Drones provide rapid, high-resolution aerial data that enhances accuracy in topographic mapping compared to traditional ground surveys. These unmanned aerial vehicles reduce labor costs and improve safety by accessing difficult terrain without physical presence. Ground surveys remain essential for precise measurements and legal boundary verification, complementing drone data in comprehensive civil engineering projects.
Table of Comparison
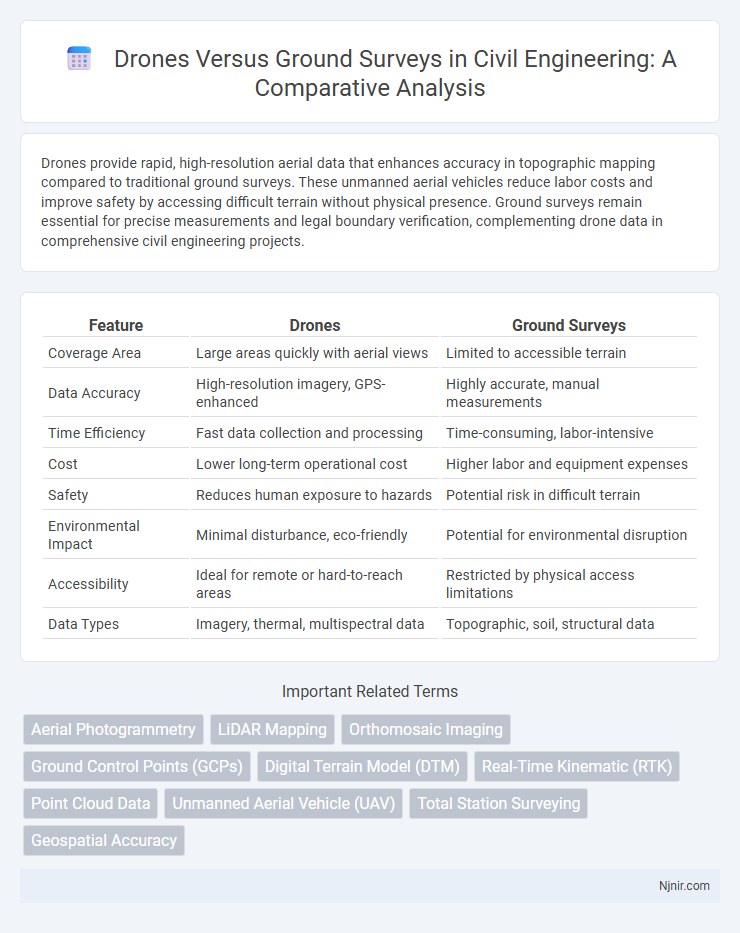
| Feature | Drones | Ground Surveys |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large areas quickly with aerial views | Limited to accessible terrain |
| Data Accuracy | High-resolution imagery, GPS-enhanced | Highly accurate, manual measurements |
| Time Efficiency | Fast data collection and processing | Time-consuming, labor-intensive |
| Cost | Lower long-term operational cost | Higher labor and equipment expenses |
| Safety | Reduces human exposure to hazards | Potential risk in difficult terrain |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal disturbance, eco-friendly | Potential for environmental disruption |
| Accessibility | Ideal for remote or hard-to-reach areas | Restricted by physical access limitations |
| Data Types | Imagery, thermal, multispectral data | Topographic, soil, structural data |
Introduction to Drones and Ground Surveys in Civil Engineering
Drones in civil engineering offer precise aerial data collection for site mapping, topographic surveys, and infrastructure inspections, enhancing efficiency and accuracy compared to traditional methods. Ground surveys rely on manual measurement techniques using tools like total stations, GPS, and theodolites to gather detailed surface data, essential for construction layout and design validation. Combining drone technology with ground surveys provides comprehensive spatial information, improving project planning and reducing survey time.
Technology Overview: Drones vs Traditional Ground Survey Methods
Drones utilize advanced sensors like LiDAR and high-resolution cameras to capture precise aerial data rapidly, enabling detailed 3D mapping and real-time analysis. Traditional ground surveys rely on manual data collection tools such as total stations and GPS devices, which often require more time and labor to achieve accurate measurements. The integration of drone technology enhances spatial data accuracy and efficiency compared to conventional surveying techniques, revolutionizing land assessment and construction monitoring.
Accuracy and Precision: Comparing Survey Results
Drones provide high-resolution aerial imagery that enhances survey accuracy by capturing detailed topographic data and reducing human error compared to traditional ground surveys. Ground surveys offer precise measurements through direct contact with survey points, ensuring reliable localized data but with potential limitations in coverage and time efficiency. Combining drone technology with ground surveys often results in comprehensive datasets that maximize overall accuracy and precision in mapping and land assessment projects.
