Autonomous inspection in mechanical engineering leverages advanced sensors and AI algorithms to identify defects with higher precision and speed compared to manual inspection. This technology reduces human error and operational downtime by enabling continuous, real-time monitoring of machinery components. Manual inspection, while reliant on skilled technicians, often faces limitations in consistency and scalability for complex or hazardous environments.
Table of Comparison
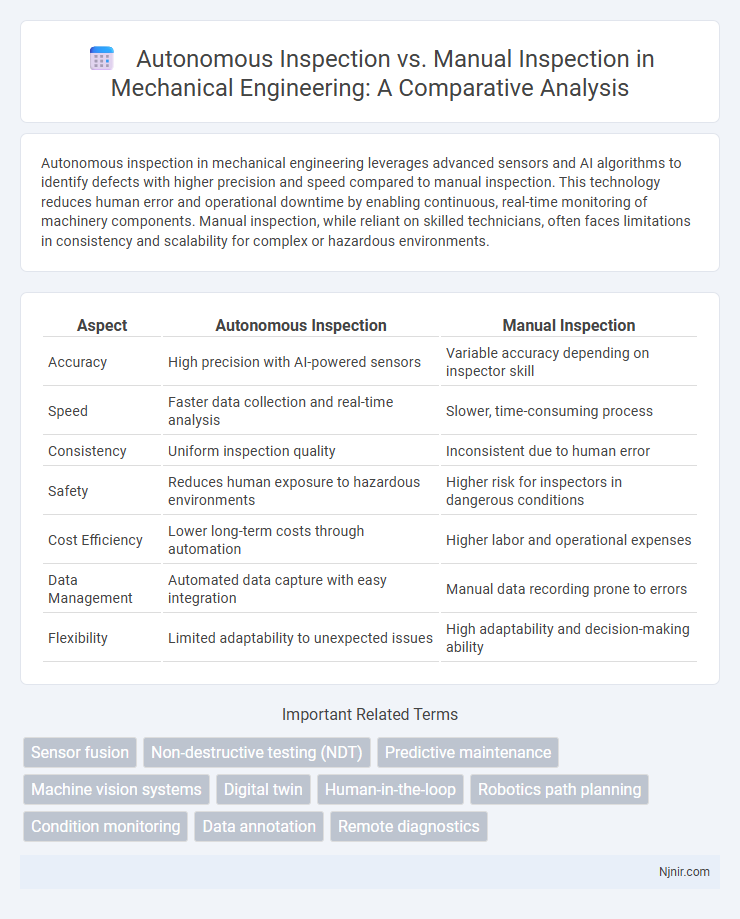
| Aspect | Autonomous Inspection | Manual Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High precision with AI-powered sensors | Variable accuracy depending on inspector skill |
| Speed | Faster data collection and real-time analysis | Slower, time-consuming process |
| Consistency | Uniform inspection quality | Inconsistent due to human error |
| Safety | Reduces human exposure to hazardous environments | Higher risk for inspectors in dangerous conditions |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower long-term costs through automation | Higher labor and operational expenses |
| Data Management | Automated data capture with easy integration | Manual data recording prone to errors |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability to unexpected issues | High adaptability and decision-making ability |
Introduction to Inspection Methods in Mechanical Engineering
Autonomous inspection in mechanical engineering leverages advanced sensors, robotics, and AI algorithms to perform precise, consistent evaluations of machinery without human intervention, significantly reducing errors and downtime. Manual inspection relies on skilled technicians to visually and physically assess equipment, offering flexibility and adaptability in complex or nuanced scenarios but with increased risk of human error and slower processing times. Integrating autonomous inspection methods improves predictive maintenance and enhances overall system reliability by continuously monitoring mechanical components.
Defining Autonomous and Manual Inspection
Autonomous inspection utilizes artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced sensors to perform evaluations without human intervention, enhancing precision and efficiency. Manual inspection involves human inspectors conducting visual or physical assessments based on experience and observation, often limited by fatigue and subjectivity. Autonomous systems deliver consistent data collection and real-time analysis, whereas manual methods rely heavily on human judgment and can vary in accuracy.
Key Technologies in Autonomous Inspection
Key technologies in autonomous inspection include advanced machine learning algorithms, computer vision systems, and sensor fusion techniques that enable precise defect detection and real-time data analysis. Robotics equipped with LiDAR, thermal imaging, and ultrasonic sensors facilitate comprehensive environment scanning and anomaly identification without human intervention. These technologies drastically improve accuracy, efficiency, and safety compared to traditional manual inspection methods.
Human Factors in Manual Inspection
Human factors in manual inspection significantly impact accuracy, consistency, and speed due to fatigue, subjective judgment, and cognitive overload. Variability in human performance often leads to errors and missed defects, affecting overall quality control. Autonomous inspection systems mitigate these risks by providing standardized, repeatable assessments without the influence of human limitations.
