YAML and JSON are popular data serialization formats used in software engineering for configuration files and data exchange. YAML offers greater readability and supports complex features like comments, multiline strings, and custom data types, making it ideal for configuration management. JSON, with its lightweight syntax and widespread language support, excels in web applications and APIs where simplicity and performance are critical.
Table of Comparison
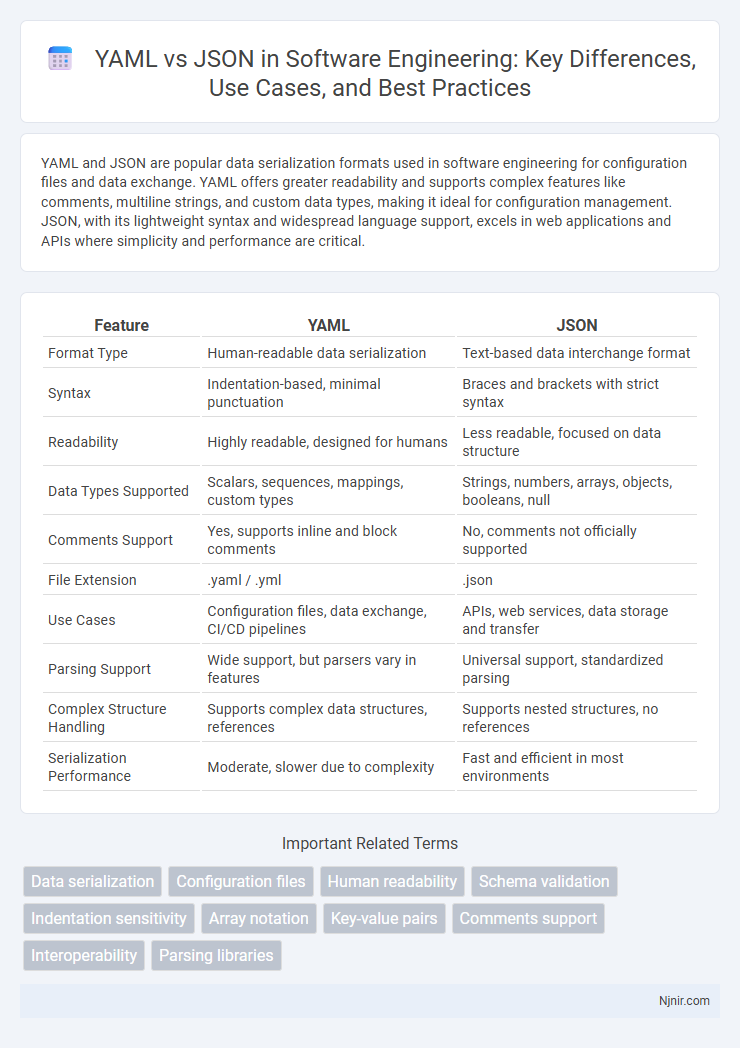
| Feature | YAML | JSON |
|---|---|---|
| Format Type | Human-readable data serialization | Text-based data interchange format |
| Syntax | Indentation-based, minimal punctuation | Braces and brackets with strict syntax |
| Readability | Highly readable, designed for humans | Less readable, focused on data structure |
| Data Types Supported | Scalars, sequences, mappings, custom types | Strings, numbers, arrays, objects, booleans, null |
| Comments Support | Yes, supports inline and block comments | No, comments not officially supported |
| File Extension | .yaml / .yml | .json |
| Use Cases | Configuration files, data exchange, CI/CD pipelines | APIs, web services, data storage and transfer |
| Parsing Support | Wide support, but parsers vary in features | Universal support, standardized parsing |
| Complex Structure Handling | Supports complex data structures, references | Supports nested structures, no references |
| Serialization Performance | Moderate, slower due to complexity | Fast and efficient in most environments |
Introduction to YAML and JSON
YAML and JSON are popular data serialization formats used for configuration files and data interchange. YAML, which stands for "YAML Ain't Markup Language," emphasizes human readability with a clean, indentation-based syntax that supports complex data structures like lists, dictionaries, and nested elements. JSON, or JavaScript Object Notation, is a lightweight, text-based format widely adopted in web development for its simplicity and ease of parsing across programming languages.
Syntax Comparison: YAML vs JSON
YAML uses indentation to denote structure, making it more human-readable compared to JSON's use of braces and brackets. JSON requires quotes around keys and string values, while YAML allows unquoted keys and supports multiple data types with simpler syntax. Both formats support arrays and objects, but YAML's flexibility with multiline strings and comments offers advantages for complex configuration files.
Readability and Human-Friendliness
YAML offers superior readability and human-friendliness compared to JSON through its clean, indentation-based structure and minimal use of symbols. It supports comments and more expressive data types, making it easier for users to write and understand configuration files. JSON's syntax, while simpler for machines, can be more cluttered and less intuitive for humans, especially in complex data representations.