Time Efficiency: Data Collection Speed and Turnaround
Drones significantly outperform ground surveys in time efficiency by capturing comprehensive aerial data rapidly, reducing data collection from days to mere hours. Their advanced imaging technology enables real-time processing and faster turnaround, facilitating quicker decision-making. Ground surveys often require extensive manpower and multiple site visits, making drones the preferred choice for projects demanding swift data acquisition and analysis.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Drones significantly reduce upfront costs compared to traditional ground surveys by lowering labor expenses and minimizing the need for extensive equipment. Long-term expenses also favor drones due to their efficiency in data collection, faster project completion times, and reduced operational risks. Maintenance and software updates for drones typically incur lower costs than continuous ground survey manpower and large-scale machinery upkeep.
Safety Considerations in Survey Operations
Drones significantly enhance safety in survey operations by minimizing the need for personnel to enter hazardous or hard-to-reach areas, reducing the risk of accidents and exposure to dangerous environments. Ground surveys often require manual data collection in uneven terrain, dense vegetation, or unstable structures, increasing the likelihood of injuries. Deploying drones equipped with high-resolution sensors ensures comprehensive data capture while maintaining a safer operational footprint.
Data Types and Visualization Capabilities
Drones capture high-resolution aerial imagery and multispectral data, enabling precise 3D models and orthomosaics for detailed spatial analysis, whereas ground surveys primarily gather point-based data such as GPS coordinates and manual measurements. Drone-collected datasets support advanced visualization techniques like digital elevation models (DEMs) and real-time mapping, enhancing decision-making processes. Ground surveys offer accurate localized data but lack the comprehensive area coverage and dynamic visual outputs provided by drone technology.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Approach
Drones face limitations such as battery life constraints, regulatory restrictions, and vulnerability to adverse weather conditions, which can hinder data collection and coverage area. Ground surveys often encounter challenges including labor-intensive processes, slower data acquisition, limited accessibility to difficult terrains, and higher operational costs. Both approaches require careful consideration of accuracy requirements, environmental factors, and logistical feasibility to determine the most effective method for specific surveying tasks.
Regulatory and Legal Aspects in Surveying
Regulatory and legal aspects in surveying using drones versus ground surveys differ significantly, with drone usage requiring strict adherence to aviation laws, airspace restrictions, and privacy regulations set by authorities such as the FAA or EASA. Ground surveys typically face fewer regulatory hurdles but must comply with property access permissions and environmental protection laws. Understanding these legal frameworks is crucial for ensuring compliance, mitigating liability risks, and obtaining necessary permits for surveying operations.
Future Trends: Integrating Drones with Ground Surveys
The future of land and resource mapping lies in integrating drones with traditional ground surveys to enhance precision and efficiency. Combining high-resolution aerial data from drones with detailed on-site measurements allows for comprehensive spatial analysis and real-time updates. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven data fusion and IoT-enabled sensors are driving more accurate and scalable survey solutions across industries.
Aerial Photogrammetry
Aerial photogrammetry using drones provides high-resolution, accurate terrain data faster and more cost-effectively than traditional ground surveys, enhancing efficiency in mapping and analysis.
LiDAR Mapping
LiDAR mapping with drones offers faster, more accurate terrain data collection than traditional ground surveys, reducing costs and enabling detailed 3D modeling in diverse environments.
Orthomosaic Imaging
Drones provide high-resolution orthomosaic imaging that enhances accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional ground surveys in mapping and land assessment.
Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Ground Control Points (GCPs) are essential in drone surveys to enhance geospatial accuracy by providing precise reference coordinates that align aerial imagery with ground realities during mapping and modeling.
Digital Terrain Model (DTM)
Drones generate highly accurate Digital Terrain Models (DTMs) faster and more cost-effectively than traditional ground surveys by capturing detailed aerial imagery and elevation data.
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK)
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) technology enhances drone surveying accuracy by providing centimeter-level positioning, outperforming traditional ground surveys in speed and precision.
Point Cloud Data
Drones generate highly accurate and dense point cloud data faster and more cost-effectively than traditional ground surveys, enhancing 3D mapping and spatial analysis precision.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) provide faster, more accurate terrain mapping and data collection compared to traditional ground surveys, significantly enhancing efficiency in construction, agriculture, and environmental monitoring.
Total Station Surveying
Total Station surveying offers precise ground measurements with sub-centimeter accuracy, whereas drones provide rapid aerial data acquisition but may lack the detailed precision required for complex terrain analysis.
Geospatial Accuracy
Drones provide higher geospatial accuracy than traditional ground surveys by capturing detailed aerial imagery with GPS-enabled sensors and real-time data processing.
Drones vs Ground Surveys Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com