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison
Autonomous inspection systems leverage advanced sensors and AI algorithms to achieve higher accuracy and consistency compared to manual inspection, reducing human error and variability. Manual inspection relies heavily on inspector experience and can suffer from fatigue, leading to inconsistent results and lower reliability in detecting defects. Autonomous systems provide repeatable and objective evaluations, enhancing reliability through continuous data analysis and real-time anomaly detection.
Efficiency and Productivity Analysis
Autonomous inspection systems dramatically enhance efficiency by leveraging AI-powered sensors and real-time data processing, reducing inspection time by up to 70% compared to manual methods. Productivity increases as autonomous technology enables continuous operation without fatigue, minimizing human error and enabling faster detection of defects. Manual inspection remains limited by human speed and consistency, often resulting in slower turnaround times and increased labor costs.
Cost Implications of Both Methods
Autonomous inspection reduces labor costs significantly by utilizing drones, AI, and robotics to perform frequent and precise assessments without human intervention, leading to lower operational expenses. Manual inspection incurs higher labor costs due to the need for skilled inspectors, longer inspection times, and potential safety risks that can result in compensation or downtime expenses. Over time, autonomous inspection shows a higher return on investment through minimized error rates and enhanced efficiency despite initial technology acquisition costs.
Safety Considerations in Inspection Processes
Autonomous inspection enhances safety by minimizing human exposure to hazardous environments such as confined spaces, high voltages, or unstable structures, significantly reducing the risk of accidents. Manual inspection requires continuous vigilance and protective measures to safeguard inspectors from potential dangers, often leading to increased operational costs and downtime due to safety protocols. Advanced autonomous systems equipped with sensors and AI enable real-time hazard detection and controlled navigation, improving overall safety compliance in inspection processes.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Autonomous inspection leverages AI-powered drones and robots to perform high-precision, real-time monitoring in industries like oil and gas, manufacturing, and infrastructure, drastically reducing human error and downtime. Manual inspection remains critical for tasks requiring expert judgment and nuanced decision-making, especially in complex environments such as aerospace and nuclear power plants. Mining, power generation, and construction increasingly adopt autonomous systems for hazardous area surveys and predictive maintenance, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Inspection Methods
Future trends in inspection methods highlight a significant shift from manual inspection to autonomous systems driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, robotics, and sensor technologies. Autonomous inspection offers enhanced accuracy, real-time data analysis, and reduced operational downtime, transforming industries such as manufacturing, infrastructure maintenance, and aerospace. Integration of machine learning algorithms and IoT connectivity is set to further evolve inspection processes, enabling predictive maintenance and smarter decision-making.
Sensor fusion
Autonomous inspection leverages advanced sensor fusion techniques combining LiDAR, thermal imaging, and ultrasonic sensors to enhance accuracy and efficiency compared to manual inspection methods relying on individual sensor data interpretation.
Non-destructive testing (NDT)
Autonomous inspection in Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) significantly enhances accuracy and efficiency by utilizing advanced sensors and AI algorithms, reducing human error and inspection time compared to traditional manual inspection methods.
Predictive maintenance
Autonomous inspection using AI-powered sensors enables continuous, precise data collection for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and costs compared to labor-intensive, error-prone manual inspections.
Machine vision systems
Machine vision systems in autonomous inspection deliver higher accuracy, faster defect detection, and consistent quality compared to manual inspection, reducing human error and operational costs.
Digital twin
Autonomous inspection leveraging digital twin technology enables real-time, precise monitoring of assets by simulating physical systems virtually, significantly outperforming manual inspection in accuracy, efficiency, and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Human-in-the-loop
Human-in-the-loop integration enhances autonomous inspection accuracy by enabling real-time expert oversight and intervention, surpassing the limitations of purely manual inspection methods.
Robotics path planning
Robotics path planning in autonomous inspection optimizes route efficiency and coverage accuracy far beyond the limitations of manual inspection, increasing speed and reducing human error.
Condition monitoring
Autonomous inspection leverages real-time sensor data and AI algorithms for continuous condition monitoring, enabling faster fault detection and predictive maintenance compared to manual inspection's periodic, labor-intensive assessments.
Data annotation
Autonomous inspection enhances data annotation accuracy and speed by leveraging AI algorithms, while manual inspection relies on human annotators, often resulting in slower, less consistent labeling.
Remote diagnostics
Autonomous inspection leverages advanced sensors and AI algorithms to enable precise remote diagnostics, reducing human error and increasing efficiency compared to traditional manual inspection methods.
Autonomous inspection vs Manual inspection Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com