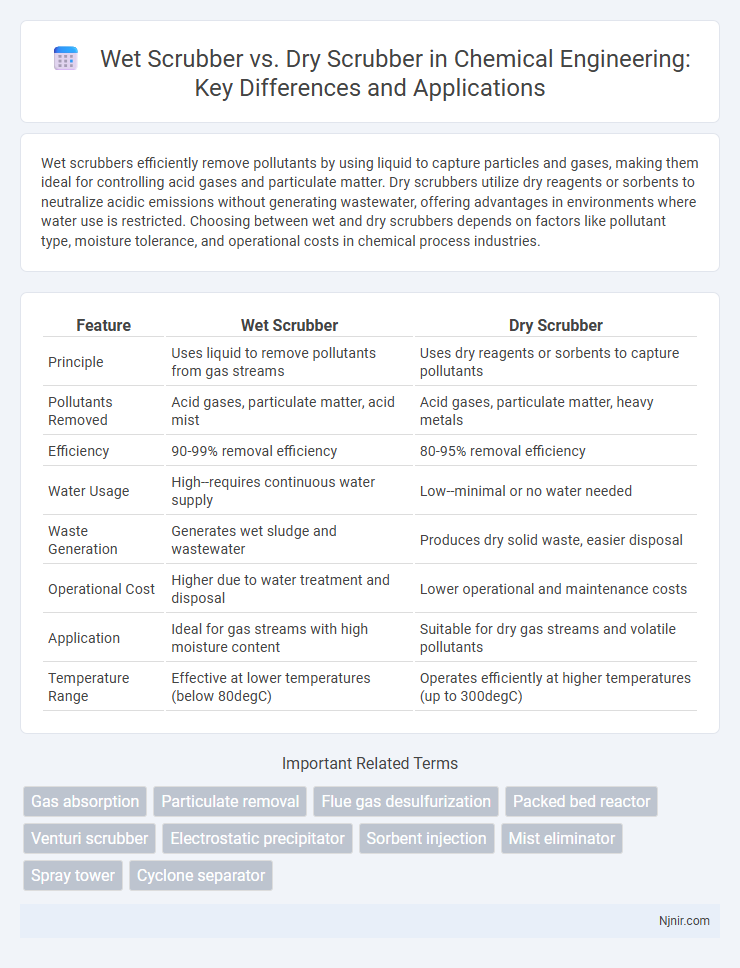
Wet scrubbers efficiently remove pollutants by using liquid to capture particles and gases, making them ideal for controlling acid gases and particulate matter. Dry scrubbers utilize dry reagents or sorbents to neutralize acidic emissions without generating wastewater, offering advantages in environments where water use is restricted. Choosing between wet and dry scrubbers depends on factors like pollutant type, moisture tolerance, and operational costs in chemical process industries.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wet Scrubber | Dry Scrubber |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Uses liquid to remove pollutants from gas streams | Uses dry reagents or sorbents to capture pollutants |
| Pollutants Removed | Acid gases, particulate matter, acid mist | Acid gases, particulate matter, heavy metals |
| Efficiency | 90-99% removal efficiency | 80-95% removal efficiency |
| Water Usage | High--requires continuous water supply | Low--minimal or no water needed |
| Waste Generation | Generates wet sludge and wastewater | Produces dry solid waste, easier disposal |
| Operational Cost | Higher due to water treatment and disposal | Lower operational and maintenance costs |
| Application | Ideal for gas streams with high moisture content | Suitable for dry gas streams and volatile pollutants |
| Temperature Range | Effective at lower temperatures (below 80degC) | Operates efficiently at higher temperatures (up to 300degC) |
Introduction to Wet and Dry Scrubbers
Wet scrubbers use liquid solutions to remove pollutants from industrial exhaust streams by capturing particles and gases through absorption and chemical reactions, making them ideal for controlling acid gases and fine particulates. Dry scrubbers involve injecting alkaline reagents or using sorbent materials in a dry form to neutralize or adsorb acidic gases and particulate matter, offering advantages in applications where water use and wastewater disposal are concerns. Both technologies are critical in air pollution control, with wet scrubbers favored for high moisture and particulate loads and dry scrubbers preferred for lower moisture and simpler maintenance requirements.
Principles of Wet Scrubbing
Wet scrubbers operate by passing polluted gas through a liquid solution, typically water or chemical absorbents, which capture contaminants through mass transfer and chemical reactions. The process relies on droplet-gas contact where particulates and gases such as sulfur dioxide dissolve or react with the scrubbing liquid, effectively removing pollutants from industrial emissions. This method is highly effective for controlling acid gases, particulate matter, and odor emissions in applications like power plants and chemical manufacturing.
Principles of Dry Scrubbing
Dry scrubbers operate by injecting alkaline materials such as lime or sodium bicarbonate into flue gas to chemically react with acidic pollutants like sulfur dioxide, forming solid byproducts that are easily collected. These systems rely on sorbent utilization and precise control of temperature and residence time to maximize pollutant removal efficiency. Unlike wet scrubbers, dry scrubbers avoid water usage, reducing wastewater treatment requirements and corrosion issues.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Scrubbers
Wet scrubbers use a liquid, often water or chemical solutions, to capture and remove pollutants from industrial exhaust gases by absorbing and neutralizing contaminants. Dry scrubbers, in contrast, utilize dry reagents or sorbents to chemically react with and remove pollutants without using liquids, making them ideal for situations where wastewater disposal is a concern. Key differences include their operational mechanisms, maintenance requirements, and the types of pollutants they effectively treat, with wet scrubbers being more effective for soluble gases and particulate matter, while dry scrubbers excel in dry, corrosive environments.
