Catamarans offer superior stability and reduced hydrodynamic resistance compared to monohulls, making them ideal for smooth and fuel-efficient marine operations. Their twin-hull design provides increased deck space and enhanced coastal maneuverability, especially beneficial in shallow waters. Monohulls, however, excel in heavy sea conditions due to their deeper draft and single hull, offering improved handling and robustness in rough waters.
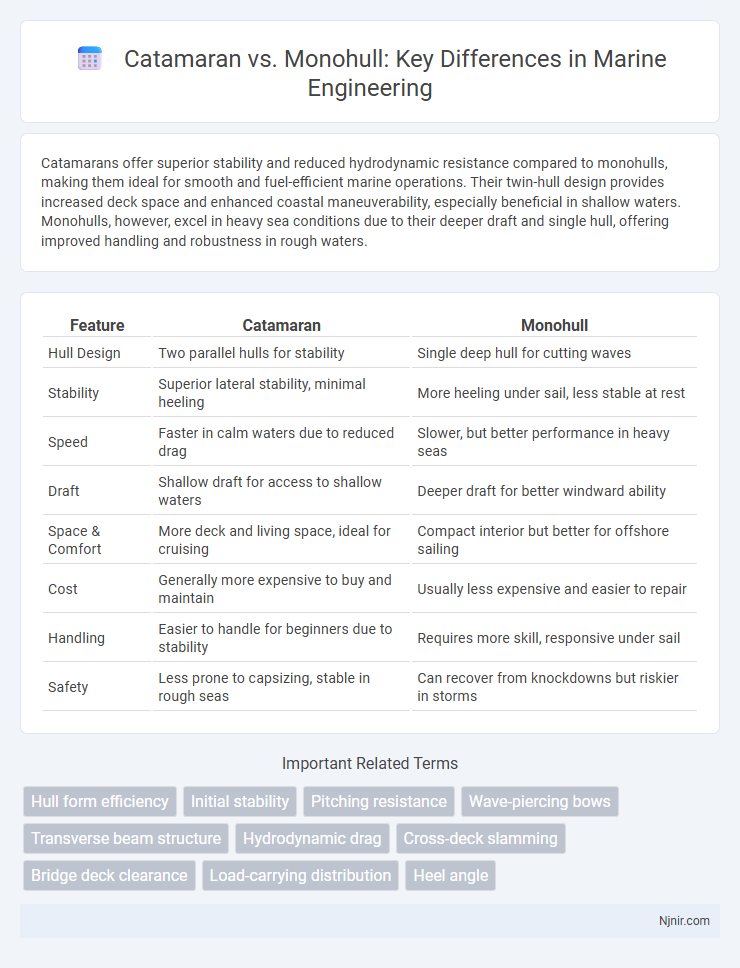
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Catamaran | Monohull |
|---|---|---|
| Hull Design | Two parallel hulls for stability | Single deep hull for cutting waves |
| Stability | Superior lateral stability, minimal heeling | More heeling under sail, less stable at rest |
| Speed | Faster in calm waters due to reduced drag | Slower, but better performance in heavy seas |
| Draft | Shallow draft for access to shallow waters | Deeper draft for better windward ability |
| Space & Comfort | More deck and living space, ideal for cruising | Compact interior but better for offshore sailing |
| Cost | Generally more expensive to buy and maintain | Usually less expensive and easier to repair |
| Handling | Easier to handle for beginners due to stability | Requires more skill, responsive under sail |
| Safety | Less prone to capsizing, stable in rough seas | Can recover from knockdowns but riskier in storms |
Introduction to Catamarans and Monohulls
Catamarans feature two parallel hulls, providing enhanced stability, increased deck space, and reduced draft compared to monohulls, making them ideal for smooth sailing in shallow waters. Monohulls, with a single hull design, offer deeper keels that enhance performance in rough sea conditions and often provide a more traditional sailing experience. Understanding the structural differences between catamarans and monohulls helps sailors choose the best type of vessel for stability, speed, and comfort preferences.
Hull Design and Structural Differences
Catamarans feature two parallel hulls connected by a central deck, providing enhanced stability and reduced drag compared to monohulls, which have a single, deeper hull designed for cutting through waves. The twin-hull design of catamarans offers a wider beam and increased deck space, while monohulls rely on ballast within the hull for stability. Structurally, catamarans require reinforced crossbeams to withstand torsional forces between hulls, whereas monohulls have a more uniform load distribution along the single hull.
Stability and Comfort at Sea
Catamarans offer superior stability at sea due to their dual hull design, which reduces rolling and provides a smoother ride compared to monohulls. The wide beam of catamarans enhances comfort by providing more spacious living areas and less motion, making them ideal for long voyages and seasickness-prone passengers. In contrast, monohulls can experience more pronounced heeling and pitching, which may impact comfort but offer a more traditional sailing feel favored by experienced sailors.
