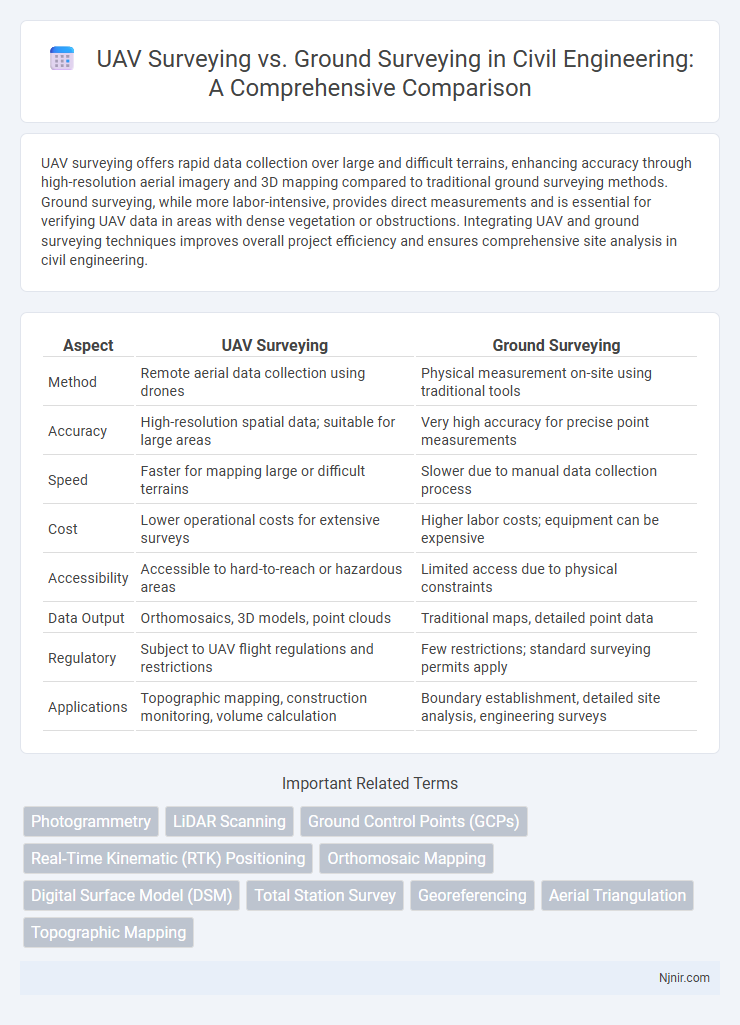
UAV surveying offers rapid data collection over large and difficult terrains, enhancing accuracy through high-resolution aerial imagery and 3D mapping compared to traditional ground surveying methods. Ground surveying, while more labor-intensive, provides direct measurements and is essential for verifying UAV data in areas with dense vegetation or obstructions. Integrating UAV and ground surveying techniques improves overall project efficiency and ensures comprehensive site analysis in civil engineering.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | UAV Surveying | Ground Surveying |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Remote aerial data collection using drones | Physical measurement on-site using traditional tools |
| Accuracy | High-resolution spatial data; suitable for large areas | Very high accuracy for precise point measurements |
| Speed | Faster for mapping large or difficult terrains | Slower due to manual data collection process |
| Cost | Lower operational costs for extensive surveys | Higher labor costs; equipment can be expensive |
| Accessibility | Accessible to hard-to-reach or hazardous areas | Limited access due to physical constraints |
| Data Output | Orthomosaics, 3D models, point clouds | Traditional maps, detailed point data |
| Regulatory | Subject to UAV flight regulations and restrictions | Few restrictions; standard surveying permits apply |
| Applications | Topographic mapping, construction monitoring, volume calculation | Boundary establishment, detailed site analysis, engineering surveys |
Introduction to UAV and Ground Surveying
UAV surveying utilizes unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-resolution cameras and LiDAR sensors to capture detailed aerial data, enabling rapid and precise mapping of large areas. Ground surveying relies on traditional instruments such as total stations, GPS receivers, and theodolites to measure distances and elevations directly on-site, offering high accuracy for smaller or complex terrain. Both methods complement each other in geospatial data collection, with UAV surveys providing extensive coverage and ground surveys ensuring precise control points.
Key Technologies in UAV and Ground Surveying
UAV surveying leverages advanced technologies such as LiDAR sensors, high-resolution multispectral cameras, and GPS-enabled drone navigation systems to capture precise aerial data quickly and with expansive coverage. Ground surveying relies on traditional tools like total stations, GNSS receivers, and laser scanners, which provide highly accurate point measurements essential for detailed topographic mapping. Integration of UAV photogrammetry with ground control points enhances data accuracy, creating a comprehensive spatial dataset for engineering and construction projects.
Accuracy Comparison: UAV vs Ground Methods
UAV surveying provides high-resolution data with centimeter-level accuracy using advanced GPS and photogrammetry, making it ideal for large or inaccessible areas. Ground surveying offers superior precision through direct measurements with total stations and GPS receivers, achieving sub-centimeter accuracy in small, controlled environments. Accuracy comparisons show UAV methods are efficient for broad terrain mapping, while ground surveying remains the gold standard for detailed, high-precision measurements.