Efficiency of Pollutant Removal
Wet scrubbers achieve pollutant removal efficiencies often exceeding 90% for gases like sulfur dioxide and particulate matter by utilizing liquid solutions to capture contaminants. Dry scrubbers typically offer removal efficiencies ranging from 70% to 90%, depending on the sorbent material and process conditions used for capturing acidic gases and particulate matter. The selection between wet and dry scrubbers depends on specific pollutant types, removal targets, and operational considerations, with wet scrubbers favored for higher moisture tolerance and dry scrubbers preferred for lower wastewater generation.
Applications in Chemical Engineering
Wet scrubbers effectively remove acidic gases, particulate matter, and hazardous vapors in chemical engineering processes such as sulfuric acid production and ammonia synthesis, where moisture presence is manageable. Dry scrubbers are preferred for flue gas desulfurization and controlling alkaline emissions in high-temperature environments, especially where water consumption or wastewater treatment is constrained. Both technologies are integral for compliance with environmental regulations in refining, petrochemical, and fertilizer manufacturing industries.
Operational and Maintenance Requirements
Wet scrubbers require continuous water supply and frequent monitoring to prevent clogging and scaling, leading to higher operational complexity and maintenance demands. Dry scrubbers generally involve simpler operation with minimal water use, resulting in lower corrosion risks and reduced maintenance intervals. Regular inspection of nozzle systems in wet scrubbers and replacement of sorbent materials in dry scrubbers are critical for maintaining optimal performance.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Wet scrubbers effectively remove pollutants like sulfur dioxide and particulate matter by using liquid solutions, resulting in lower air emissions and improved air quality compared to dry scrubbers. Dry scrubbers, while generating less wastewater and solid waste, may be less efficient in capturing fine particulates and acidic gases, potentially leading to higher atmospheric emissions. Choosing between wet and dry scrubbers depends on balancing wastewater management concerns with the necessity for stringent air pollution control in industrial applications.
Cost Considerations and Economic Analysis
Wet scrubbers generally have higher initial capital costs due to complex liquid handling systems and corrosion-resistant materials, but offer lower operational expenses with efficient pollutant removal and reduced maintenance. Dry scrubbers exhibit lower upfront investment and simpler installation but can incur higher ongoing costs from frequent replacement of sorbents and handling of solid waste byproducts. Economic analysis should weigh long-term operational savings of wet scrubbers against the lower installation budget of dry scrubbers, considering factors like pollutant type, volume, and disposal requirements.
Choosing the Right Scrubber: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right scrubber hinges on factors such as the type of pollutants, gas temperature, and moisture content in the exhaust stream. Wet scrubbers excel in removing soluble gases and particulates with high moisture, while dry scrubbers are preferred for dry gas streams and easier waste disposal. Operational costs, maintenance requirements, and environmental regulations also play critical roles in selecting the optimal scrubber system.
Gas absorption
Wet scrubbers use liquid solvents to efficiently absorb and remove gaseous pollutants, while dry scrubbers rely on solid sorbents or reagents for gas absorption with less moisture handling.
Particulate removal
Wet scrubbers achieve higher particulate removal efficiency by capturing fine particles with liquid sprays, whereas dry scrubbers primarily target gaseous pollutants and are less effective for fine particulate removal.
Flue gas desulfurization
Wet scrubbers utilize liquid absorbents to efficiently remove sulfur dioxide from flue gas, whereas dry scrubbers use dry alkaline materials for flue gas desulfurization with lower water consumption and reduced wastewater generation.
Packed bed reactor
Wet scrubbers in packed bed reactors efficiently remove acidic gases by using liquid absorbents, while dry scrubbers rely on solid sorbents for gas pollutant capture without moisture involvement.
Venturi scrubber
Venturi scrubbers, a type of wet scrubber, use high-velocity gas streams to efficiently remove fine particulate matter and pollutants by liquid droplet impaction, offering superior performance in dust control compared to dry scrubbers.
Electrostatic precipitator
Electrostatic precipitators offer higher particulate removal efficiency and lower operating costs compared to wet and dry scrubbers by using electric charges to capture dust and smoke particles.
Sorbent injection
Wet scrubbers use liquid sorbent injection for pollutant absorption, while dry scrubbers rely on dry sorbent injection to capture contaminants through chemical reactions or physical adsorption.
Mist eliminator
Wet scrubbers use mist eliminators to efficiently remove liquid droplets and particulate matter, enhancing gas cleaning performance compared to dry scrubbers which typically lack this feature.
Spray tower
Spray tower wet scrubbers efficiently remove particulate matter and soluble gases by using liquid sprays, whereas dry scrubbers rely on dry reagents or sorbents for pollutant capture without liquid involvement.
Cyclone separator
Wet scrubbers with cyclone separators efficiently remove particulate matter by utilizing liquid sprays, while dry scrubbers rely on dry materials and cyclones to capture particles through centrifugal forces without liquid usage.
Wet scrubber vs Dry scrubber Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com