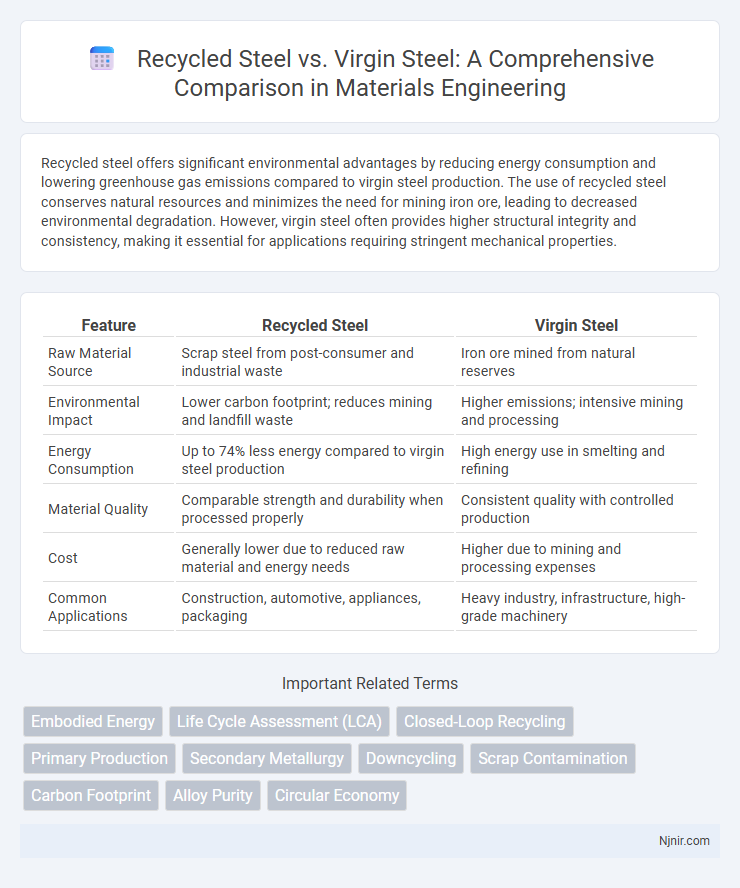
Recycled steel offers significant environmental advantages by reducing energy consumption and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin steel production. The use of recycled steel conserves natural resources and minimizes the need for mining iron ore, leading to decreased environmental degradation. However, virgin steel often provides higher structural integrity and consistency, making it essential for applications requiring stringent mechanical properties.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Steel | Virgin Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | Scrap steel from post-consumer and industrial waste | Iron ore mined from natural reserves |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint; reduces mining and landfill waste | Higher emissions; intensive mining and processing |
| Energy Consumption | Up to 74% less energy compared to virgin steel production | High energy use in smelting and refining |
| Material Quality | Comparable strength and durability when processed properly | Consistent quality with controlled production |
| Cost | Generally lower due to reduced raw material and energy needs | Higher due to mining and processing expenses |
| Common Applications | Construction, automotive, appliances, packaging | Heavy industry, infrastructure, high-grade machinery |
Introduction to Recycled Steel and Virgin Steel
Recycled steel is produced by melting down scrap steel to create new steel products, significantly reducing energy consumption and environmental impact compared to virgin steel. Virgin steel is manufactured from iron ore through processes such as blast furnace smelting, requiring higher raw material inputs and energy usage. Both materials have distinct supply chains and environmental footprints, with recycled steel offering a sustainable alternative to virgin steel production.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Recycled steel primarily consists of scrap metal melted down and purified to remove impurities, maintaining a similar chemical composition to virgin steel but often requiring less energy-intensive processing. Virgin steel is produced from iron ore through blast furnaces or electric arc furnaces, involving complex steps like smelting, refining, and alloying to achieve desired properties. The manufacturing process of recycled steel reduces carbon emissions and preserves natural resources by reusing existing materials without compromising on strength or durability.
Environmental Impact: Energy Consumption and Emissions
Recycled steel significantly reduces energy consumption by using up to 74% less energy compared to virgin steel production, which relies heavily on raw ore extraction and processing. The emissions associated with recycled steel are substantially lower, cutting greenhouse gases by approximately 58%, mitigating climate change and air pollution. Utilizing recycled steel supports circular economy goals by minimizing resource depletion and reducing landfill waste.