Cost Efficiency in Surveying Approaches
UAV surveying significantly reduces costs by minimizing labor and time compared to traditional ground surveying methods, especially in large or difficult terrains. While ground surveying requires extensive manpower and equipment setup, UAVs capture high-resolution aerial data quickly, enhancing overall efficiency. Investment in UAV technology leads to long-term savings by accelerating project timelines and lowering operational expenses.
Time Requirements and Project Timelines
UAV surveying drastically reduces time requirements by capturing high-resolution data over large areas within hours, compared to ground surveying that can take days or weeks due to manual measurements. Project timelines benefit significantly from UAV efficiency, enabling faster data processing and quicker decision-making. Ground surveying remains essential for detailed, localized measurements but generally extends overall project duration.
Safety Considerations in Surveying Techniques
UAV surveying significantly reduces safety risks by minimizing the need for personnel to access hazardous or difficult terrain, unlike traditional ground surveying which often requires physical presence in potentially dangerous environments. UAVs can quickly capture high-resolution data from elevated positions, lowering the chances of accidents related to falls, exposure to wildlife, or unstable ground conditions. Ground surveying remains essential for detailed onsite measurements but carries inherent safety challenges such as vehicle operation risks and exposure to adverse weather conditions.
Data Collection and Processing Capabilities
UAV surveying leverages advanced aerial imaging technology to collect high-resolution geospatial data rapidly over large areas, enabling detailed 3D mapping and real-time data acquisition. Ground surveying relies on traditional instruments like total stations and GPS units for precise point measurements but is more time-consuming and limited by terrain accessibility. Data processing for UAV surveys utilizes automated software and machine learning algorithms to generate orthomosaics, digital elevation models, and point clouds efficiently, whereas ground survey data often requires manual interpretation and integration into CAD or GIS systems.
Applications in Civil Engineering Projects
UAV surveying offers high-resolution aerial data ideal for topographic mapping, volume calculation, and infrastructure monitoring in civil engineering projects, enhancing efficiency and accuracy over expansive or inaccessible sites. Ground surveying remains essential for detailed boundary measurements, precise control points, and quality control during construction phases requiring direct measurement. Integrating UAV and ground surveying techniques optimizes project outcomes by combining broad-scale spatial data with precise ground-level details.
Limitations and Challenges of Both Methods
UAV surveying faces limitations such as restricted flight duration, vulnerability to adverse weather conditions, and regulatory constraints on airspace usage. Ground surveying encounters challenges including limited accessibility in rough or hazardous terrain, higher labor intensity, and slower data collection processes. Both methods require specialized skills and technology, which can impact project cost and accuracy depending on the survey environment and objectives.
Future Trends in Surveying Technologies
UAV surveying leverages advanced drone technology and AI-driven data analysis to provide rapid, high-resolution aerial mapping, reducing time and costs compared to traditional ground surveying methods. Future trends emphasize the integration of real-time 3D modeling, enhanced GPS precision, and autonomous drones equipped with LiDAR sensors, increasing accuracy in complex terrains. Ground surveying will continue evolving with augmented reality (AR) tools and IoT-enabled sensors to complement UAV data, creating hybrid solutions for comprehensive spatial analysis.
Photogrammetry
UAV surveying captures high-resolution photogrammetric data rapidly over large areas with greater accuracy and lower costs compared to traditional ground surveying methods.
LiDAR Scanning
UAV surveying with LiDAR scanning offers faster data acquisition, higher resolution, and safer access to difficult terrain compared to traditional ground surveying methods.
Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Ground Control Points (GCPs) are essential for both UAV surveying and ground surveying, providing precise georeferencing to enhance the accuracy of spatial data collection.
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Positioning
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) positioning in UAV surveying delivers centimeter-level accuracy and faster data acquisition compared to traditional ground surveying methods, significantly enhancing efficiency in geospatial mapping and construction projects.
Orthomosaic Mapping
UAV surveying enables faster and more cost-effective orthomosaic mapping with higher spatial resolution compared to traditional ground surveying methods, enhancing accuracy for large-area topographic analysis.
Digital Surface Model (DSM)
UAV surveying creates high-resolution Digital Surface Models (DSMs) faster and with greater topographic detail than traditional ground surveying methods.
Total Station Survey
Total Station Survey in UAV surveying offers faster data collection and higher accuracy over large areas compared to traditional ground surveying methods, enhancing efficiency and detail in topographic and construction site analysis.
Georeferencing
UAV surveying enhances georeferencing accuracy by integrating GPS data with high-resolution aerial imagery, surpassing traditional ground surveying methods that rely on limited physical reference points.
Aerial Triangulation
UAV surveying enhances aerial triangulation accuracy and efficiency by capturing high-resolution images from multiple angles, surpassing traditional ground surveying limitations in data density and terrain accessibility.
Topographic Mapping
UAV surveying offers faster and more precise topographic mapping with higher resolution data compared to traditional ground surveying methods, enabling efficient terrain analysis and detailed elevation models.
UAV Surveying vs Ground Surveying Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com