Speed and Performance Comparison
Catamarans typically achieve higher speeds due to their dual-hull design, which reduces drag and increases stability in various sea conditions. Monohulls, with a single hull, often perform better in heavy seas by cutting through waves more efficiently but generally sacrifice speed for smooth handling. Performance metrics such as acceleration, top speed, and fuel efficiency consistently favor catamarans, especially in calm to moderate waters.
Draft, Maneuverability, and Access
Catamarans feature a shallow draft, typically around 1 to 2 feet, allowing access to shallow waters and secluded anchorages inaccessible to monohulls that usually have drafts between 4 to 7 feet. Monohulls provide superior maneuverability in tight marinas and during docking due to their single-hull design and keel, while catamarans rely on twin engines for precise handling but can be less agile in confined spaces. Access to narrow channels and shallow bays is easier with catamarans, making them ideal for tropical cruising, whereas monohulls excel in deep-water sailing and handling rough offshore conditions.
Safety Features and Seaworthiness
Catamarans offer enhanced stability and reduced roll due to their twin-hull design, significantly improving safety in rough seas compared to monohulls. Monohulls excel in heavy weather performance with deep keels providing superior righting moments and better heeling response, contributing to seaworthiness in stormy conditions. The wider beam of catamarans increases deck space but may be more susceptible to capsizing in extreme conditions, while monohulls typically provide a more forgiving and self-righting experience.
Space Utilization and Living Accommodations
Catamarans offer superior space utilization with wide beam widths providing expansive deck areas, multiple cabins, and ample storage, enhancing comfort for extended living aboard. Monohulls, while narrower, often feature more efficient single-hull designs that optimize below-deck living accommodations, maximizing vertical space in compact layouts. The dual-hull structure of catamarans reduces pitching, creating more stable and versatile living environments compared to traditional monohull vessels.
Operational Costs and Maintenance
Catamarans generally incur higher initial operational costs due to their dual engines and complex systems but benefit from lower fuel consumption and greater stability, reducing wear and tear over time. Monohulls typically have simpler mechanical setups, leading to easier and less costly routine maintenance, but their single-hull design can result in higher fuel usage and more frequent repairs related to hull stress. Maintenance expenses vary significantly by size and usage, with catamarans demanding specialized dockage and parts, while monohulls offer broader availability of service options and parts.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Catamarans offer superior stability and spaciousness, making them ideal for leisure cruising, family outings, and long-distance voyaging in calm to moderate seas. Monohulls excel in performance sailing and handling rougher conditions, suited for competitive racing, solo circumnavigation, and traditional offshore adventures. The choice depends on the intended use, with catamarans favored for comfort and social space, while monohulls provide a more dynamic and responsive sailing experience.
Summary: Choosing the Right Vessel Type
Catamarans offer greater stability, increased deck space, and shallower drafts, making them ideal for calm waters and social sailing. Monohulls provide a traditional sailing experience with superior upwind performance and better handling in rough seas, preferred by long-distance cruisers. Selecting between catamaran and monohull depends on sailing style, comfort preferences, intended waters, and budget considerations.
Hull form efficiency
Catamarans offer superior hull form efficiency with reduced drag and increased stability compared to monohulls, resulting in higher speeds and better fuel economy.
Initial stability
Catamarans offer superior initial stability compared to monohulls due to their wide beam and twin-hull design, which reduces roll and enhances comfort in calm waters.
Pitching resistance
Catamarans offer superior pitching resistance compared to monohulls due to their dual-hull design which reduces both vertical movement and wave impact.
Wave-piercing bows
Wave-piercing bows on catamarans significantly reduce wave resistance and improve stability compared to traditional monohull bows, enhancing speed and comfort in rough seas.
Transverse beam structure
Catamarans feature a wider transverse beam structure than monohulls, enhancing stability and deck space while reducing hull resistance for improved performance.
Hydrodynamic drag
Catamarans experience lower hydrodynamic drag than monohulls due to their slender twin hulls, resulting in greater speed and fuel efficiency.
Cross-deck slamming
Catamarans experience significantly less cross-deck slamming than monohulls due to their wider beam and dual-hull design, which provides greater stability and reduces impact forces during rough sea conditions.
Bridge deck clearance
Catamarans offer significantly higher bridge deck clearance than monohulls, reducing wave impact and enhancing stability in rough seas.
Load-carrying distribution
Catamarans evenly distribute load across two hulls, enhancing stability and cargo capacity compared to the single-hull load concentration of monohulls.
Heel angle
Catamarans maintain a minimal heel angle of less than 5 degrees due to their wide beam and dual hulls, while monohulls experience significantly greater heel angles often exceeding 20 degrees under similar sailing conditions.
Catamaran vs Monohull Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com