireless communication, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in monitoring marine environments. Traditional sensors rely on analog signals and require external processing units, limiting their functionality in dynamic marine applications such as corrosion detection and structural health monitoring. Advanced smart sensor technologies improve reliability and reduce maintenance costs by offering adaptive sensing capabilities crucial for complex marine systems.
Defining Smart Sensors and Traditional Sensors
Smart sensors integrate sensing elements with processing capabilities, enabling real-time data analysis, self-calibration, and communication through digital interfaces. Traditional sensors rely solely on physical mechanisms to detect changes in the environment and output analog signals without internal data processing. The shift towards smart sensors enhances accuracy, reduces external processing needs, and supports seamless integration in IoT and automation systems.
Key Functional Differences
Smart sensors integrate processing capabilities with sensing elements, enabling data analysis and decision-making at the sensor level, unlike traditional sensors that solely capture raw data. They often feature embedded microcontrollers, communication interfaces, and self-calibration functions, enhancing accuracy and reducing external processing requirements. Traditional sensors depend on external systems for data interpretation and lack built-in intelligence, leading to slower response times and limited adaptability.
Data Collection and Processing Capabilities
Smart sensors integrate data collection and on-board processing capabilities, enabling real-time analysis and immediate response without relying on external systems. Traditional sensors primarily capture raw data, requiring external devices or systems to process and interpret information, which can introduce delays. The embedded microprocessors in smart sensors facilitate advanced functionalities such as self-calibration, diagnostics, and adaptive data filtering, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in data handling.
Reliability and Accuracy in Marine Environments
Smart sensors in marine environments offer enhanced reliability and accuracy compared to traditional sensors by integrating advanced signal processing and self-calibration capabilities that reduce noise and drift. These sensors continuously monitor environmental conditions such as temperature, salinity, and pressure, adapting in real-time to harsh maritime factors like biofouling and corrosion. Traditional sensors often struggle with data degradation over time and require frequent manual calibration, making smart sensors the preferred choice for long-term, precise marine monitoring applications.
Integration with Marine Systems and Automation
Smart sensors offer seamless integration with marine systems and automation platforms through advanced connectivity protocols like NMEA 2000 and Modbus, enabling real-time data exchange and enhanced system responsiveness. Traditional sensors often rely on analog outputs requiring additional converters, limiting their compatibility and slowing automation processes in complex marine environments. The enhanced processing capabilities of smart sensors facilitate predictive maintenance and adaptive control, optimizing vessel performance and safety more effectively than conventional sensors.
Maintenance and Operational Efficiency
Smart sensors enhance maintenance efficiency by providing real-time data analytics and predictive diagnostics, reducing downtime through early fault detection. Traditional sensors lack advanced processing capabilities, resulting in reactive maintenance and longer operational interruptions. Implementing smart sensors leads to streamlined operations and lower lifecycle costs compared to conventional sensor systems.
Cost Implications and Lifecycle Analysis
Smart sensors offer higher initial costs compared to traditional sensors due to embedded processing capabilities and connectivity features, but they reduce long-term expenses through predictive maintenance and improved operational efficiency. Traditional sensors have lower upfront investment but often incur higher lifecycle costs caused by frequent replacements, manual calibrations, and downtime. Lifecycle analysis reveals smart sensors enhance overall value by minimizing total cost of ownership and extending equipment lifespan in industrial and commercial applications.
Impact on Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Smart sensors enhance safety by providing real-time data analytics and automated alerts, enabling rapid response to hazardous conditions, whereas traditional sensors typically offer limited, raw data requiring manual interpretation. The integration of smart sensors facilitates compliance with stringent regulatory standards through continuous monitoring, documentation, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Regulatory bodies increasingly mandate advanced sensor systems to ensure operational safety, minimize human error, and support proactive risk management.
Future Trends in Marine Sensor Technology
Smart sensors in marine technology integrate advanced data processing and wireless communication, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance that surpass traditional sensors limited to basic data collection. Future trends emphasize the development of self-calibrating smart sensors with AI-driven analytics to enhance underwater environmental monitoring, improving accuracy and operational efficiency. Enhanced connectivity through IoT frameworks will drive the adoption of smart sensors in autonomous marine vessels, optimizing navigation and resource management.
Real-time data acquisition
Smart sensors enable real-time data acquisition with integrated processing and wireless communication, surpassing traditional sensors that rely on external systems for data analysis and transmission.
Predictive maintenance
Smart sensors enable predictive maintenance by continuously analyzing real-time data and detecting anomalies, whereas traditional sensors provide limited, reactive monitoring based on predefined thresholds.
Condition-based monitoring
Smart sensors provide real-time data and predictive analytics for condition-based monitoring, significantly enhancing fault detection and maintenance efficiency compared to traditional sensors that offer limited monitoring capabilities.
Wireless sensor networks
Wireless sensor networks leverage smart sensors' real-time data processing and communication capabilities, significantly enhancing efficiency and scalability compared to traditional sensors reliant on wired connections and limited functionality.
Data fusion algorithms
Smart sensors leverage advanced data fusion algorithms to integrate multiple data sources for enhanced accuracy and real-time decision-making, while traditional sensors typically rely on single-source data with limited processing capabilities.
Prognostics and health management (PHM)
Smart sensors enhance Prognostics and Health Management (PHM) by providing real-time data processing and predictive analytics, unlike traditional sensors that primarily offer raw data without advanced diagnostic capabilities.
Remote diagnostics
Smart sensors enable real-time remote diagnostics with enhanced data accuracy and predictive maintenance capabilities, unlike traditional sensors that require manual data retrieval and offer limited diagnostic information.
Analog signal processing
Smart sensors integrate on-chip analog signal processing to convert, filter, and amplify signals directly, vastly improving accuracy and reducing noise compared to traditional sensors that rely on external analog circuitry.
Self-calibration
Smart sensors feature advanced self-calibration capabilities that continuously adjust measurement accuracy, unlike traditional sensors which require manual recalibration.
Edge computing
Smart sensors leverage edge computing to process data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to traditional sensors that rely on centralized data processing.
Smart sensors vs Traditional sensors Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com