Data Structure Representation
YAML and JSON both serve as popular data serialization formats, with YAML offering a more human-readable structure through indentation and support for complex data types like anchors and aliases. JSON uses a strict syntax with braces, brackets, and key-value pairs, ensuring simplicity and universality in representing objects, arrays, and primitive data types. YAML's flexibility accommodates hierarchical data structures more intuitively, making it suited for configuration files, whereas JSON's widespread compatibility benefits API communication and web applications.
Use Cases in Software Engineering
YAML excels in configuration management due to its human-readable syntax, making it ideal for deployment files in Kubernetes and CI/CD pipelines. JSON is preferred for web APIs and data interchange in software engineering because of its lightweight structure and native support in JavaScript. Both formats are integral for serialization, but YAML's support for complex data types suits infrastructure-as-code, while JSON's simplicity enhances real-time client-server communication.
Performance and Parsing Speed
YAML tends to have slower parsing speeds compared to JSON due to its complex syntax and flexibility, which requires more processing time to interpret various data structures. JSON's lightweight and straightforward format enables faster parsing and better performance in most programming environments, making it ideal for performance-critical applications. Benchmarks typically show JSON parsers outperforming YAML parsers, especially in large-scale data processing where parsing speed directly impacts overall system efficiency.
Support and Tooling Ecosystem
YAML and JSON both enjoy widespread support across programming languages, with JSON being natively supported in most modern environments like JavaScript, Python, and Java, making it highly accessible for web APIs and configuration files. YAML offers richer features for complex configurations, such as comments and multi-line strings, supported by popular tools like Ansible, Kubernetes, and Docker Compose, which rely on its human-readable syntax. JSON benefits from a vast tooling ecosystem including validators, linters, and formatters integrated into IDEs and online platforms, while YAML's tooling is growing steadily with enhanced parsers and serializers improving its reliability and adoption.
Security Considerations
YAML and JSON differ significantly in security considerations due to their parsing mechanisms; YAML's support for complex data types and anchors can introduce risks such as arbitrary code execution if not properly sanitized. JSON's simpler syntax and strict data types reduce attack surfaces, making it less vulnerable to injection attacks compared to YAML. Developers must implement strict input validation and use secure parsing libraries to mitigate potential vulnerabilities inherent in both formats.
Integration with DevOps and CI/CD
YAML and JSON are widely used for configuration management in DevOps and CI/CD pipelines, with YAML favored for its readability and support for complex data structures, enabling easier management of infrastructure as code (IaC) tools like Ansible, Kubernetes, and GitLab CI. JSON offers simplicity and is highly compatible with web APIs and JavaScript-based tools, making it efficient for automated validation and quick parsing in CI/CD workflows. Both formats support seamless integration with version control systems and automation scripts, but YAML's ability to handle multi-document files and anchors streamlines complex pipeline requirements.
Choosing the Right Format for Your Project
YAML offers human-readable syntax and supports complex data structures, making it ideal for configuration files and scenarios requiring clear hierarchy visualization. JSON provides faster parsing, widespread support across programming languages, and compatibility with web APIs, making it suitable for data interchange and web development projects. Selecting the right format depends on project requirements such as readability, complexity, and integration needs.
Data serialization
YAML offers human-readable data serialization with support for complex data types and comments, while JSON provides a lightweight, language-independent format optimized for data interchange and ease of parsing.
Configuration files
YAML configuration files offer improved readability and support for complex data structures compared to JSON, making them ideal for human-friendly configuration management in software applications.
Human readability
YAML offers superior human readability compared to JSON due to its minimal syntax, indentation-based structure, and support for comments.
Schema validation
YAML supports complex schema validation through tools like Kwalify and Yamale, while JSON schema validation is widely standardized and supported by JSON Schema specifications, enabling consistent structure enforcement across applications.
Indentation sensitivity
YAML is indentation-sensitive, requiring consistent spacing to define structure, while JSON uses explicit braces and brackets, making it indentation-insensitive for parsing.
Array notation
YAML uses hyphens to denote array elements in a readable, line-by-line format, while JSON represents arrays with brackets and commas for compactness and strict syntax.
Key-value pairs
YAML offers a more human-readable syntax with indentation-based key-value pairs, while JSON uses a stricter, bracketed key-value pair format ideal for data interchange.
Comments support
YAML supports comments using the '#' symbol for inline and block comments, whereas JSON does not natively support comments, limiting its ability to annotate data.
Interoperability
YAML offers enhanced interoperability by supporting complex data structures and multiple data types, while JSON provides widespread compatibility and simplicity across web applications and APIs.
Parsing libraries
YAML parsing libraries like PyYAML and ruamel.yaml offer extensive features for complex data structures, while JSON parsing libraries such as Jackson and Newtonsoft.Json provide faster performance and broader language support for simpler data interchange.
YAML vs JSON Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com