Mechanical Properties and Performance Comparison
Recycled steel offers comparable tensile strength and hardness to virgin steel, with slight variations depending on the recycling process and quality control. Virgin steel typically exhibits more consistent mechanical properties such as ductility and impact resistance due to its controlled composition and manufacturing. Performance differences between the two are minimal in structural applications, though recycled steel may require careful grade selection for high-stress environments.
Cost Analysis: Production and Market Prices
Recycled steel production consumes 40-70% less energy than virgin steel, significantly reducing operational costs and carbon emissions. Market prices for recycled steel fluctuate based on scrap availability but generally remain 15-20% lower than those of virgin steel, which require more intensive mining and refining processes. Cost efficiency in recycled steel makes it a preferred choice for construction and manufacturing sectors aiming to minimize expenses and environmental impact.
Life Cycle Assessment and Sustainability
Recycled steel significantly reduces environmental impact by consuming up to 75% less energy and lowering carbon emissions by approximately 58% compared to virgin steel production. Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) highlight recycled steel's benefits in minimizing raw material extraction and reducing landfill waste, thereby enhancing resource efficiency. Sustainable steel manufacturing prioritizes recycled content to support circular economy goals and mitigate climate change effects.
Applications in Construction and Manufacturing
Recycled steel is extensively used in construction for structural components, roofing, and reinforcement bars due to its sustainability and comparable strength to virgin steel. Virgin steel offers superior consistency and is preferred in manufacturing precision equipment, automotive parts, and heavy machinery where material properties are critical. Both materials contribute significantly to reducing carbon footprint and resource depletion in industrial applications.
Quality Control and Certification Standards
Recycled steel undergoes stringent quality control measures including remelting, descaling, and testing to meet industry standards such as ISO 9001 and ASTM specifications, ensuring its structural integrity matches that of virgin steel. Virgin steel benefits from tightly regulated production processes with certifications like CE marking and EN 10025, guaranteeing consistent mechanical properties and composition. Both recycled and virgin steel certifications emphasize traceability, composition analysis, and mechanical testing to uphold safety and performance in construction and manufacturing applications.
Supply Chain and Resource Availability
Recycled steel significantly reduces supply chain dependency on raw iron ore, enhancing resource availability by reusing existing materials and lowering extraction demand. Virgin steel production relies heavily on mining operations and complex logistics to transport raw materials, increasing vulnerability to supply disruptions and geopolitical risks. Recycling processes streamline supply chains, minimize lead times, and promote sustainable resource management in the steel industry.
Future Trends in Steel Recycling Technologies
Emerging advancements in steel recycling technologies prioritize enhancing the efficiency of scrap steel processing through innovative methods like advanced sensor-based sorting and electric arc furnace (EAF) automation. Future trends emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize recycling workflows, minimize impurities, and reduce energy consumption compared to the production of virgin steel from iron ore. The global push for sustainable manufacturing is accelerating the development of closed-loop recycling systems, enabling higher recovery rates and supporting circular economy initiatives within the steel industry.
Embodied Energy
Recycled steel reduces embodied energy by up to 75% compared to virgin steel, significantly lowering environmental impact during production.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) reveals recycled steel reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions by up to 58% compared to virgin steel during production.
Closed-Loop Recycling
Closed-loop recycling of recycled steel reduces environmental impact by repeatedly reprocessing scrap steel into new steel products without quality loss, unlike virgin steel production which relies on raw iron ore extraction and energy-intensive smelting.
Primary Production
Primary production of virgin steel consumes approximately 20-30% more energy and emits significantly higher CO2 levels compared to recycled steel derived from scrap metal.
Secondary Metallurgy
Secondary metallurgy in recycled steel enhances impurity removal and alloy consistency compared to virgin steel, improving overall steel quality and sustainability.
Downcycling
Recycled steel reduces environmental impact but often undergoes downcycling, resulting in lower-quality products compared to virgin steel made from raw iron ore.
Scrap Contamination
Recycled steel faces challenges with scrap contamination that can reduce material quality and increase processing costs compared to virgin steel.
Carbon Footprint
Recycled steel reduces carbon emissions by up to 58% compared to virgin steel, significantly lowering the overall carbon footprint in steel production.
Alloy Purity
Recycled steel often contains lower alloy purity compared to virgin steel due to contamination from mixed scrap sources, impacting its performance in high-strength applications.
Circular Economy
Recycled steel reduces energy consumption by up to 74% compared to virgin steel, significantly advancing the circular economy through sustainable resource reuse and minimizing environmental impact.
Recycled Steel vs Virgin Steel Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com